初始kbmmw 中的ORM
Posted Delphi 窑洞
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了初始kbmmw 中的ORM相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在kbmmw 5.02.1 中,加入了ORM 的功能(这里可能和其他语言的定义不完全一样),我们就简单的认为
它就是一个类与数据库的转换吧。今天就先介绍一下如何通过kbmmw 的ORM 功能,实现类与数据库的相互
转换和操作。
前提条件:delphi 10.2.1
kbmmw 5.02.1
unidac 7.0.2
haosql for sql server 2008 非常不错的一个sql 管理器
启动haosql for sqlserver2008 管理器,启动数据库。
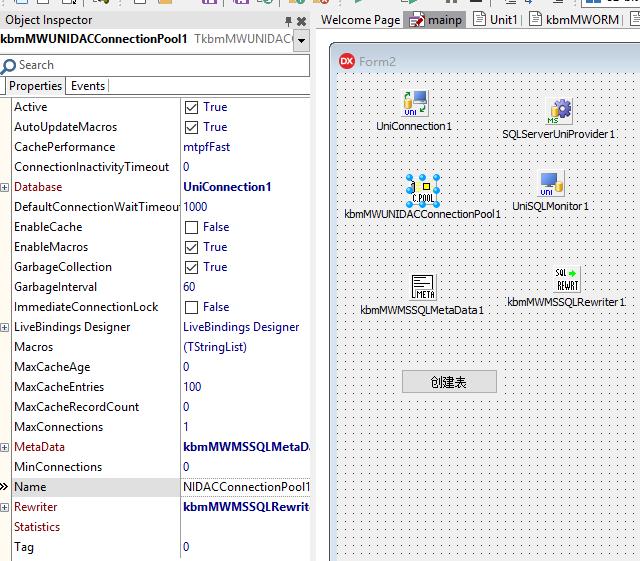
打开delphi ,建立一个标准的工程,放置如图的几个控件
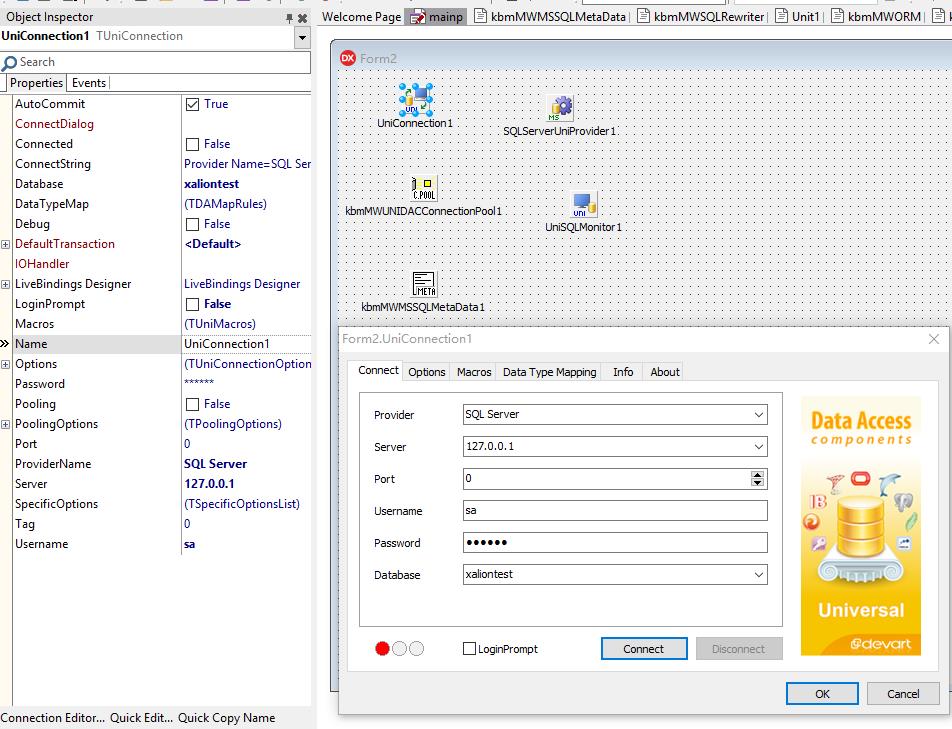
设置uniconnection1 连接sql server 2008 数据库
ok
加入几个必要的单元,并设置好初始化代码。
unit mainp; interface uses Winapi.Windows, Winapi.Messages, System.SysUtils, System.Variants, System.Classes, Vcl.Graphics, Vcl.Controls, Vcl.Forms, Vcl.Dialogs, kbmMWORM, Vcl.StdCtrls, Data.DB, DBAccess, Uni, kbmMWCustomConnectionPool, kbmMWCustomSQLMetaData, kbmMWMSSQLMetaData, kbmMWUniDAC, UniProvider, SQLServerUniProvider, DASQLMonitor, UniSQLMonitor ; type TForm2 = class(TForm) kbmMWUNIDACConnectionPool1: TkbmMWUNIDACConnectionPool; kbmMWMSSQLMetaData1: TkbmMWMSSQLMetaData; UniConnection1: TUniConnection; Button1: TButton; SQLServerUniProvider1: TSQLServerUniProvider; UniSQLMonitor1: TUniSQLMonitor; Button2: TButton; procedure FormCreate(Sender: TObject); procedure FormDestroy(Sender: TObject); procedure Button1Click(Sender: TObject); private { Private declarations } public { Public declarations } ORM:TkbmMWORM; end; var Form2: TForm2; implementation {$R *.dfm} procedure TForm2.FormCreate(Sender: TObject); begin ORM:=TkbmMWORM.Create(kbmMWUNIDACConnectionPool1); // 建立ORM 对象 ORM.QueryMode:=mwoqmMixed; end; procedure TForm2.FormDestroy(Sender: TObject); begin ORM.Free; // 释放ORM对象 end; end.
