如何实现一个 Virtual DOM 及源码分析
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了如何实现一个 Virtual DOM 及源码分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
如何实现一个 Virtual DOM 及源码分析
Virtual DOM算法
web页面有一个对应的DOM树,在传统开发页面时,每次页面需要被更新时,都需要手动操作DOM来进行更新,但是我们知道DOM操作对性能来说是非常不友好的,会影响页面的重排,从而影响页面的性能。因此在React和VUE2.0+引入了虚拟DOM的概念,他们的原理是:把真实的DOM树转换成javascript对象树,也就是虚拟DOM,每次数据需要被更新的时候,它会生成一个新的虚拟DOM,并且和上次生成的虚拟DOM进行对比,对发生变化的数据做批量更新。---(因为操作JS对象会更快,更简单,比操作DOM来说)。
我们知道web页面是由一个个html元素嵌套组合而成的,当我们使用javascript来描述这些元素的时候,这些元素可以简单的被表示成纯粹的JSON对象。
比如如下HTML代码:
<div id="container" class="container"> <ul id="list"> <li class="item">111</li> <li class="item">222</li> <li class="item">333</li> </ul> <button class="btn btn-blue"><em>提交</em></button> </div>
上面是真实的DOM树结构,我们可以使用javascript中的json对象来表示的话,变成如下:
var element = { tagName: \'div\', props: { // DOM的属性 id: \'container\', class: \'container\' }, children: [ { tagName: \'ul\', props: { id: \'list\' }, children: [ {tagName: \'li\', props: {class: \'item\'}, children: [\'111\']}, {tagName: \'li\', props: {class: \'item\'}, children: [\'222\']}, {tagName: \'li\', props: {class: \'item\'}, children: [\'333\']} ] }, { tagName: \'button\', props: { class: \'btn btn-blue\' }, children: [ { tagName: \'em\', children: [\'提交\'] } ] } ] };
因此我们可以使用javascript对象表示DOM的信息和结构,当状态变更的时候,重新渲染这个javascript对象的结构,然后可以使用新渲染的对象树去和旧的树去对比,记录两颗树的差异,两颗树的差异就是我们需要对页面真正的DOM操作,然后把他们应用到真正的DOM树上,页面就得到更新。视图的整个结构确实全渲染了,但是最后操作DOM的时候,只变更不同的地方。
因此我们可以总结一下 Virtual DOM算法:
1. 用javascript对象结构来表示DOM树的结构,然后用这个树构建一个真正的DOM树,插入到文档中。
2. 当状态变更的时候,重新构造一颗新的对象树,然后使用新的对象树与旧的对象树进行对比,记录两颗树的差异。
3. 把记录下来的差异用到步骤1所构建的真正的DOM树上。视图就更新了。
算法实现:
2-1 使用javascript对象模拟DOM树。
使用javascript来表示一个DOM节点,有如上JSON的数据,我们只需要记录它的节点类型,属性和子节点即可。
element.js 代码如下:
function Element(tagName, props, children) { this.tagName = tagName; this.props = props; this.children = children; } Element.prototype.render = function() { var el = document.createElement(this.tagName); var props = this.props; // 遍历子节点,依次设置子节点的属性 for (var propName in props) { var propValue = props[propName]; el.setAttribute(propName, propValue); } // 保存子节点 var childrens = this.children || []; // 遍历子节点,使用递归的方式 渲染 childrens.forEach(function(child) { var childEl = (child instanceof Element) ? child.render() // 如果子节点也是虚拟DOM,递归构建DOM节点 : document.createTextNode(child); // 如果是字符串的话,只构建文本节点 el.appendChild(childEl); }); return el; }; module.exports = function(tagName, props, children) { return new Element(tagName, props, children); }
入口index.js代码如下:
var el = require(\'./element\'); var element = el(\'div\', {id: \'container\', class: \'container\'}, [ el(\'ul\', {id: \'list\'},[ el(\'li\', {class: \'item\'}, [\'111\']), el(\'li\', {class: \'item\'}, [\'222\']), el(\'li\', {class: \'item\'}, [\'333\']), ]), el(\'button\', {class: \'btn btn-blue\'}, [ el(\'em\', {class: \'\'}, [\'提交\']) ]) ]); var elemRoot = element.render(); document.body.appendChild(elemRoot);
打开页面即可看到效果。
2-2 比较两颗虚拟DOM树的差异及差异的地方进行dom操作
上面的div只会和同一层级的div对比,第二层级的只会和第二层级的对比,这样的算法的复杂度可以达到O(n).
