STL标准库-容器-rb_tree
Posted 勿在浮沙筑高台
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了STL标准库-容器-rb_tree相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
技术在于交流、沟通,本文为博主原创文章转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性
红黑树,关联式容器底层实现(map set),在使用中基本运用不到,但是还是想了解一下他的运作方式
Red_Black tree是平衡二分搜寻树(balanced binary search tree),它是高度平衡的二叉树,这样有利于search和insert.
红黑树提供遍历,如果如果按正常规则(++iter)遍历,便能获得排序状态

如上图,你会发现返回迭代器头的begin()函数指向的是"5"这个点.end()记录着最大点"15",它永远先走左边后走右边.
如果你遍历上面的红黑树就会得到 5,6,7,8,10,11,12,13,15
但是我们不应该使用红黑树的迭代器改变其元素,如果改变就会破坏原树的结构,但是编程的层面没有禁止(是可以改,但是我们不应该改).
因为rb_tree是为了实现set和map,而map允许元素data的改变,但是map的key不能够改变.
rb_tree提供两种insertion操作:insert_unique()[插入的key是第一无二的,否则插入失败]. insert_equal()[允许key重复] .
先说一下红黑数的基本性质
红黑树的性质:
a.每个节点或是红的,或是黑的
b.根节点是黑色的
c.每个叶节点(NULL)是黑色的
d.如果一个节点是红色的,则它的两个子节点都是黑色的
e.对每个节点,从该节点到其所有后代叶节点的简单路径上,均含有相同数目的黑色节点
Source Code
介绍rb_tree的部分源码
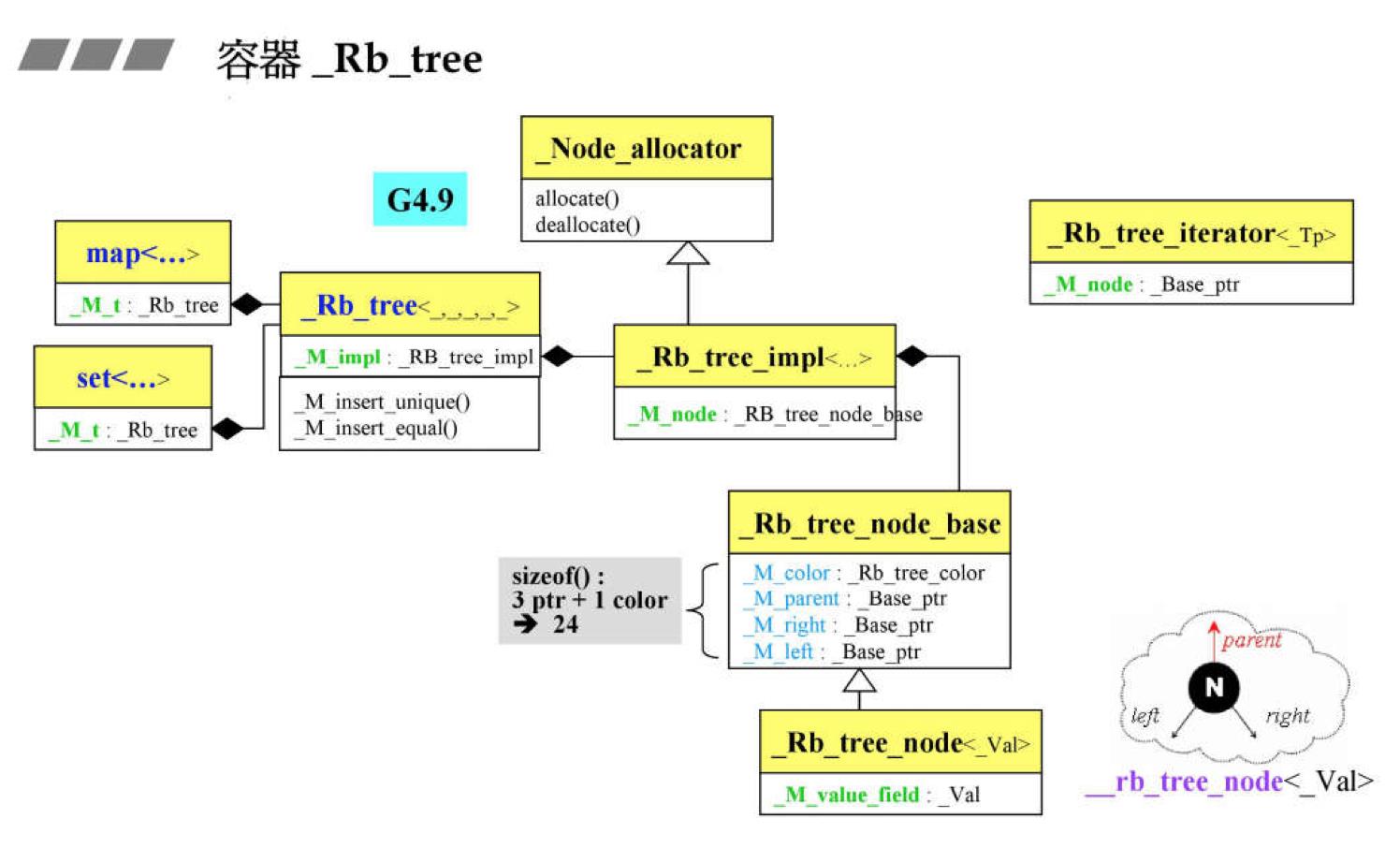
一 数据类
先看红黑树的数据类 _Rb_tree_node_base
enum _Rb_tree_color { _S_red = false, _S_black = true };//红黑树的颜色 红色0 黑色1 struct _Rb_tree_node_base { typedef _Rb_tree_node_base* _Base_ptr; //节点指针 typedef const _Rb_tree_node_base* _Const_Base_ptr;//const节点指针 _Rb_tree_color _M_color;//颜色 _Base_ptr _M_parent;//父节点 _Base_ptr _M_left;//左节点 _Base_ptr _M_right;//右节点 static _Base_ptr//最小节点,即最左节点 _S_minimum(_Base_ptr __x) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT { while (__x->_M_left != 0) __x = __x->_M_left;//只要左节点不为空就一直向左走,取得最小节点 return __x; } static _Const_Base_ptr _S_minimum(_Const_Base_ptr __x) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT { while (__x->_M_left != 0) __x = __x->_M_left; return __x; } static _Base_ptr//最大节点,即最右节点 _S_maximum(_Base_ptr __x) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT { while (__x->_M_right != 0) __x = __x->_M_right; return __x; } static _Const_Base_ptr _S_maximum(_Const_Base_ptr __x) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT { while (__x->_M_right != 0) __x = __x->_M_right; return __x; } };
其子类_Rb_tree_node
template<typename _Val>//红黑树的节点结构 struct _Rb_tree_node : public _Rb_tree_node_base { typedef _Rb_tree_node<_Val>* _Link_type;//节点指针 指向数据节点 #if __cplusplus < 201103L _Val _M_value_field;//数据类型 _Val* _M_valptr() { return std::__addressof(_M_value_field); } const _Val* _M_valptr() const { return std::__addressof(_M_value_field); } #else __gnu_cxx::__aligned_buffer<_Val> _M_storage;//对齐处理后数据 _Val* _M_valptr() //返回对应数据的指针 { return _M_storage._M_ptr(); } const _Val* _M_valptr() const { return _M_storage._M_ptr(); } #endif };
std::_addressof()的实现在 move.h中找到其实现 用于取变量和函数的内存地址
template<typename _Tp> inline _Tp* __addressof(_Tp& __r) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT { return reinterpret_cast<_Tp*> (&const_cast<char&>(reinterpret_cast<const volatile char&>(__r))); }
volatitle是一种类型修饰符,用它声明的类型变量表示可以被某些编译器未知的因素更改.