现在新建一个单元,定义一个联系人类,并加入对应的标注信息
unit uContact; interface uses System.Generics.Collections,kbmMWNullable,kbmMWRTTI, kbmMWORM,DB; type [kbmMW_Table(\'name:CONTACT\')] // 表名为 contact TContact = class private FID:kbmMWNullable<string>; FName:kbmMWNullable<string>; FAddress:kbmMWNullable<string>; FZipCode:kbmMWNullable<string>; FCity:kbmMWNullable<string>; FComments:kbmMWNullable<string>; public [kbmMW_Field(\'primary:true, generator:shortGuid\',ftString,40)] //主键,并自动生成为GUID property ID:kbmMWNullable<string> read FID write FID; [kbmMW_Field(\'name:NAME\',ftString,50)] property Name:kbmMWNullable<string> read FName write FName; [kbmMW_Field(\'name:ADDRESS\',ftString,80)] property Address:kbmMWNullable<string> read FAddress write FAddress; [kbmMW_Field(\'name:ZIPCODE\',ftInteger)] property ZipCode:kbmMWNullable<string> read FZipCode write FZipCode; [kbmMW_Field(\'name:city\',ftString,50)] property City:kbmMWNullable<string> read FCity write FCity; [kbmMW_Field(\'name:comments\',ftString,200)] property Comments:kbmMWNullable<string> read FComments write FComments; end; implementation initialization TkbmMWRTTI.EnableRTTI([TContact]); //开启RTTI kbmMWRegisterKnownClasses([TContact]);//注册 对象 end.
好了,我们返回主窗体, 加入对应的代码,我们先建立对应的表。
procedure TForm2.Button1Click(Sender: TObject); begin ORM.CreateTable([Tcontact]); end;
编译运行,点创建库 按钮,显示建表成功。

我们看看背后发生了什么?首先我们先在 sql monitor 里面,看看后台做了什么?
