2017 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Shenyang Online
Posted BobHuang
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了2017 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Shenyang Online相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
cable cable cable
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2084 Accepted Submission(s): 1348
Problem Description
Connecting the display screen and signal sources which produce different color signals by cables, then the display screen can show the color of the signal source.Notice that every signal source can only send signals to one display screen each time.
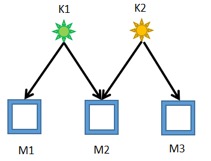
Now you have M display screens and K different signal sources(K≤M≤232?1). Select K display screens from M display screens, how many cables are needed at least so that **any** K display screens you select can show exactly K different colors.
Now you have M display screens and K different signal sources(K≤M≤232?1). Select K display screens from M display screens, how many cables are needed at least so that **any** K display screens you select can show exactly K different colors.
Input
Multiple cases (no more than 100), for each test case:
there is one line contains two integers M and K.
there is one line contains two integers M and K.
Output
Output the minimum number of cables N.
Sample Input
3 2
20 15
Sample Output
4
90
Hint

就是这两个数字组合下嘛,很容易直接观察出结果的
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef unsigned long long ull; const int N = 1e6+5; const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f; int main() { ll n,k; while(cin>>n>>k) { cout<<k*(n-k+1)<<endl; } return 0; }
array array array
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 2917 Accepted Submission(s): 1170
Problem Description
One day, Kaitou Kiddo had stolen a priceless diamond ring. But detective Conan blocked Kiddo‘s path to escape from the museum. But Kiddo didn‘t want to give it back. So, Kiddo asked Conan a question. If Conan could give a right answer, Kiddo would return the ring to the museum.
Kiddo: "I have an array A and a number k, if you can choose exactly k elements from A and erase them, then the remaining array is in non-increasing order or non-decreasing order, we say A is a magic array. Now I want you to tell me whether A is a magic array. " Conan: "emmmmm..." Now, Conan seems to be in trouble, can you help him?
Kiddo: "I have an array A and a number k, if you can choose exactly k elements from A and erase them, then the remaining array is in non-increasing order or non-decreasing order, we say A is a magic array. Now I want you to tell me whether A is a magic array. " Conan: "emmmmm..." Now, Conan seems to be in trouble, can you help him?
Input
The first line contains an integer T indicating the total number of test cases. Each test case starts with two integers n and k in one line, then one line with n integers: A1,A2…An.
1≤T≤20
1≤n≤105
0≤k≤n
1≤Ai≤105
1≤T≤20
1≤n≤105
0≤k≤n
1≤Ai≤105
Output
For each test case, please output "A is a magic array." if it is a magic array. Otherwise, output "A is not a magic array." (without quotes).
Sample Input
3
4 1
1 4 3 7
5 2
4 1 3 1 2
6 1
1 4 3 5 4 6
Sample Output
A is a magic array.
A is a magic array.
A is not a magic array.
最长递增子序列
#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<stdio.h> using namespace std; const int N=1e6+10; const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f; int a[N],g[N],f[N],b[N],c[N],n,h[N]; int main() { int t,n,last,l,i,m,x; cin>>t; while(t--) { cin>>n>>m; for(int i=0; i<n; i++) cin>>a[i],h[n-i-1]=a[i]; fill(g,g+n,INF); b[0]=1; for(int i=0; i<n; i++) { int j=lower_bound(g, g+n,a[i])-g; g[j]=a[i]; b[i]=j; } l=lower_bound(g, g+n,INF)-g-1; last=INF; for(i=n-1;i>=0;i--) { if(l==-1)break; if(b[i]==l&&a[i]<last) { last=a[i]; c[l]=last; l--; } } l=lower_bound(g, g+n,INF)-g; l=n-l;x=l; fill(g,g+n,INF); b[0]=1; for(int i=0; i<n; i++) { int j=lower_bound(g, g+n,h[i])-g; g[j]=h[i]; b[i]=j; } l=lower_bound(g, g+n,INF)-g-1; last=INF; for(i=n-1;i>=0;i--) { if(l==-1)break; if(b[i]==l&&a[i]<last) { last=a[i]; c[l]=last; l--; } } l=lower_bound(g, g+n,INF)-g; if(x>n-l) x=n-l; if(x<=m) puts("A is a magic array."); else puts("A is not a magic array."); //printf("%d\n",l); } return 0; }
number number number
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 2021 Accepted Submission(s): 1068
Problem Description
We define a sequence F:
? F0=0,F1=1;
? Fn=Fn?1+Fn?2 (n≥2).
Give you an integer k, if a positive number n can be expressed by
n=Fa1+Fa2+...+Fak where 0≤a1≤a2≤?≤ak, this positive number is mjf?good. Otherwise, this positive number is mjf?bad.