比如:操作系统、硬件或者其它线程等。遇到这个关键字声明的变量,编译器对访问该变量的代码就不再进行优化,从而可以提供对特殊地址的稳定访问。
声明时语法:int volatile vInt; 当要求使用 volatile 声明的变量的值的时候,系统总是重新从它所在的内存读取数据,即使它前面的指令刚刚从该处读取过数据。而且读取的数据立刻被保存
二 迭代器 _Rb_tree_iterator
template<typename _Tp>
struct _Rb_tree_iterator
{
typedef _Tp value_type;
typedef _Tp& reference;
typedef _Tp* pointer;
typedef bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category; //迭代器类型
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type; //两个迭代器间距离
typedef _Rb_tree_iterator<_Tp> _Self;
typedef _Rb_tree_node_base::_Base_ptr _Base_ptr;//节点指针
typedef _Rb_tree_node<_Tp>* _Link_type;//节点指针
//ctor
_Rb_tree_iterator() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
: _M_node() { }
explicit
_Rb_tree_iterator(_Link_type __x) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
: _M_node(__x) { }
reference
operator*() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return *static_cast<_Link_type>(_M_node)->_M_valptr(); }
//操作符重载返回节点指针
pointer
operator->() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return static_cast<_Link_type> (_M_node)->_M_valptr(); }
_Self&
operator++() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{
_M_node = _Rb_tree_increment(_M_node);//这个函数的实现在4.9中没有找到 用一下其他版本的 其实现原理基本相似
return *this;
}
_Self
operator++(int) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{
_Self __tmp = *this;
_M_node = _Rb_tree_increment(_M_node);//++操作
return __tmp;
}
_Self&
operator--() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT//--也没找到
{
_M_node = _Rb_tree_decrement(_M_node);
return *this;
}
_Self
operator--(int) _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{
_Self __tmp = *this;
_M_node = _Rb_tree_decrement(_M_node);
return __tmp;
}
bool
operator==(const _Self& __x) const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return _M_node == __x._M_node; }
bool
operator!=(const _Self& __x) const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return _M_node != __x._M_node; }
_Base_ptr _M_node;
};
operator++
//RB-Tree的后继点 void _M_increment() { //the right subtree of node x is not empty //存在右子树,则找出右子树的最小节点 if (_M_node->_M_right != 0) {//如果有右子树 _M_node = _M_node->_M_right;//向右边走 while (_M_node->_M_left != 0)//往右子树中的左边一直走到底 _M_node = _M_node->_M_left;//最左节点就是后继结点 } //the right subtree of node x is empty,and the node of x has a successor node y //没有右子树,但是RB-Tree中节点node存在后继结点 else { _Base_ptr __y = _M_node->_M_parent;//沿其父节点向上查找 while (_M_node == __y->_M_right) { //若节点是其父节点的右孩子,则向上查找, _M_node = __y; //一直向上查找,直到“某节点不是其父节点的右孩子”为止 __y = __y->_M_parent; } if (_M_node->_M_right != __y)//若此时的右子节点不等于此时的父节点 _M_node = __y;//此时的父节点即为解答 //否则此时的node为解答 } }
operator--
//RB-Tree的前驱节点 void _M_decrement() { if (_M_node->_M_color == _S_rb_tree_red &&// 如果是红节点,且 _M_node->_M_parent->_M_parent == _M_node)// 父节点的父节点等于自己 _M_node = _M_node->_M_right; //右子节点即为解答。 /* 以上情况发生于node为header时(亦即node为end()时)。注意,header之右孩子即 mostright,指向整棵树的max节点。 */ else if (_M_node->_M_left != 0) {//若有左孩子节点。左子树的最大值即为前驱节点 _Base_ptr __y = _M_node->_M_left;//向左边走,即令y指向左孩子 while (__y->_M_right != 0)//y存在右孩子, __y = __y->_M_right;//一直往右走到底 _M_node = __y;//最后即为解答 } else {//即非根节点,且没有左孩子节点 _Base_ptr __y = _M_node->_M_parent;//找出父节点 while (_M_node == __y->_M_left) {//node节点是其父节点的左孩子 _M_node = __y;//一直交替上溯 __y = __y->_M_parent;//直到不为左孩子结点 } _M_node = __y;//此时父节点即为解答 } } };