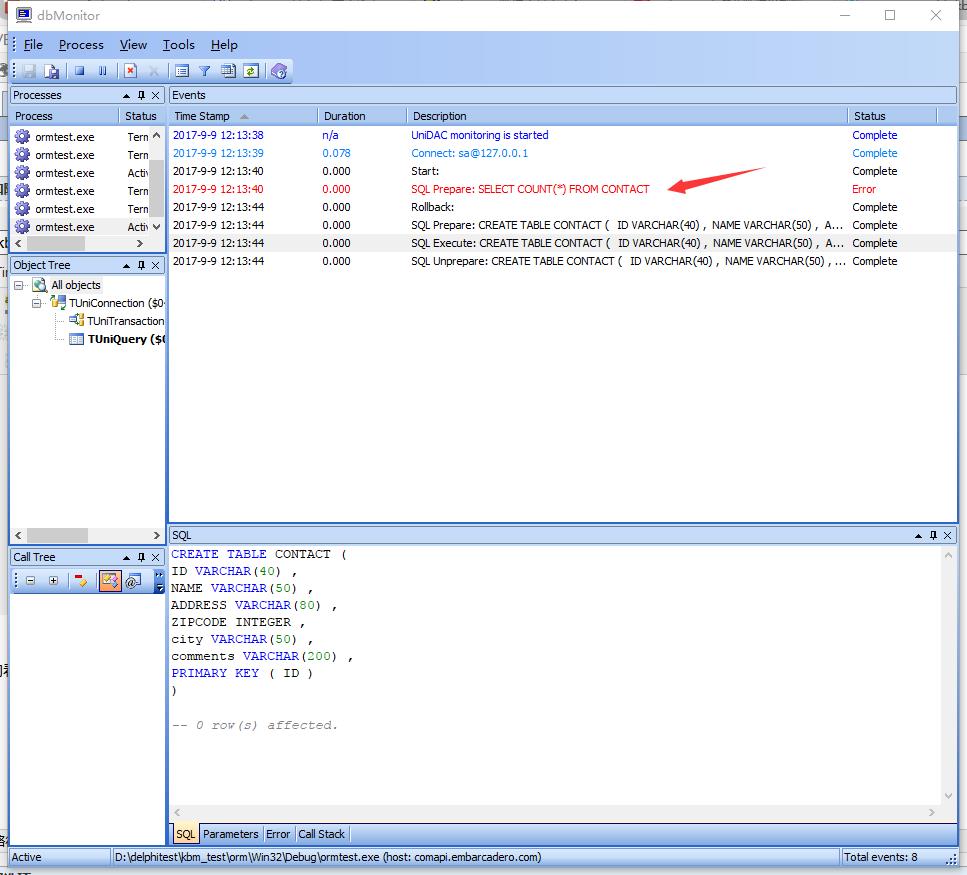
通过sql monitor, 我们可以非常清晰的看见,kbmmw 先在次数据库中查询是否有这个表,如果没有这个表,则根据Tcontact 中定义的
字段来生成对应的SQL 语句,执行这个SQL,在数据库中生成对应的表。
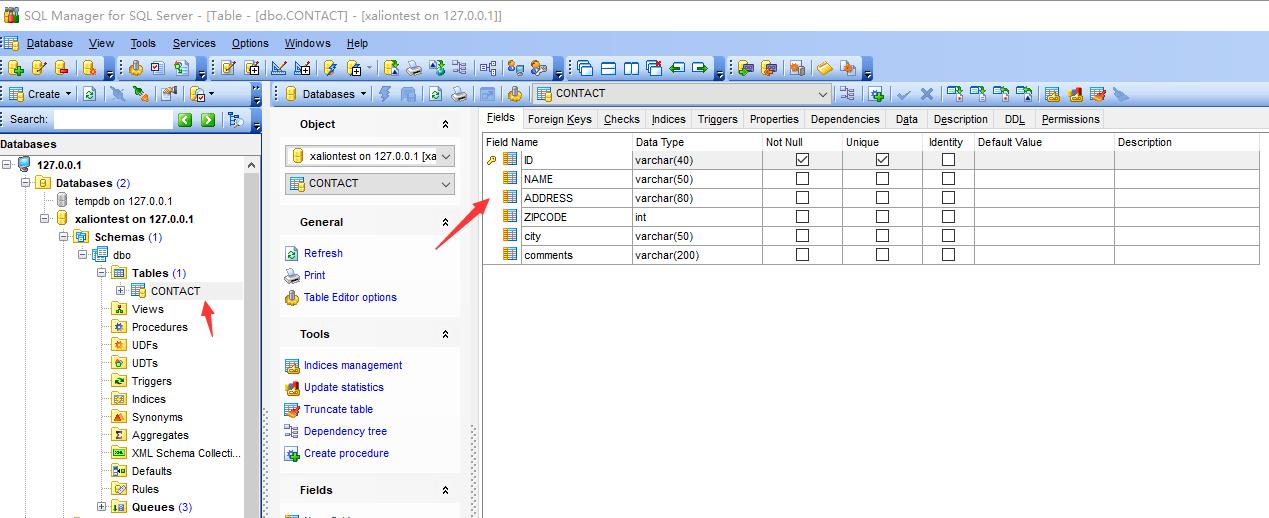
数据库中生产的完全没问题。我们下一步生成一些数据,看看是否正常。
生成数据代码
procedure TForm2.Button3Click(Sender: TObject); var t1,t2,t3:TContact ; begin t1:=TContact.Create; t1.Name:=\'红鱼儿\'; t1.Address:=\'不告诉你\'; t1.ZipCode:=\'1234567\'; t1.City:=\'四平\'; t1.Comments:=\'老牌程序猿\'; ORM.Persist(t1); t2:=TContact.Create; t2.Name:=\'努力的干\'