第45课 递归的思想与应用(下)
Posted 浅墨浓香
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了第45课 递归的思想与应用(下)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 函数调用栈的回顾
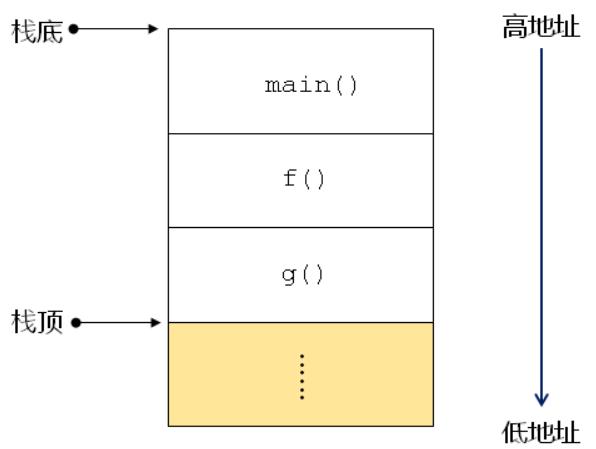
(1)用于保存函数中的实参、局部变量、临时变量等。
(2)从起始地址开始往一个方向增长(如:高地址→低地址)
(3)有一个专用“指针”标识当前已使用内存的“顶部”
(4)当函数调用结束时,栈会恢复到被调用前的状态。可以利用这个时机进行一些的回溯算法的设计。
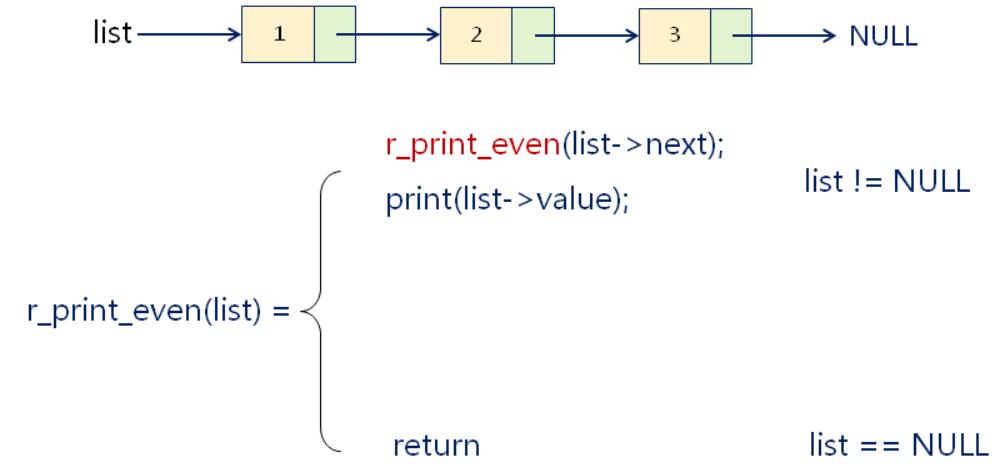
【实例分析】函数调用栈分析:逆序打印单链表中的偶数结点(void r_print_even(Node* list)),见本课后面的源码
2. 回溯求解八皇后问题
(1)回溯算法:实际上一个类似枚举的搜索尝试过程,主要是在搜索尝试过程中寻找问题的解,当发现已不满足求解条件时,就“回溯”返回,尝试别的路径。八皇后问题就是回溯算法的典型,第一步按照顺序放一个皇后,然后第二步符合要求放第2个皇后,如果没有位置符合要求,那么就要改变第一个皇后的位置,再重新放第2个皇后的位置,直到找到符合条件的位置,以此方法放其他皇后…
(2)八皇后问题

①在一个8×8的国际象棋棋盘上,有8个皇后,每个皇后占一格;
②要求皇后间不会出现相互“攻击”的现象(不能有两个皇后处在同一行、 同一列或同一对角线上)
(3)关键数据结构定义
①棋盘:二维数组(8 × 8):0表示位置为空,1表示皇后。
②位置:struct Pos; 其中的x字段表示列坐标,y表示行坐标。
③方向:
水平:向左(-1,0),向右(1,0)
垂直:向上(0,1),向下(0,-1)
对角线:左上(-1,1),左下(-1,-1),右上(1,1),右下(1,-1)
(3)算法思路:
①从第一行开始,为皇后找到安全位置,然后跳到下一行,通过递归进行深度搜索。
②如果在第n行出现死胡同,当该行为第一行,棋局失败,否则后退到上一行,进行回溯,并从该行的下一列位置继续查找安全位置。
③如果在第8行上找到了安全位置,则棋局成功。
【编程实验】八皇后问题的递归解法
#include <iostream> #include "LinkList.h" using namespace std; using namespace DTLib; struct Node { int value; Node* next; }; //创建无表头结点的单链表(己填充数据):v结点的值,len链表长度 Node* create_list(int v, int len) { Node* ret = NULL; Node* slider = NULL; for(int i=0; i<len; i++){ Node* node = new Node(); node->value = v++; node->next = NULL; //每创建好一个节点,slider指向这个节点 if( slider == NULL ){ slider = node; ret = node; }else{ slider->next = node; slider = node; } } return ret; } void destroy_list(Node* list) { while(list){ Node* del = list; list = list->next; delete del; } } //打印链表的内容 void print_list(Node* list) { while(list){ cout << list->value << "->"; list = list->next; } cout << "NULL" << endl; } //逆序打印单链表中的偶数结点 void r_print_even(Node* list) { if(list != NULL){ //深度搜索,直到最后一个节点 r_print_even(list->next); //回溯算法设计:上一行递归结束,开始回溯并判断节点的值是否为偶数 if(list->value % 2 == 0){ cout << list->value << " "; } } } template<int N> class QueenSolution : public Object { protected: struct Pos : public Object { int x; int y; Pos(int px = 0, int py = 0):x(px),y(py){} }; int m_chessboard[N][N]; //棋盘: 原点0,0在左下角,x轴正方向向右,y轴正方向向上 Pos m_direction[3]; //三个方向向量 LinkList<Pos> m_solution; int m_count; void init() { m_count = 0; //初始化棋盘 for(int i=0; i<N; i++){ for (int j=0; j<N; j++){ m_chessboard[i][j] = 0; } } //初始化方向矢量 //左下角 m_direction[0].x =-1; m_direction[0].y =-1; //向下 m_direction[1].x =0; m_direction[1].y =-1; //右下角 m_direction[2].x =1; m_direction[2].y =-1; } //打印棋盘内容 void print() { typename LinkList<Pos>::iterator iter = m_solution.begin(); while(iter != m_solution.end()){ cout << "(" << (*iter).x <<"," <<(*iter).y <<") "; iter++; } cout << endl; for(int y=0; y<N; y++){ for (int x=0; x<N; x++){ switch (m_chessboard[x][y]) { case 0:cout << " ."; break; case 1:cout << " #"; break; } } cout << endl; } cout << endl; } bool isInner(int x, int y) { return (0<=x) && (x<N) && (0<=y) && (y<N); } //检测在棋盘的(x,y)位置是否可以放置皇后 bool check(int x, int y, int d) { bool ret = true; while(ret && isInner(x, y)) { ret = ret && (m_chessboard[x][y] == 0); x += m_direction[d].x; y += m_direction[d].y; } return ret; } //在第row行尝试放置皇后 void place(int row) { int y = row; if(row < N){ for(int x=0; x<N; x++){ if(check(x, y, 0) && check(x, y, 1) && check(x, y, 2)){ m_chessboard[x][y] = 1; //放置皇后 m_solution.insert(Pos(x,y)); //将该位置加入链表 place(row + 1); //在下一行放置皇后。 //当place(row+1)函数返回时,表示第row+1行无法找到放置皇后的地方(或找到解决方案后正常返回) m_chessboard[x][y] = 0; //回溯,将当前位置的皇后移除。 m_solution.remove(m_solution.length() - 1); } } }else{ //由于采用深度优先搜索,所以放置到第SIZE行时,表示己经找到解决方案 m_count++; //每找到一行方案,m_count加1。 