但是在实际代码中,会对新旧两颗树进行一个深度优先的遍历,因此每个节点都会有一个标记。如下图所示: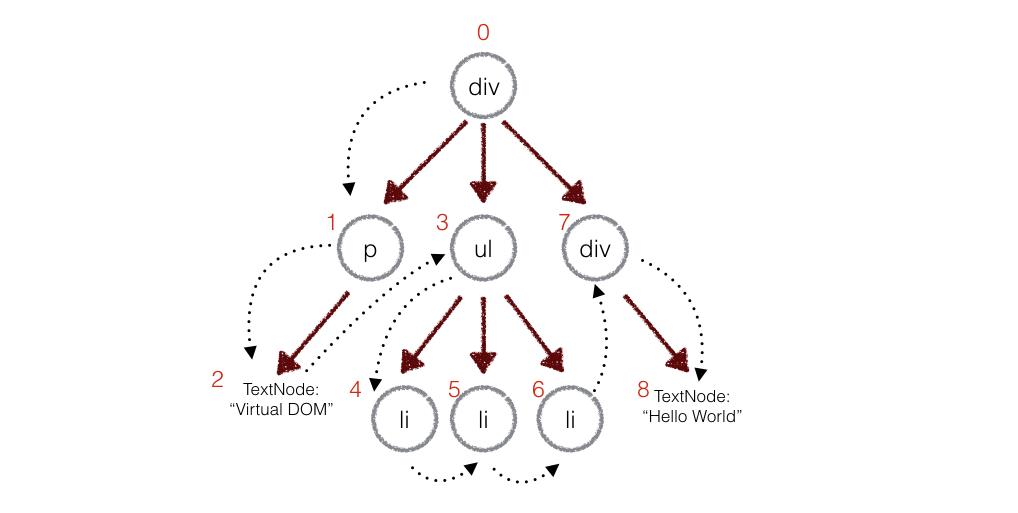
在遍历的过程中,每次遍历到一个节点就把该节点和新的树进行对比,如果有差异的话就记录到一个对象里面。
现在我们来看下我的目录下 有哪些文件;然后分别对每个文件代码进行解读,看看做了哪些事情,旧的虚拟dom和新的虚拟dom是如何比较的,且是如何更新页面的 如下目录:
目录结构如下:
vdom ---- 工程名 | | ---- index.html html页面 | | ---- element.js 实例化元素组成json数据 且 提供render方法 渲染页面 | | ---- util.js 提供一些公用的方法 | | ---- diff.js 比较新旧节点数据 如果有差异保存到一个对象里面去 | | ---- patch.js 对当前差异的节点数据 进行DOM操作 | | ---- index.js 页面代码初始化调用
首先是 index.js文件 页面渲染完成后 变成如下html结构
<div id="container"> <h1 style="color: red;">simple virtal dom</h1> <p>the count is :1</p> <ul> <li>Item #0</li> </ul> </div>
假如发生改变后,变成如下结构
<div id="container"> <h1 style="color: blue;">simple virtal dom</h1> <p>the count is :2</p> <ul> <li>Item #0</li> <li>Item #1</li> </ul> </div>
可以看到 新旧节点页面数据的改变,h1标签从属性 颜色从红色 变为蓝色,p标签的文本发生改变,ul新增了一项元素li。
基本的原理是:先渲染出页面数据出来,生成第一个模板页面,然后使用定时器会生成一个新的页面数据出来,对新旧两颗树进行一个深度优先的遍历,因此每个节点都会有一个标记。
然后调用diff方法对比对象新旧节点遍历进行对比,找出两者的不同的地方存入到一个对象里面去,最后通过patch.js找出对象不同的地方,分别进行dom操作。
index.js代码如下:
var el = require(\'./element\'); var diff = require(\'./diff\'); var patch = require(\'./patch\'); var count = 0; function renderTree() { count++; var items = []; var color = (count % 2 === 0) ? \'blue\' : \'red\'; for (var i = 0; i < count; i++) { items.push(el(\'li\', [\'Item #\' + i])); } return el(\'div\', {\'id\': \'container\'}, [ el(\'h1\', {style: \'color: \' + color}, [\'simple virtal dom\']), el(\'p\', [\'the count is :\' + count]), el(\'ul\', items) ]); } var tree = renderTree() var root = tree.render() document.body.appendChild(root) setInterval(function () { var newTree = renderTree() var patches = diff(tree, newTree) console.log(patches) patch(root, patches) tree = newTree }, 1000);
执行 var tree = renderTree()方法后,会调用element.js,
1. 依次遍历子节点(从内到外调用)依次为 li, h1, p, ul, li和h1和p有一个文本子节点,因此遍历完成后,count就等于1,
但是遍历ul的时候,因为有一个子节点li,因此 count += 1; 所以调用完成后,ul的count等于2. 因此会对每个element属性添加count属性。对于最外层的container容器就是对每个子节点的依次增加,h1子节点默认为1,循环完成后 +1;因此变为2, p节点默认为1,循环完成后 +1,因此也变为2,ul为2,循环完成后 +1,因此变为3,因此container节点的count=2+2+3 = 7;
element.js部分代码如下:
function Element(tagName, props, children) { if (!(this instanceof Element)) { // 判断子节点 children 是否为 undefined if (!utils.isArray(children) && children !== null) { children = utils.slice(arguments, 2).filter(utils.truthy); } return new Element(tagName, props, children); } // 如果没有属性的话,第二个参数是一个数组,说明第二个参数传的是子节点 if (utils.isArray(props)) { children = props; props = {}; } this.tagName = tagName; this.props = props || {}; this.children = children || []; // 保存key键 如果有属性 保存key,否则返回undefined this.key = props ? props.key : void 0; var count = 0; utils.each(this.children, function(child, i) { // 如果是元素的实列的话 if (child instanceof Element) { count += child.count; } else { // 如果是文本节点的话,直接赋值 children[i] = \'\' + child; } count++; }); this.count = count; }