; t2.Address:=\'还是不告诉你\'; t2.ZipCode:=\'54565552\'; t2.City:=\'泸州\'; t2.Comments:=\'变形金刚制造者\'; ORM.Persist(t2); t3:=TContact.Create; t3.Name:=\'清幽傲竹\'; t3.Address:=\'就是不告诉你\'; t3.ZipCode:=\'252556\'; t3.City:=\'福州\'; t3.Comments:=\'真的很帅的!\'; ORM.Persist(t3); showmessage(\'操作成功\'); end;


看看后台都有那些sql.实际上这个Persist 是更新和插入,如果更新失败就插入。
看看数据库里面的生成数据的效果。
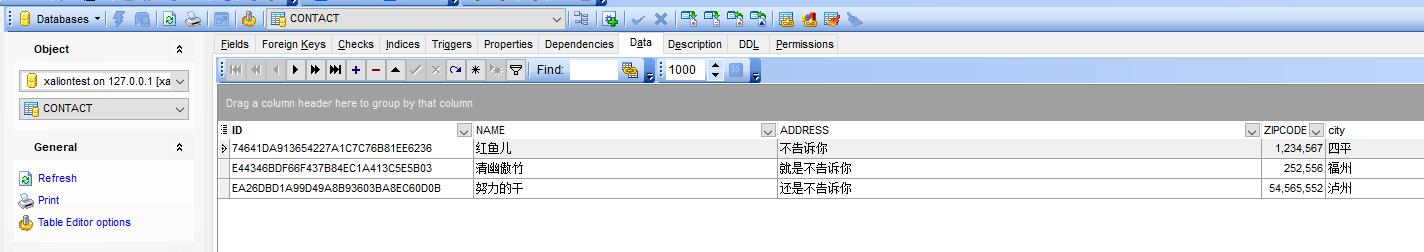
完全正确。
下面看一下如何通过ORM 查询数据。
kbmmw orm 查询数据有三种方式。
// Query mode controls what syntax to use for queries.
