数据结构-二叉树笔记
Posted pathjh
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构-二叉树笔记相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
看完《数据结构与算法分析》(c描述)后对二叉树的一点总结
树的节点声明:
1 typedef int ElementType; 2 typedef struct TreeNode* Position; 3 typedef Position BiSearchTree; 4 5 struct TreeNode 6 { 7 ElementType Element; 8 Position Left,Right; 9 10 };
二叉查找树的定义如下:
1.二叉查找树首先是一棵二叉树;
2.二叉查找树除了是二叉树外,还具有以下性质:对于树中的任何一个节点X,其左子树中的所有节点的关键字均小于X的关键字的值;而其右子树中的所有关键字的值均大于X的关键字的值。
二叉查找树的常用操作:
BiSearchTree MakeEmpty(BiSearchTree Tree);
Position FindMin(BiSearchTree T);
Position FindMax(BiSearchTree T);
BiSearchTree Insert(ElementType X,BiSearchTree T);
BiSearchTree Delete(ElementType X, BiSearchTree T);
树的操作过程中大多数用到了递归,理解起来相对简单,下面主要讲一下删除操作
对于要被删除的节点
- 如果节点是一片树叶,那么可以直接删除
- 如果节点有一个儿子,则该节点可以在其父亲节点调整指针绕过该节点后被删除,如图
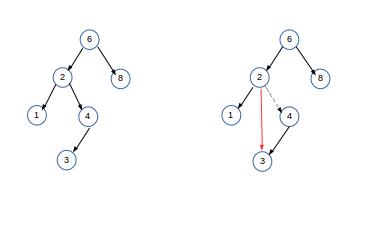
若要删除节点4,则只需将其父亲节点2调整指针指向4的儿子节点3,如右图。需要注意的是,所删除的节点只有在指向它的指针已被省去的情况下才能被去掉
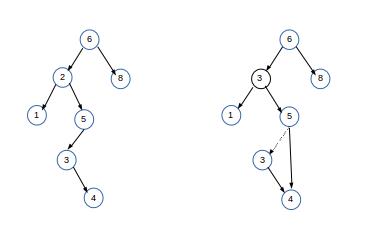
3.对于有两个儿子的节点。一般用其右子树中的最小的数据代替该节点的数据,并用递归的方法同样去删除掉那个节点。因为右子树中的最小的节点不可能有左儿子,所以第二次删除就很容易。如下图显示一颗初始的树及其一个节点被删除后的结果。要被删除的节点是根的左儿子,其关键字为2.它被右子树中的最小数据3所代替,然后关键字3的原节点如前例那样被删除
二叉树的常用操作:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 5 typedef int ElementType; 6 typedef struct TreeNode* Position; 7 typedef Position BiSearchTree; 8 9 struct TreeNode 10 { 11 ElementType Element; 12 Position Left,Right; 13 14 }; 15 16 BiSearchTree MakeEmpty(BiSearchTree Tree); 17 Position FindMin(BiSearchTree T); 18 Position FindMax(BiSearchTree T); 19 BiSearchTree Insert(ElementType X,BiSearchTree T); 20 BiSearchTree Delete(ElementType X, BiSearchTree T); 21 22 23 //建立一颗空树 24 BiSearchTree MakeEmpty(BiSearchTree Tree) 25 { 26 if(!Tree) 27 { 28 MakeEmpty(Tree->Left); 29 MakeEmpty(Tree->Right); 30 free(Tree); 31 } 32 33 return NULL; 34 } 35 36 //二叉查找树的查找 37 Position Find(ElementType X,BiSearchTree T) 38 39 { 40 if(T==NULL) 41 { 42 return NULL; 43 } 44 else 45 { 46 if(X<T->Element) 47 { 48 return Find(X,T->Left); 49 } 50 else if(X>T->Element) 51 { 52 return Find(X,T->Right); 53 } 54 55 else 56 { 57 return T; 58 } 59 } 60 61 } 62 63 64 //查找最小值(递归写法) 65 Position FindMin(BiSearchTree T) 66 { 67 if(T==NULL) 68 { 69 return NULL; 70 } 71 else 72 { 73 if (T->Left==NULL) 74 { 75 return T; 76 } 77 else 78 { 79 return FindMin(T->Left); 80 } 81 } 82 } 83 84 85 //查找最大值(非递归写法) 86 Position FindMax(BiSearchTree T) 87 { 88 if(T!=NULL) 89 { 90 while(T->Right!=NULL) 91 { 92 T=T->Right; 93 } 94 } 95 return T; 96 } 97 98 99 100 //插入元素 101 BiSearchTree Insert(ElementType X,BiSearchTree T) 102 103 { if(T==NULL) //树为空时 104 { 105 T=malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode)); 106 if(T==NULL) 107 { 108 fprintf(stderr,"out of place");//stderr:标准错误文件 109 } 110 else 111 { 112 T->Element = X; 113 T->Left=NULL; 114 T->Right=NULL; 115 } 116 } 117 else //树不为空时 118 { 119 if(X<T->Element) 120 { 121 T->Left=Insert(X,T->Left); 122 } 123 124 if(X>T->Element) 125 { 126 T->Right=Insert(X,T->Right); 127 } 128 else 129 { 130 //do nothing 131 } 132 } 133 134 return T; 135 } 136 137 138 139 140 //删除节点X 141 BiSearchTree Delete(ElementType X,BiSearchTree T) 142 { 143 Position TmpCell; 144 if(T==NULL) 145 { 146 fprintf(stderr,"Element does not exist!"); 147 } 148 else if(X<T->Element) 149 { 150 T->Left=Delete(X,T->Left); 151 } 152 else if(X>T->Element) 153 { 154 T->Right=Delete(X,T->Right); 155 } 156 else if(T->Left&&T->Right) //被删节点有两个孩子 157 { 158 TmpCell = FindMin(T->Right); 159 T->Element = TmpCell->Element; 160 T->Right = Delete(T->Element,T->Right); 161 } 162 else //被删节点有1个或是没有孩子 163 { 164 TmpCell =T; 165 if(T->Left==NULL) 166 { 167 T=T->Right; 168 } 169 if(T->Right==NULL) 170 { 171 T=T->Left; 172 } 173 free(TmpCell); 174 } 175 return T; 176 } 177 178 179 int main() 180 { 181 BiSearchTree T; 182 int index; 183 int arr[11]={2,8,45,78,111,354,5,676,89,34,45}; 184 T=NULL; 185 for(index=0;index<11;index++) 186 { 187 T=Insert(arr[index],T); 188 } 189 T=Insert(100,T); 190 T=Insert(11,T); 191 printf("最小数是:%d\\n",FindMin(T)->Element); 192 printf("最大数是:%d\\n",FindMax(T)->Element); 193 194 return 0; 195 }
以上是关于数据结构-二叉树笔记的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章