oldTree数据最终变成如下:
var oldTree = { tagName: \'div\', key: undefined, count: 7, props: {id: \'container\'}, children: [ { tagName: \'h1\', key: undefined count: 1 props: {style: \'colod: red\'}, children: [\'simple virtal dom\'] }, { tagName: \'p\', key: undefined count: 1 props: {}, children: [\'the count is :1\'] }, { tagName: \'ul\', key: undefined count: 2 props: {}, children: [ { tagName: \'li\', key: undefined, count: 1, props: {}, children: [\'Item #0\'] } ] }, ] };
定时器 执行 var newTree = renderTree()后,调用方法步骤还是和第一步一样:
2. 依次遍历子节点(从内到外调用)依次为 li, h1, p, ul, li和h1和p有一个文本子节点,因此遍历完成后,count就等于1,因为有2个子元素li,count都为1,因此ul每次遍历依次在原来的基础上加1,因此遍历完成第一个li时候,ul中的count为2,当遍历完成第二个li的时候,ul的count就为4了。因此ul中的count为4. 对于最外层的container容器就是对每个子元素依次增加。
所以 container节点的count = 2 + 2 + 5 = 9;
newTree数据最终变成如下数据:
var newTree = { tagName: \'div\', key: undefined, count: 9, props: {id: \'container\'}, children: [ { tagName: \'h1\', key: undefined count: 1 props: {style: \'colod: red\'}, children: [\'simple virtal dom\'] }, { tagName: \'p\', key: undefined count: 1 props: {}, children: [\'the count is :1\'] }, { tagName: \'ul\', key: undefined count: 4 props: {}, children: [ { tagName: \'li\', key: undefined, count: 1, props: {}, children: [\'Item #0\'] }, { tagName: \'li\', key: undefined, count: 1, props: {}, children: [\'Item #1\'] } ] }, ] }
var patches = diff(oldTree, newTree);
调用diff方法可以比较新旧两棵树节点的数据,把两颗树的不同节点找出来。(注意,查看diff对比数据的方法,找到不同的节点,可以查看这篇文章diff算法)如下调用代码:
function diff (oldTree, newTree) { var index = 0; var patches = {}; deepWalk(oldTree, newTree, index, patches); return patches; }
执行deepWalk如下代码:
function deepWalk(oldNode, newNode, index, patches) { var currentPatch = []; // 节点被删除掉 if (newNode === null) { // 真正的DOM节点时,将删除执行重新排序,所以不需要做任何事 } else if(utils.isString(oldNode) && utils.isString(newNode)) { // 替换文本节点 if (newNode !== oldNode) { currentPatch.push({type: patch.TEXT, content: newNode}); } } else if(oldNode.tagName === newNode.tagName && oldNode.key === newNode.key) { // 相同的节点,但是新旧节点的属性不同的情况下 比较属性 // diff props var propsPatches = diffProps(oldNode, newNode); if (propsPatches) { currentPatch.push({type: patch.PROPS, props: propsPatches}); } // 不同的子节点 if (!isIgnoreChildren(newNode)) { diffChildren( oldNode.children, newNode.children, index, patches, currentPatch ) } } else { // 不同的节点,那么新节点替换旧节点 currentPatch.push({type: patch.REPLACE, node: newNode}); } if (currentPatch.length) { patches[index] = currentPatch; } }
1. 判断新节点是否为null,如果为null,说明节点被删除掉。
2. 判断新旧节点是否为字符串,如果为字符串说明是文本节点,并且新旧两个文本节点不同的话,存入数组里面去,如下代码:
currentPatch.push({type: patch.TEXT, content: newNode});
patch.TEXT 为 patch.js里面的 TEXT = 3;content属性为新节点。
3. 如果新旧tagName相同的话,并且新旧节点的key相同的话,继续比较新旧节点的属性,如下代码:
var propsPatches = diffProps(oldNode, newNode);
diffProps方法的代码如下:
function diffProps(oldNode, newNode) { var count = 0; var oldProps = oldNode.props; var newProps = newNode.props; var key, value; var propsPatches = {}; // 找出不同的属性值 for (key in oldProps) { value = oldProps[key]; if (newProps[key] !== value) { count++; propsPatches[key] = newProps[key]; } } // 找出新增属性 for (key in newProps) { value = newProps[key]; if (!oldProps.hasOwnProperty(key)) { count++; propsPatches[key] = newProps[key]; } } // 如果所有的属性都是相同的话 if (count === 0) { return null; } return propsPatches; }
diffProps代码解析如下:
for (key in oldProps) { value = oldProps[key]; if (newProps[key] !== value) { count++; propsPatches[key] = newProps[key]; } }
如上代码是 判断旧节点的属性值是否在新节点中找到,如果找不到的话,count++; 把新节点的属性值赋值给 propsPatches 存储起来。
for (key in newProps) { value = newProps[key]; if (!oldProps.hasOwnProperty(key)) { count++; propsPatches[key] = newProps[key]; } }
如上代码是 判断新节点的属性是否能在旧节点中找到,如果找不到的话,count++; 把新节点的属性值赋值给 propsPatches 存储起来。
if (count === 0) { return null; } return propsPatches;
最后如果count 等于0的话,说明所有属性都是相同的话,所以不需要做任何变化。否则的话,返回新增的属性。
如果有 propsPatches 的话,执行如下代码:
if (propsPatches) { currentPatch.push({type: patch.PROPS, props: propsPatches}); }
因此currentPatch数组里面也有对应的更新的属性,props就是需要更新的属性对象。
继续代码:
// 不同的子节点 if (!isIgnoreChildren(newNode)) { diffChildren( oldNode.children, newNode.children, index, patches, currentPatch ) } function isIgnoreChildren(node) { return (node.props && node.props.hasOwnProperty(\'ignore\')); }
如上代码判断子节点是否相同,diffChildren代码如下:
function diffChildren(oldChildren, newChildren, index, patches, currentPatch) { var diffs = listDiff(oldChildren, newChildren, \'key\'); newChildren = diffs.children; if (diffs.moves.length) { var recorderPatch = {type: patch.REORDER, moves: diffs.moves}; currentPatch.push(recorderPatch); } var leftNode = null; var currentNodeIndex = index; utils.each(oldChildren, function(child, i) { var newChild = newChildren[i]; currentNodeIndex = (leftNode && leftNode.count) ? currentNodeIndex + leftNode.count + 1 : currentNodeIndex + 1; // 递归 deepWalk(child, newChild, currentNodeIndex, patches); leftNode = child; }); }
如上代码:var diffs = listDiff(oldChildren, newChildren, \'key\'); 新旧节点按照key来比较,目前key为undefined,所以diffs 为如下:
diffs = { moves: [], children: [ { tagName: \'h1\', key: undefined count: 1 props: {style: \'colod: blue\'}, children: [\'simple virtal dom\'] }, { tagName: \'p\', key: undefined count: 1 props: {}, children: [\'the count is :2\'] }, { tagName: \'ul\', key: undefined count: 4 props: {}, children: [ { tagName: \'li\', key: undefined, count: 1, props: {}, children: [\'Item #0\'] }, { tagName: \'li\', key: undefined, count: 1, props: {}, children: [\'Item #1\'] } ] } ] };
newChildren = diffs.children;
oldChildren数据如下:
oldChildren = [ { tagName: \'h1\', key: undefined count: 1 props: {style: \'colod: red\'}, children: [\'simple virtal dom\'] }, { tagName: \'p\', key: undefined count: 1 props: {}, children: [\'the count is :1\'] }, { tagName: \'ul\', key: undefined count: 2 props: {}, children: [ { tagName: \'li\', key: undefined, count: 1, props: {}, children: [\'Item #0\'] } ] } ];
接着就是遍历 oldChildren, 第一次遍历时 leftNode 为null,因此 currentNodeIndex = currentNodeIndex + 1 = 0 + 1 = 1; 不是第一次遍历,那么leftNode都为上一次遍历的子节点,因此不是第一次遍历的话,那么 currentNodeIndex = currentNodeIndex + leftNode.count + 1;
然后递归调用 deepWalk(child, newChild, currentNodeIndex, patches); 方法,接着把child赋值给leftNode,leftNode = child;
所以一直递归遍历,最终把不相同的节点 会存储到 currentPatch 数组内。最后执行
if (currentPatch.length) { patches[index] = currentPatch; }
把对应的currentPatch 存储到 patches对象内中的对应项,最后就返回 patches对象。
4. 返回到index.js 代码内,把两颗不相同的树节点的提取出来后,需要调用patch.js方法传进;把不相同的节点应用到真正的DOM上.
不相同的节点 patches数据如下:
patches = { 1: [{type: 2, props: {style: \'color: blue\'}}], 4: [{type: 3, content: \'the count is :2\'}], 5: [ { type: 1, moves: [ { index: 1, item: { tagName: \'li\', props: {}, count: 1, key: undefined, children: [\'Item #1\'] } } ] } ] }
如下代码调用:
patch(root, patches);
执行patch方法,代码如下:
function patch(node, patches) { var walker = {index: 0}; deepWalk(node, walker, patches); }
deepWalk 代码如下:
function deepWalk(node, walker, patches) { var currentPatches = patches[walker.index]; // node.childNodes 返回指定元素的子元素集合,包括HTML节点,所有属性,文本节点。 var len = node.childNodes ? node.childNodes.length : 0; for (var i = 0; i < len; i++) { var child = node.childNodes[i]; walker.index++; // 深度复制 递归遍历 deepWalk(child, walker, patches); } if (currentPatches) { applyPatches(node, currentPatches); } }
1. 首次调用patch的方法,root就是container的节点,因此调用deepWalk方法,因此 var currentPatches = patches[0] = undefined,
var len = node.childNodes ? node.childNodes.length : 0; 因此 len = 3; 很明显该子节点的长度为3,因为子节点有 h1, p, 和ul元素;
2. 然后进行for循环,获取该父节点的子节点,因此第一个子节点为 h1 元素,walker.index++; 因此walker.index = 1; 再进行递归 deepWalk(child, walker, patches); 此时子节点为h1, walker.index为1, 因此获取 currentPatches = patches[1]; 获取值,再获取 h1的子节点的长度,len = 1; 然后再for循环,获取child为文本节点,此时 walker.index++; 所以此时walker.index 为2, 在调用deepwalk方法递归,因此再继续获取 currentPatches = patches[2]; 值为undefined,再获取len = 0; 因为文本节点么有子节点,所以for循环跳出,所以判断currentPatches是否有值,因为此时 currentPatches 为undefined,所以递归结束,再返回到 h1元素上来,所以currentPatches = patches[1]; 所以有值,所以调用 applyPatches()方法来更新dom元素。
3. 继续循环 i, 此时i = 1; 获取子节点 child = p元素,walker.index++,此时walker.index = 3, 继续调用 deepWalk方法,获取 var currentPatches = patches[walker.index] = patches[3]的值,var len = 1; 因为p元素下有一个子节点(文本节点),再进for循环,此时 walker.index++; 因此walker.index = 4; child此时为文本节点,在调用 deepwalk方法的时候,再获取var currentPatches = patches[walker.index] = patches[4]; 再执行len 代码的时候 len = 0;因此跳出for循环,判断 currentPatches是否有值,有值的话,更新对应的DOM元素。