// mwoqmMW (default) use kbmMW\'s SQL syntax and automatically
// rewrite the query to match supported databases.
// mwoqmNative provides the query string without alterations to the
// database.
// mwoqmMixed default use kbmMW\'s SQL syntax with automatic rewrite
// unless the first character in the query statement is #
TkbmMWORMQueryMode = (mwoqmMW,mwoqmNative,mwoqmMixed);
缺省使用kbmmw 自身的SQL 语法,并自动转换成对应的数据库语法
第二种是直接使用目标数据库的语法
第三种是混合方式, 如果查询首字母不是# 的话,就用kbmmw 自身的sql 语法。
我们使用混合模式查询
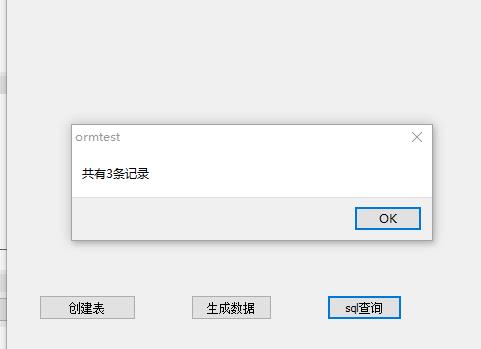
procedure TForm2.Button5Click(Sender: TObject); var o:TObjectList<Tcontact>; begin o:=TObjectList<Tcontact>(orm.Query(Tcontact,\'#SELECT * FROM contact\',true)); showmessage(\'共有\'+o.Count.ToString +\'条记录\'); o.Free; end;
或者
procedure TForm2.Button5Click(Sender: TObject); var o:TObjectList<Tcontact>; begin o:=orm.QueryList<Tcontact>(\'#SELECT * FROM contact\'); showmessage(\'共有\'+o.Count.ToString +\'条记录\'); o.Free; end;
运行结果
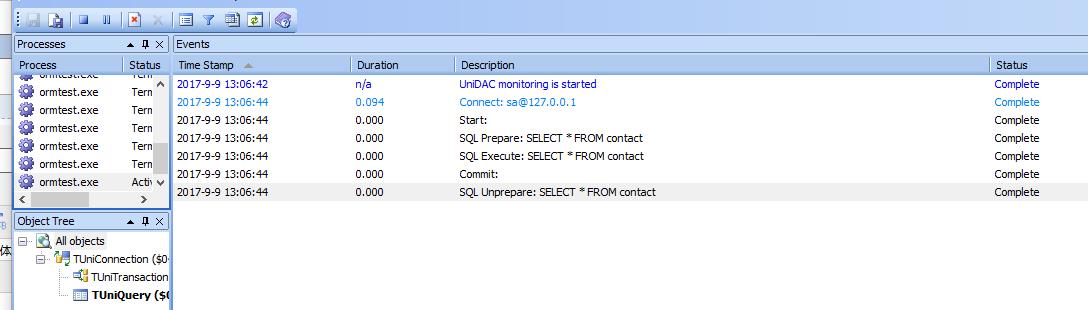