Now, give you an integer k, you task is to find the minimal positive mjf?bad number.
The answer may be too large. Please print the answer modulo 998244353.
? F0=0,F1=1;
? Fn=Fn?1+Fn?2 (n≥2).
Give you an integer k, if a positive number n can be expressed by
n=Fa1+Fa2+...+Fak where 0≤a1≤a2≤?≤ak, this positive number is mjf?good. Otherwise, this positive number is mjf?bad.
Now, give you an integer k, you task is to find the minimal positive mjf?bad number.
The answer may be too large. Please print the answer modulo 998244353.
Input
There are about 500 test cases, end up with EOF.
Each test case includes an integer k which is described above. (1≤k≤109)
Each test case includes an integer k which is described above. (1≤k≤109)
Output
For each case, output the minimal mjf?bad number mod 998244353.
Sample Input
1
Sample Output
4
找规律+矩阵快速幂
#include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<iostream> using namespace std; const long long M =998244353; struct Matrix { long long a[2][2]; Matrix() { memset(a, 0, sizeof(a)); } Matrix operator * (const Matrix y) { Matrix ans; for(long long i = 0; i <= 1; i++) for(long long j = 0; j <= 1; j++) for(long long k = 0; k <= 1; k++) ans.a[i][j] += a[i][k]*y.a[k][j]; for(long long i = 0; i <= 1; i++) for(long long j = 0; j <= 1; j++) ans.a[i][j] %= M; return ans; } void operator = (const Matrix b) { for(long long i = 0; i <= 1; i++) for(long long j = 0; j <= 1; j++) a[i][j] = b.a[i][j]; } }; long long solve(long long x) { Matrix ans, trs; ans.a[0][0] = ans.a[1][1] = 1; trs.a[0][0] = trs.a[1][0] = trs.a[0][1] = 1; while(x) { if(x&1) ans = ans*trs; trs = trs*trs; x >>= 1; } return ans.a[0][0]; } int main() { long long n; while(~scanf("%lld", &n)) { cout <<(solve(2*n+2)-1+M)%M << endl; } return 0; }
transaction transaction transaction
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 132768/132768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2245 Accepted Submission(s): 682
Problem Description
Kelukin is a businessman. Every day, he travels around cities to do some business. On August 17th, in memory of a great man, citizens will read a book named "the Man Who Changed China". Of course, Kelukin wouldn‘t miss this chance to make money, but he doesn‘t have this book. So he has to choose two city to buy and sell.
As we know, the price of this book was different in each city. It is ai yuan in it city. Kelukin will take taxi, whose price is 1yuan per km and this fare cannot be ignored.
There are n?1 roads connecting n cities. Kelukin can choose any city to start his travel. He want to know the maximum money he can get.
As we know, the price of this book was different in each city. It is ai yuan in it city. Kelukin will take taxi, whose price is 1yuan per km and this fare cannot be ignored.
There are n?1 roads connecting n cities. Kelukin can choose any city to start his travel. He want to know the maximum money he can get.
Input
The first line contains an integer T (1≤T≤10) , the number of test cases.
For each test case:
first line contains an integer n (2≤n≤100000) means the number of cities;
second line contains n numbers, the ith number means the prices in ith city; (1≤Price≤10000)
then follows n?1 lines, each contains three numbers x, y and z which means there exists a road between x and y, the distance is zkm (1≤z≤1000).
For each test case:
first line contains an integer n (2≤n≤100000) means the number of cities;
second line contains n numbers, the ith number means the prices in ith city; (1≤Price≤10000)
then follows n?1 lines, each contains three numbers x, y and z which means there exists a road between x and y, the distance is zkm (1≤z≤1000).
Output
For each test case, output a single number in a line: the maximum money he can get.
Sample Input
1
4
10 40 15 30
1 2 30
1 3 2
3 4 10
Sample Output
8
dfs直接维护下两个值的大小就好,别来理解错题意
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int N=1e5+5; vector<pair<int,int> >G[N]; int sell[N],buy[N],ans; int vis[N]; void dfs(int x) { for(int i=0;i<(int)G[x].size();i++) { int v=G[x][i].first; int w=G[x][i].second; if(vis[v])continue; vis[v]=1; dfs(v); buy[x]=min(buy[x],buy[v]+w); sell[x]=max(sell[x],sell[v]-w); } ans=max(ans,buy[x]-sell[x]); ans=max(ans,sell[x]-buy[x]); } int main() { int T; scanf("%d",&T); while(T--) { int n; scanf("%d",&n); memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) G[i].clear(); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { scanf("%d",&sell[i]); buy[i]=sell[i]; } for(int i=1;i<n;i++) { int u,v,w; scanf("%d%d%d",&u,&v,&w); G[u].push_back({v,w}); G[v].push_back({u,w}); } ans=0; vis[1]=1; dfs(1); printf("%d\n",ans); } return 0; }
card card card
Time Limit: 8000/4000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 2684 Accepted Submission(s): 755
Problem Description
As a fan of Doudizhu, WYJ likes collecting playing cards very much.