4. 继续循环i = 2; 获取子节点 child = ul元素,walker.index++; 此时walker.index = 5; 在调用deepWalk方法递归,因此再获取 var currentPatches = patches[walker.index] = patches[5]; 然后len = 1, 因为ul元素下有一个li元素,在继续for循环遍历,获取子节点li,此时walker.index++; walker.index = 6; 再递归调用deepwalk方法,再获取var currentPatches = patches[walker.index] = patches[6]; len = 1; 因为li的元素下有一个文本节点,再进行for循环,此时child为文本节点,walker.index++;此时walker.index = 7; 再执行 deepwalk方法,再获取 var currentPatches = patches[walker.index] = patches[7]; 这时候 len = 0了,因此跳出for循环,判断 当前的currentPatches是否有值,没有,就跳出,然后再返回ul元素,获取该自己li的时候,walker.index 等于5,因此var currentPatches = patches[walker.index] = patches[5]; 然后判断 currentPatches是否有值,有值就进行更新DOM元素。
最后就是 applyPatches 方法更新dom元素了,如下代码:
function applyPatches(node, currentPatches) { utils.each(currentPatches, function(currentPatch) { switch (currentPatch.type) { case REPLACE: var newNode = (typeof currentPatch.node === \'string\') ? document.createTextNode(currentPatch.node) : currentPatch.node.render(); node.parentNode.replaceChild(newNode, node); break; case REORDER: reorderChildren(node, currentPatch.moves); break; case PROPS: setProps(node, currentPatch.props); break; case TEXT: if(node.textContent) { node.textContent = currentPatch.content; } else { // ie bug node.nodeValue = currentPatch.content; } break; default: throw new Error(\'Unknow patch type\' + currentPatch.type); } }); }
判断类型,替换对应的属性和节点。
最后就是对子节点进行排序的操作,代码如下:
// 对子节点进行排序 function reorderChildren(node, moves) { var staticNodeList = utils.toArray(node.childNodes); var maps = {}; utils.each(staticNodeList, function(node) { // 如果是元素节点 if (node.nodeType === 1) { var key = node.getAttribute(\'key\'); if (key) { maps[key] = node; } } }) utils.each(moves, function(move) { var index = move.index; if (move.type === 0) { // remove Item if (staticNodeList[index] === node.childNodes[index]) { node.removeChild(node.childNodes[index]); } staticNodeList.splice(index, 1); } else if(move.type === 1) { // insert item var insertNode = maps[move.item.key] ? maps[move.item.key].cloneNode(true) : (typeof move.item === \'object\') ? move.item.render() : document.createTextNode(move.item); staticNodeList.splice(index, 0, insertNode); node.insertBefore(insertNode, node.childNodes[index] || null); } }); }
遍历moves,判断moves.type 是等于0还是等于1,等于0的话是删除操作,等于1的话是新增操作。比如现在moves值变成如下:
moves = { index: 1, type: 1, item: { tagName: \'li\', key: undefined, props: {}, count: 1, children: [\'#Item 1\'] } };
node节点 就是 \'ul\'元素,var staticNodeList = utils.toArray(node.childNodes); 把ul的旧子节点li转成Array形式,由于没有属性key,所以直接跳到下面遍历代码来,遍历moves,获取某一项的索引index,判断move.type 等于0 还是等于1, 目前等于1,是新增一项,但是没有key,因此调用move.item.render(); 渲染完后,对staticNodeList数组里面的旧节点的li项从第二项开始插入节点li,然后执行node.insertBefore(insertNode, node.childNodes[index] || null); node就是ul父节点,insertNode节点插入到 node.childNodes[1]的前面。因此把在第二项的前面插入第一项。
查看github上源码
以上是关于如何实现一个 Virtual DOM 及源码分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章