后台SQL 亦是如此
我们来查询单条数据,单挑数据有两种查询方式
一种是SQL 方式,一种ORM 方式
先介绍一下sql 方式
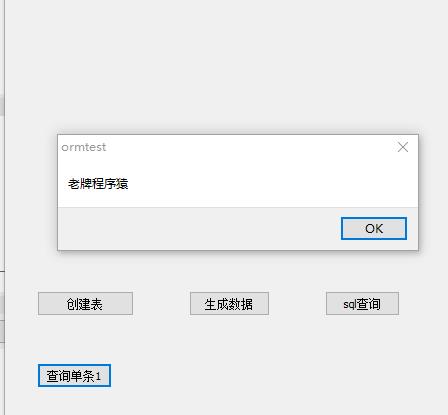
procedure TForm2.Button6Click(Sender: TObject); var o:Tcontact; begin o:=orm.Query<Tcontact>(\'#SELECT * FROM contact WHERE NAME=\'\'红鱼儿\'\'\'); if o=nil then begin showmessage(\'没有查询到数据!\'); exit; end; showmessage(o.Comments); o.Free; end;
运行效果
使用kbmw ORM 方式查询
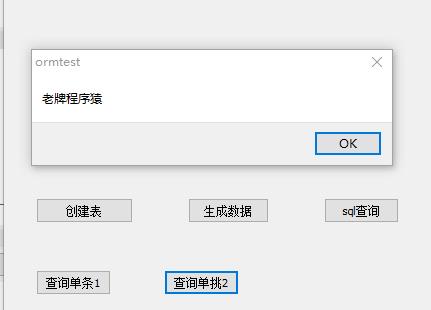
procedure TForm2.Button7Click(Sender: TObject); var o:Tcontact; b:boolean; begin o:=orm.Query<Tcontact>([\'name\'],[\'红鱼儿\'],mwoqoEQ); if o=nil then begin showmessage(\'没有查询到数据!\'); exit; end; showmessage(o.Comments); o.Free; end;
运行结果
修改数据库
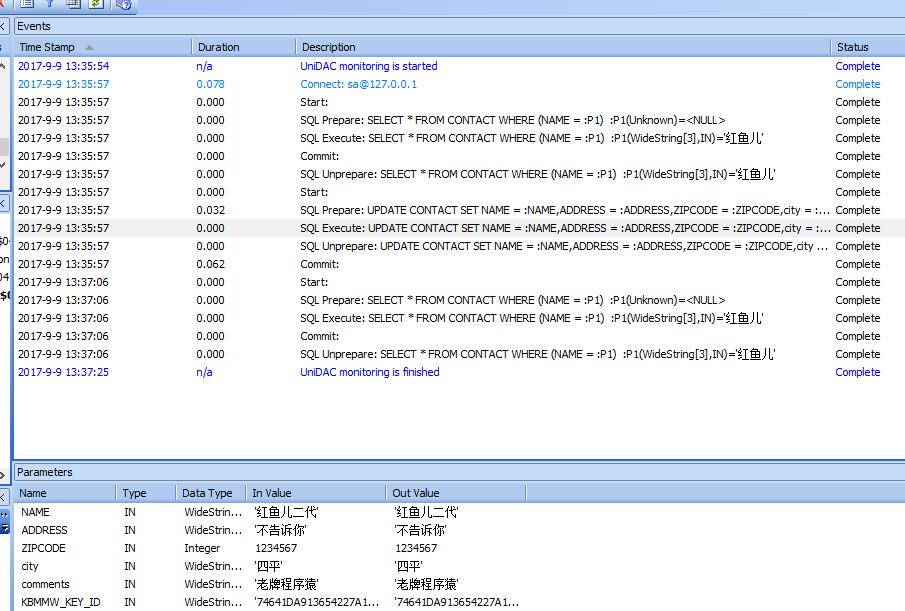
procedure TForm2.Button8Click(Sender: TObject); var o:Tcontact; begin o:=orm.Query<Tcontact>([\'name\'],[\'红鱼儿\'],mwoqoEQ); if o=nil then begin showmessage(\'没有查询到数据!\'); exit; end; o.Name:=\'红鱼儿二代\'; orm.Update(o); showmessage(\'修改成功!\'); o.Free; end;
结果也一切正常
看看后台发生了什么?
数据库是否保存正确?