_Rb_tree_impl
template<typename _Key, typename _Val, typename _KeyOfValue, typename _Compare, typename _Alloc = allocator<_Val> > class _Rb_tree { //先说一下说这五个参数
/*
参数1 key key类型
参数2 val value和key的数据包
参数3 在数据包中取key得方法
参数4 key的排序方法
参数5 分配器
*/
... protected: template<typename _Key_compare, bool _Is_pod_comparator = __is_pod(_Key_compare)> struct _Rb_tree_impl : public _Node_allocator { _Key_compare _M_key_compare; _Rb_tree_node_base _M_header; size_type _M_node_count; // Keeps track of size of tree. _Rb_tree_impl() : _Node_allocator(), _M_key_compare(), _M_header(), _M_node_count(0) { _M_initialize(); } _Rb_tree_impl(const _Key_compare& __comp, const _Node_allocator& __a) : _Node_allocator(__a), _M_key_compare(__comp), _M_header(), _M_node_count(0) { _M_initialize(); } #if __cplusplus >= 201103L _Rb_tree_impl(const _Key_compare& __comp, _Node_allocator&& __a) : _Node_allocator(std::move(__a)), _M_key_compare(__comp), _M_header(), _M_node_count(0) { _M_initialize(); } #endif private: void _M_initialize() { this->_M_header._M_color = _S_red; this->_M_header._M_parent = 0; this->_M_header._M_left = &this->_M_header; this->_M_header._M_right = &this->_M_header; } }; _Rb_tree_impl<_Compare> _M_impl; ... }
4.9的红黑树源码封装的比较严密,导致我没找到一些函数的实现,那么下面的源码分析,我就以我的学习笔记代替了
// 以下都是全域函式:__rb_tree_rotate_left(), __rb_tree_rotate_right(), // __rb_tree_rebalance(), __rb_tree_rebalance_for_erase() //新节点必须为红色节点。如果安插处的父节点为红色,就违反了红黑色规则 //此时要旋转和改变颜色 //左旋转 //节点x为左旋转点 inline void _Rb_tree_rotate_left(_Rb_tree_node_base* __x, _Rb_tree_node_base*& __root) { _Rb_tree_node_base* __y = __x->_M_right;//获取左旋转节点x的右孩子y __x->_M_right = __y->_M_left;//把y节点的左孩子作为旋转节点x的右孩子 if (__y->_M_left !=0) __y->_M_left->_M_parent = __x;//更新节点y左孩子父节点指针,指向新的父节点x __y->_M_parent = __x->_M_parent;//y节点替换x节点的位置 //令y完全顶替x的地位(必须将x对其父节点的关系完全接收过来) if (__x == __root)//若原始位置节点x是根节点 __root = __y;//则y为新的根节点 //否则,若x节点是其父节点的左孩子 else if (__x == __x->_M_parent->_M_left) __x->_M_parent->_M_left = __y;//则更新节点y为原始x父节点的左孩子 else//若x节点是其父节点的右孩子 __x->_M_parent->_M_right = __y;//则更新节点y为原始x父节点的右孩子 __y->_M_left = __x;//旋转后旋转节点x作为节点y的左孩子 __x->_M_parent = __y;//更新x节点的父节点指针 } //右旋转 //节点x为右旋转点 inline void _Rb_tree_rotate_right(_Rb_tree_node_base* __x, _Rb_tree_node_base*& __root) { _Rb_tree_node_base* __y = __x->_M_left;//获取右旋转节点x的左孩子y __x->_M_left = __y->_M_right;//把y节点的右孩子作为旋转节点x的左孩子 if (__y->_M_right != 0) __y->_M_right->_M_parent = __x;//更新节点y右孩子父节点指针,指向新的父节点x __y->_M_parent = __x->_M_parent;//y节点替换x节点的位置 //令y完全顶替x的地位(必须将x对其父节点的关系完全接收过来) if (__x == __root)//若原始位置节点x是根节点 __root = __y;//则y为新的根节点 //否则,若x节点是其父节点的右孩子 else if (__x == __x->_M_parent->_M_right) __x->_M_parent->_M_right = __y;//则更新节点y为原始x父节点的右孩子 else//若x节点是其父节点的左孩子 __x->_M_parent->_M_left = __y;//则更新节点y为原始x父节点的左孩子 __y->_M_right = __x;//旋转后旋转节点x作为节点y的右孩子 __x->_M_parent = __y;//更新x节点的父节点指针 } //重新令RB-tree平衡(改变颜色和旋转) //参数一为新增节点x,参数二为root节点 inline void _Rb_tree_rebalance(_Rb_tree_node_base* __x, _Rb_tree_node_base*& __root) { __x->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_red;//新插入的节点必须为红色,这样不会违反性质5. //若新插入节点不是为RB-Tree的根节点,且其父节点color属性也是红色,即违反了性质4. //则进入while循环. //此时根据节点x的父节点x->parent是其祖父节点x->parent->parent的左孩子还是右孩子进行讨论, //但是左右孩子之间是对称的,所以思想是类似的. while (__x != __root && __x->_M_parent->_M_color == _S_rb_tree_red) { //case1:节点x的父节点x->parent是其祖父节点x->parent->parent的左孩子 if (__x->_M_parent == __x->_M_parent->_M_parent->_M_left) { //节点y为x节点的叔叔节点,即是节点x父节点x->parent的兄弟 _Rb_tree_node_base* __y = __x->_M_parent->_M_parent->_M_right; if (__y && __y->_M_color == _S_rb_tree_red) {//情况1:若其叔叔节点y存在,且为红色 /* 此时x->parent和y都是红色的,解决办法是将x的父节点x->parent和叔叔结点y都着为黑色, 而将x的祖父结点x->parent->parent着为红色, 然后从祖父结点x->parent->parent继续向上判断是否破坏红黑树的性质。 */ __x->_M_parent->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_black;//将其父节点x->parent改变成黑色 __y->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_black;//将其叔叔节点y改变成黑色 __x->_M_parent->_M_parent->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_red;//将其祖父节点变成红色 //把祖父节点作为当前节点,一直上溯,继续判断是否破坏RB-Tree性质. __x = __x->_M_parent->_M_parent; } else {//若无叔叔节点或者其叔叔节点y为黑色 /* 情况2:x的叔叔节点y是黑色且x是一个右孩子 情况3:x的叔叔节点y是黑色且x是一个左孩子 情况2和情况3中y都是黑色的,通过x是parent[x]的左孩子还是右孩子进行区分的。 情况2中x是右孩子,可以在parent[x]结点将情况2通过左旋转为情况3,使得x变为左孩子。 无论是间接还是直接的通过情况2进入到情况3,x的叔叔y总是黑色的。 在情况3中,将parent[x]着为黑色,parent[parent[x]]着为红色,然后从parent[parent[x]]处进行一次右旋转。 情况2、3修正了对性质4的违反,修正过程不会导致其他的红黑性质被破坏。 */ if (__x == __x->_M_parent->_M_right) {//若节点x为其父节点x->parent的右孩子 //则以其父节点作为旋转节点 //进行一次左旋转 __x = __x->_M_parent; _Rb_tree_rotate_left(__x, __root); //旋转之后,节点x变成其父节点的左孩子 } __x->_M_parent->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_black;//改变其父节点x->parent颜色 __x->_M_parent->_M_parent->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_red;//改变其祖父节点x->parent->parent颜色 _Rb_tree_rotate_right(__x->_M_parent->_M_parent, __root);//对其祖父节点进行一次右旋转 } } //case2:节点x的父节点x->parent是其祖父节点x->parent->parent的右孩子 //这种情况是跟上面的情况(父节点为其祖父节点的左孩子)是对称的. else { //节点y为x节点的叔叔节点,即是节点x父节点x->parent的兄弟 _Rb_tree_node_base* __y = __x->_M_parent->_M_parent->_M_left; if (__y && __y->_M_color == _S_rb_tree_red) {//若叔叔节点存在,且为红色 __x->_M_parent->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_black;//改变父节点颜色 __y->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_black;//改变叔叔节点颜色 __x->_M_parent->_M_parent->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_red;//改变祖父节点颜色 __x = __x->_M_parent->_M_parent;//上溯祖父节点,判断是否违背RB-Tree的性质 } else {//若叔叔节点不存在或叔叔节点为黑色 if (__x == __x->_M_parent->_M_left) {//新节点x为其父节点的左孩子 //对其父节点进行一次右旋转 __x = __x->_M_parent; _Rb_tree_rotate_right(__x, __root); } __x->_M_parent->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_black;//改变父节点颜色 __x->_M_parent->_M_parent->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_red;//改变祖父节点颜色 _Rb_tree_rotate_left(__x->_M_parent->_M_parent, __root);//进行一次左旋转 } } } //若新插入节点为根节点,则违反性质2 //只需将其重新赋值为黑色即可 __root->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_black; } //删除节点 inline _Rb_tree_node_base* _Rb_tree_rebalance_for_erase(_Rb_tree_node_base* __z, _Rb_tree_node_base*& __root, _Rb_tree_node_base*& __leftmost, _Rb_tree_node_base*& __rightmost) { _Rb_tree_node_base* __y = __z; _Rb_tree_node_base* __x = 0; _Rb_tree_node_base* __x_parent = 0; if (__y->_M_left == 0) // __z has at most one non-null child. y == z. __x = __y->_M_right; // __x