print(); //打印解决方案 } } public: QueenSolution(){init();} void solve() { place(0); //从第0行开始放置 cout << "total : " << m_count << endl; } }; int main() { //测试:逆序打印单链表中的偶数结点 Node* list = create_list(1, 10); print_list(list); r_print_even(list); destroy_list(list); cout << endl; //测试:八皇后解决方案 QueenSolution<8> qs; qs.solve(); return 0; } /*测试结果: 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->8->9->10->NULL 10 8 6 4 2 (0,0) (4,1) (7,2) (5,3) (2,4) (6,5) (1,6) (3,7) //显示时,使用的坐标系(原点在左上角,x向右为正,y向下为正) # . . . . . . . . . . . # . . . . . . . . . . # . . . . . # . . . . # . . . . . . . . . . . # . . # . . . . . . . . . # . . . . (0,0) (5,1) (7,2) (2,3) (6,4) (3,5) (1,6) (4,7) # . . . . . . . . . . . . # . . . . . . . . . # . . # . . . . . . . . . . . # . . . . # . . . . . # . . . . . . . . . . # . . . //省略其余解决方案... total : 92 */
3. 经典面试题
(1)三羊献瑞

(2)解题思路
①给“祥瑞生辉三羊献气”编号0、1、2、3、4、5、6、7。
②利用深度优先递归+回溯方法穷举
【编程实验】三羊献瑞
//main.cpp
#include <iostream> using namespace std; //问题:求“三羊献瑞”所代表的4位数字 // 祥 瑞 生 辉 // + 三 羊 献 瑞 //---------------------- // 三 羊 生 瑞 气 //注意:相同汉字代表相同数字,不同汉字代表的不同数字 //给“祥瑞生辉三羊献气”等汉字编号,放入a数组中。 //即“祥”代表a[0],“瑞”为a[1],“生”为a[2]...等。 int a[8] = {0}; int visited[10] = {0}; //0~9只能用1次,己访问1,未访问0 //深度优先递归 + 回溯算法。 //参数curr:表示当前正在尝试放置a[curr]元素。 void threeSheep(int curr) { //递归出口 if(curr == 8){ //当curr为8时,表示a数组中的数字全部填满 int x, y, z; x = a[0]*1000 + a[1]*100 + a[2]*10 + a[3]; y = a[4]*1000 + a[5]*100 + a[6]*10 + a[1]; z = a[4]*10000 + a[5]*1000 + a[2]*100 + a[1]*10 + a[7]; //判断找到的8个数字是否满足上述“算式”,若满足则递归结束 if((x + y) == z){ cout << a[4] << a[5] << a[6] << a[1] << endl; } return; } //将0~9数字一个一个放入a[curr]中试试 for(int i=0; i<=9; i++){ if(curr==0 && i==0) //a[0]不能等于0 continue; if(curr==4 && i!=1) //a[4]代表“三”字,必须为1 continue; if(!visited[i]){ //i数字是否己被放入a数组中。 visited[i] = 1; //标记i数字己被使用 a[curr] = i; //尝试将i放入a[curr] threeSheep(curr + 1); //放置a[curr+1]这个数字 visited[i] = 0; //回溯 } } } int main() { threeSheep(0); //从a[0]开始放置数字 return 0; } /*输出结果: e:\\Study\\test>g++ main.cpp e:\\Study\\test>a.exe 1085 */
4. 小结
(1)程序运行后的栈存储区专供函数调用使用
(2)栈存储区用于保存实参、局部变量和临时变量等。
(3)利用栈存储区能够方便的实现回溯算法
(4)八皇后问题是栈回溯的经典应用。
以上是关于第45课 递归的思想与应用(下)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章