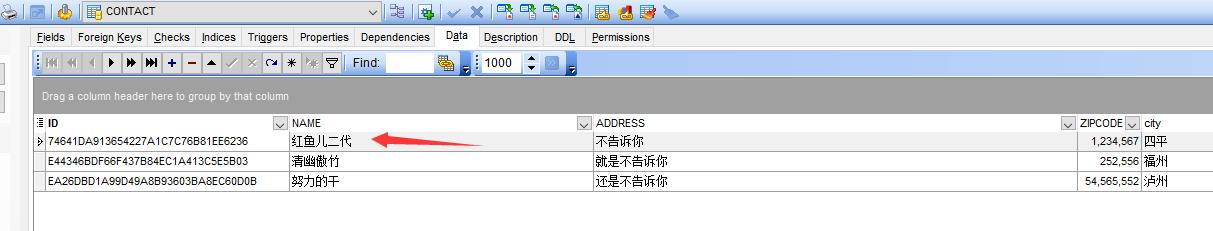
没问题,太爽了。
顺便添加一下删除的代码
procedure TForm2.Button9Click(Sender: TObject); var o:Tcontact; begin o:=orm.Query<Tcontact>([\'name\'],[\'红鱼儿\'],mwoqoEQ); if o=nil then begin showmessage(\'没有查询到数据!\'); exit; end; orm.Delete(o); showmessage(\'删除成功!\'); o.Free; end;
清除全部的数据
procedure TForm2.Button4Click(Sender: TObject); begin orm.PurgeTable(Tcontact); end;
删除建的表
procedure TForm2.Button2Click(Sender: TObject); begin ORM.DeleteTable([Tcontact]) end;
终于写完了。
大家对上面kbmmw 标注肯定很头疼,第一要记很多标注名,第二不能笔误,这个确实麻烦,
好消息是,作者已经把自动生产这些标注列入计划,期待后面的版本能直接自动生产,那就方便多了。
在没有自动声场之前,请大家参照一下说明,自己手工处理。
// ORM attribute syntax
// ====================
//
// kbmMW_Table - Define a table.
// Must be used on classes.
//
// Define a table named person.
// [kbmMW_Table(\'name:person\')]
//
// Define 2 ascending indexes i_fieldname, and i_anotherfieldname on the field fieldname and anotherfieldname.
// [kbmMW_Table(\'name:person, index:fieldname, index:anotherfieldname...
//
// Define an ascending index named i1, on the field name
// [kbmMW_Table(\'name:person, index:{name:i1,field:name},...
//
// Define a descending index named i1, on the field name
// [kbmMW_Table(\'name:person, index:{name:i1,field:name,descending:true},...
//
// Define a compound unique index named i2, on the fields name and age. Name field part is descending.
// [kbmMW_Table(\'name:person, index:{name:i2,unique:true,fields:[{name:name,descending:true},{name:age}]
//
//
// kbmMW_Field - Define fields in a table.
// Must be used on properties within a class if they are to be persisted.
//
// Define a field that will be persisted. Its type will be decided for
// from the property type. String type fields will have a size of 50.
// Table field name will be the same as the property name.
// [kbmMW_Field]
//
// Define a field that will be persisted. It will accept unicode data of max 50 characters.
// It will have the same name as the property.
// [kbmMW_Field(ftWideString,50)]
//
// Define a field named id, and make it primary key. It will be automatically populated bu the generator shortGuid.
// [kbmMW_Field(\'name:id, primary:true, generator:shortGuid\',ftString,40)]
// property ID:kbmMWNullable<string> read FID write FID;
//
// These generators exists:
// GUID - Returns a GUID formatted as a regular GUID {123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426655440000}
// SHORTGUID - Returns a short GUID where braces and dashes are missing: 123e4567e89b12d3a456426655440000
// SEQUENCE - Returns next unique number from a sequence. Provide name of sequencer in sequence property
// and optional sequencestart property (not supported by all databases!)
// DATETIME - Returns a date time value, formatted according to the dateFormat property.
//
// Define a field named id, and make it primary key. It will be populated by a sequence generator.
// Since no sequencer was given, one is automatically generated named s_tablename_fieldname
// [kbmMW_Field(\'name:id, primary:true, generator:sequence\',ftInteger)]
// property ID:kbmMWNullable<integer> read FID write FID;
//
// Define a field named id, and make it primary key. It will be populated by sequence generator SEQ, starting from value 10.