One day, MJF takes a stack of cards and talks to him: let‘s play a game and if you win, you can get all these cards. MJF randomly assigns these cards into n heaps, arranges in a row, and sets a value on each heap, which is called "penalty value".
Before the game starts, WYJ can move the foremost heap to the end any times.
After that, WYJ takes the heap of cards one by one, each time he needs to move all cards of the current heap to his hands and face them up, then he turns over some cards and the number of cards he turned is equal to the penaltyvalue.
If at one moment, the number of cards he holds which are face-up is less than the penaltyvalue, then the game ends. And WYJ can get all the cards in his hands (both face-up and face-down).
Your task is to help WYJ maximize the number of cards he can get in the end.So he needs to decide how many heaps that he should move to the end before the game starts. Can you help him find the answer?
MJF also guarantees that the sum of all "penalty value" is exactly equal to the number of all cards.
One day, MJF takes a stack of cards and talks to him: let‘s play a game and if you win, you can get all these cards. MJF randomly assigns these cards into n heaps, arranges in a row, and sets a value on each heap, which is called "penalty value".
Before the game starts, WYJ can move the foremost heap to the end any times.
After that, WYJ takes the heap of cards one by one, each time he needs to move all cards of the current heap to his hands and face them up, then he turns over some cards and the number of cards he turned is equal to the penaltyvalue.
If at one moment, the number of cards he holds which are face-up is less than the penaltyvalue, then the game ends. And WYJ can get all the cards in his hands (both face-up and face-down).
Your task is to help WYJ maximize the number of cards he can get in the end.So he needs to decide how many heaps that he should move to the end before the game starts. Can you help him find the answer?
MJF also guarantees that the sum of all "penalty value" is exactly equal to the number of all cards.
Input
There are about 10 test cases ending up with EOF.
For each test case:
the first line is an integer n (1≤n≤106), denoting n heaps of cards;
next line contains n integers, the ith integer ai (0≤ai≤1000) denoting there are ai cards in ith heap;
then the third line also contains n integers, the ith integer bi (1≤bi≤1000) denoting the "penalty value" of ith heap is bi.
For each test case:
the first line is an integer n (1≤n≤106), denoting n heaps of cards;
next line contains n integers, the ith integer ai (0≤ai≤1000) denoting there are ai cards in ith heap;
then the third line also contains n integers, the ith integer bi (1≤bi≤1000) denoting the "penalty value" of ith heap is bi.
Output
For each test case, print only an integer, denoting the number of piles WYJ needs to move before the game starts. If there are multiple solutions, print the smallest one.
Sample Input
5
4 6 2 8 4
1 5 7 9 2
Sample Output
4
Hint
For the sample input: + If WYJ doesn‘t move the cards pile, when the game starts the state of cards is: 4 6 2 8 4 1 5 7 9 2 WYJ can take the first three piles of cards, and during the process, the number of face-up cards is 4-1+6-5+2-7. Then he can‘t pay the the "penalty value" of the third pile, the game ends. WYJ will get 12 cards. + If WYJ move the first four piles of cards to the end, when the game starts the state of cards is: 4 4 6 2 8 2 1 5 7 9 WYJ can take all the five piles of cards, and during the process, the number of face-up cards is 4-2+4-1+6-5+2-7+8-9. Then he takes all cards, the game ends. WYJ will get 24 cards. It can be improved that the answer is 4. **huge input, please use fastIO.**
直接模拟下,但是有个细节就是全部都可以取到
#include<stdio.h> #include<algorithm> #include<string.h> using namespace std; int a[1000005],b[1000005]; int main() { int n,x,i,s,p,y,q,r; while(~scanf("%d",&n)) { for(i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]),b[i]=a[i]; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { scanf("%d",&x); a[i]-=x; } s=0;p=i;y=0;q=0;r=0; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { s+=a[i]; if(s<0) { if(q<y) { q=y,r=p; } y=0; s=0; p=i+1; } y+=b[i]; } if(p==n) { printf("%d\n",r); continue; } for(i=0;i<p;i++) { s+=a[i]; if(s<0) { if(q<y) { q=y,r=p; } break; } y+=b[i]; } if(q<y) { q=y,r=p; } printf("%d\n",r); } }
以上是关于2017 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Shenyang Online的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章