might be null. else if (__y->_M_right == 0) // __z has exactly one non-null child. y == z. __x = __y->_M_left; // __x is not null. else { // __z has two non-null children. Set __y to __y = __y->_M_right; // __z\'s successor. __x might be null. while (__y->_M_left != 0) __y = __y->_M_left; __x = __y->_M_right; } if (__y != __z) { // relink y in place of z. y is z\'s successor __z->_M_left->_M_parent = __y; __y->_M_left = __z->_M_left; if (__y != __z->_M_right) { __x_parent = __y->_M_parent; if (__x) __x->_M_parent = __y->_M_parent; __y->_M_parent->_M_left = __x; // __y must be a child of _M_left __y->_M_right = __z->_M_right; __z->_M_right->_M_parent = __y; } else __x_parent = __y; if (__root == __z) __root = __y; else if (__z->_M_parent->_M_left == __z) __z->_M_parent->_M_left = __y; else __z->_M_parent->_M_right = __y; __y->_M_parent = __z->_M_parent; __STD::swap(__y->_M_color, __z->_M_color); __y = __z; // __y now points to node to be actually deleted } else { // __y == __z __x_parent = __y->_M_parent; if (__x) __x->_M_parent = __y->_M_parent; if (__root == __z) __root = __x; else if (__z->_M_parent->_M_left == __z) __z->_M_parent->_M_left = __x; else __z->_M_parent->_M_right = __x; if (__leftmost == __z) if (__z->_M_right == 0) // __z->_M_left must be null also __leftmost = __z->_M_parent; // makes __leftmost == _M_header if __z == __root else __leftmost = _Rb_tree_node_base::_S_minimum(__x); if (__rightmost == __z) if (__z->_M_left == 0) // __z->_M_right must be null also __rightmost = __z->_M_parent; // makes __rightmost == _M_header if __z == __root else // __x == __z->_M_left __rightmost = _Rb_tree_node_base::_S_maximum(__x); } if (__y->_M_color != _S_rb_tree_red) { while (__x != __root && (__x == 0 || __x->_M_color == _S_rb_tree_black)) if (__x == __x_parent->_M_left) { _Rb_tree_node_base* __w = __x_parent->_M_right; if (__w->_M_color == _S_rb_tree_red) { __w->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_black; __x_parent->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_red; _Rb_tree_rotate_left(__x_parent, __root); __w = __x_parent->_M_right; } if ((__w->_M_left == 0 || __w->_M_left->_M_color == _S_rb_tree_black) && (__w->_M_right == 0 || __w->_M_right->_M_color == _S_rb_tree_black)) { __w->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_red; __x = __x_parent; __x_parent = __x_parent->_M_parent; } else { if (__w->_M_right == 0 || __w->_M_right->_M_color == _S_rb_tree_black) { if (__w->_M_left) __w->_M_left->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_black; __w->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_red; _Rb_tree_rotate_right(__w, __root); __w = __x_parent->_M_right; } __w->_M_color = __x_parent->_M_color; __x_parent->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_black; if (__w->_M_right) __w->_M_right->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_black; _Rb_tree_rotate_left(__x_parent, __root); break; } } else { // same as above, with _M_right <-> _M_left. _Rb_tree_node_base* __w = __x_parent->_M_left; if (__w->_M_color == _S_rb_tree_red) { __w->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_black; __x_parent->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_red; _Rb_tree_rotate_right(__x_parent, __root); __w = __x_parent->_M_left; } if ((__w->_M_right == 0 || __w->_M_right->_M_color == _S_rb_tree_black) && (__w->_M_left == 0 || __w->_M_left->_M_color == _S_rb_tree_black)) { __w->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_red; __x = __x_parent; __x_parent = __x_parent->_M_parent; } else { if (__w->_M_left == 0 || __w->_M_left->_M_color == _S_rb_tree_black) { if (__w->_M_right) __w->_M_right->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_black; __w->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_red; _Rb_tree_rotate_left(__w, __root); __w = __x_parent->_M_left; } __w->_M_color = __x_parent->_M_color; __x_parent->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_black; if (__w->_M_left) __w->_M_left->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_black; _Rb_tree_rotate_right(__x_parent, __root); break; } } if (__x) __x->_M_color = _S_rb_tree_black; } return __y; } // Base class to encapsulate the differences between old SGI-style // allocators and standard-conforming allocators. In order to avoid // having an empty base class, we arbitrarily move one of rb_tree\'s // data members into the base class. //以下是对内存分配的管理 #ifdef __STL_USE_STD_ALLOCATORS // _Base for general standard-conforming allocators. template <class _Tp, class _Alloc, bool _S_instanceless> class _Rb_tree_alloc_base { public: typedef typename _Alloc_traits<_Tp, _Alloc>::allocator_type allocator_type; allocator_type get_allocator() const { return _M_node_allocator; }//空间配置器的类型 _Rb_tree_alloc_base(const allocator_type& __a) : _M_node_allocator(__a), _M_header(0) {} protected: typename _Alloc_traits<_Rb_tree_node<_Tp>, _Alloc>::allocator_type _M_node_allocator; _Rb_tree_node<_Tp>* _M_header;//定义头指针,指向Rb_tree的根节点 _Rb_tree_node<_Tp>* _M_get_node() //分配一个节点空间 { return _M_node_allocator.allocate(1); } void _M_put_node(_Rb_tree_node<_Tp>* __p) //释放一个节点空间 { _M_node_allocator.deallocate(__p, 1); } }; // Specialization for instanceless allocators. template <class _Tp, class _Alloc> class _Rb_tree_alloc_base<_Tp, _Alloc, true> { public: typedef typename _Alloc_traits<_Tp, _Alloc>::allocator_type allocator_type; allocator_type get_allocator() const { return allocator_type(); } _Rb_tree_alloc_base(const allocator_type&) : _M_header(0) {} protected: _Rb_tree_node<_Tp>* _M_header; typedef typename _Alloc_traits<_Rb_tree_node<_Tp>, _Alloc>::_Alloc_type _Alloc_type; _Rb_tree_node<_Tp>* _M_get_node() { return _Alloc_type::allocate(1); } void _M_put_node(_Rb_tree_node<_Tp>* __p) { _Alloc_type::deallocate(__p, 1); } }; //RB-Tree基本结构,即基类,继承_Rb_tree_alloc_base template <class _Tp, class _Alloc> struct _Rb_tree_base : public _Rb_tree_alloc_base<_Tp, _Alloc, _Alloc_traits<_Tp, _Alloc>::_S_instanceless> { typedef _Rb_tree_alloc_base<_Tp, _Alloc, _Alloc_traits<_Tp, _Alloc>::_S_instanceless> _Base; typedef typename _Base::allocator_type allocator_type; _Rb_tree_base(const allocator_type& __a) : _Base(__a) { _M_header = _M_get_node(); } ~_Rb_tree_base() { _M_put_node(_M_header); } }; #else /* __STL_USE_STD_ALLOCATORS */ //RB-Tree基本结构,即基类,没有继承_Rb_tree_alloc_base template <class _Tp,