// (not all databases supports sequencers with a defined start!)
// [kbmMW_Field(\'name:id, primary:true, generator:sequence, seqneuce:SEQ1, sequenceStart:10\',ftInteger)]
// property ID:kbmMWNullable<integer> read FID write FID;
//
// Define a field named id, and make it primary key. It will be populated automatically by the database.
// (not all databases support auto increment type fields!)
// [kbmMW_Field(\'name:id, primary:true\',ftAutoInc)]
// property ID:kbmMWNullable<integer> read FID write FID;
//
// Define a field named datetime containing date/time values as Delphi local time values.
// [kbmMW_Field(\'name:datetime\',ftDateTime)]
// property DateTime:TkbmMWDateTime read FDateTime write FDateTime;
//
// Define a field named datetime containing date/time values as Delphi UTC values.
// [kbmMW_Field(\'name:datetime, dateFormat:UTC\',ftDateTime)]
// property DateTime:TkbmMWDateTime read FDateTime write FDateTime;
//
// Define a field named datetime containing date/time values as Unix local time millisecs since EPOC.
// [kbmMW_Field(\'name:datetime, dateFormat:LOCALSINCEEPOCHMS\',ftInt64)]
// property DateTime:TkbmMWDateTime read FDateTime write FDateTime;
//
// Define a field named datetime containing date/time values as Unix UTC time millisecs since EPOC.
// [kbmMW_Field(\'name:datetime, dateFormat:UTCSINCEEPOCHMS\',ftInt64)]
// property DateTime:TkbmMWDateTime read FDateTime write FDateTime;
//
// Define a field named datetime containing date/time values as Unix local time secs since EPOC.
// [kbmMW_Field(\'name:datetime, dateFormat:LOCALSINCEEPOCH\',ftInt64)]
// property DateTime:TkbmMWDateTime read FDateTime write FDateTime;
//
// Define a field named datetime containing date/time values as Unix UTC time secs since EPOC.
// [kbmMW_Field(\'name:datetime, dateFormat:UTCSINCEEPOCH\',ftInt64)]
// property DateTime:TkbmMWDateTime read FDateTime write FDateTime;
//
// Define a field named datetime containing date/time values as ISO8601 formatted string.
// [kbmMW_Field(\'name:datetime, dateFormat:ISO8601\',ftString,50)]
// property DateTime:TkbmMWDateTime read FDateTime write FDateTime;
//
// Define a field named datetime containing date/time values as RFC1123 formatted string.
// [kbmMW_Field(\'name:datetime, dateFormat:RFC1123\',ftString,50)]
// property DateTime:TkbmMWDateTime read FDateTime write FDateTime;
//
// Define a field named datetime containing date/time values as NCSA formatted string.
// [kbmMW_Field(\'name:datetime, dateFormat:NCSA\',ftString,50)]
// property DateTime:TkbmMWDateTime read FDateTime write FDateTime;
//
// kbmMW_Null - Specify NULL conversion.
// (This attribute is also used for object marshalling).
//
// If, for example, a property is of type integer, the property is not directly able to indicate a NULL state since
// all values of an integer are considered non NULL values.
// However its possible to define a specific value to be interpreted as NULL.
// Eg.
// [kbmMW_Field(\'name:somefield\',ftInteger)]
// [kbmMW_Null(-1)]
// property MyProperty:integer read FMyProperty write FMyProperty;
//
// This will define that the value -1 must be interpreted as NULL when storing and retrieving data
// from the database.
//
// kbmMW_NotNull - Indicate that the property must never contain the NULL value (either interpreted via the kbmMW_Null attribute or actual).
// Eg.
// [kbmMW_Field(\'name:somefield\',ftInteger)]
// [kbmMW_NotNull]
// property MyProperty:kbmMWNullable<integer> read FMyProperty write FMyProperty;
以上是关于初始kbmmw 中的ORM的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章