JTA的使用与理解
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JTA的使用与理解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.介绍
事物的ACID。
事务是计算机应用中不可或缺的组件模型,它保证了用户操作的原子性 ( Atomicity )、一致性 ( Consistency )、隔离性 ( Isolation ) 和持久性 ( Durabilily )。
操作必须保正 ACID 的事务属性:即要么全部成功,要么全部失败
2.本地事物
紧密依赖于底层资源管理器(例如数据库连接 ),事务处理局限在当前事务资源内。
此种事务处理方式不存在对应用服务器的依赖,因而部署灵活却无法支持多数据源的分布式事务。
3.数据库连接中使用本地事务

1 package Local; 2 3 import java.sql.Connection; 4 import java.sql.DriverManager; 5 import java.sql.PreparedStatement; 6 import java.sql.ResultSet; 7 import java.sql.SQLException; 8 import java.sql.Statement; 9 10 public class LocalTractionTest { 11 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 traction(); 14 } 15 public static void traction() { 16 Connection connection=null; 17 Statement statement=null; 18 PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null; 19 ResultSet resultSet=null; 20 try { 21 String driverClass="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; 22 String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"; 23 String user="root"; 24 String password="123456"; 25 Class.forName(driverClass); 26 connection=DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); 27 connection.setAutoCommit(false); 28 statement=connection.createStatement(); 29 //原始数据 30 String sql="SELECT * FROM t_account"; 31 preparedStatement=connection.prepareStatement(sql); 32 resultSet=preparedStatement.executeQuery(); 33 while(resultSet.next()) { 34 String id=resultSet.getString(1); 35 String amount=resultSet.getString(2); 36 System.out.println(id+"......."+amount); 37 } 38 //操作 39 // 将 A 账户中的金额减少¥ 500 40 String sql1="update t_account set amount = amount - 500 where account_id = ‘A‘"; 41 statement.execute(sql1); 42 // 将 B 账户中的金额增加¥ 500 43 String sql2="update t_account set amount = amount + 500 where account_id = ‘B‘"; 44 statement.execute(sql2); 45 // 提交 46 connection.commit(); 47 //新的数据 48 preparedStatement=connection.prepareStatement(sql); 49 resultSet=preparedStatement.executeQuery(); 50 while(resultSet.next()) { 51 String id=resultSet.getString(1); 52 String amount=resultSet.getString(2); 53 System.out.println(id+"......."+amount); 54 } 55 }catch(ClassNotFoundException e1) { 56 e1.getMessage(); 57 }catch(SQLException e2) { 58 try { 59 connection.rollback(); 60 connection.close(); 61 statement.close(); 62 } catch (SQLException e3) { 63 e3.printStackTrace(); 64 } 65 e2.printStackTrace(); 66 } 67 } 68 69 }
4.效果
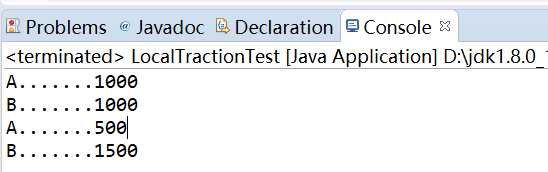
5.sql语句
1 SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0; 2 3 -- ---------------------------- 4 -- Table structure for t_account 5 -- ---------------------------- 6 DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_account`; 7 CREATE TABLE `t_account`( 8 `account_id` varchar(64) NOT NULL, 9 `amount` int(64) DEFAULT NULL, 10 PRIMARY KEY (`account_id`) 11 ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; 12 13 -- ---------------------------- 14 -- Records of t_account 15 -- ---------------------------- 16 INSERT INTO `t_account` VALUES (‘A‘, ‘500‘); 17 INSERT INTO `t_account` VALUES (‘B‘, ‘1500‘);
以上是关于JTA的使用与理解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
