NOIP2008 双栈排序
Posted 心之所向 素履以往
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了NOIP2008 双栈排序相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
题目描述
Tom最近在研究一个有趣的排序问题。如图所示,通过2个栈S1和S2,Tom希望借助以下4种操作实现将输入序列升序排序。
操作a
如果输入序列不为空,将第一个元素压入栈S1
操作b
如果栈S1不为空,将S1栈顶元素弹出至输出序列
操作c
如果输入序列不为空,将第一个元素压入栈S2
操作d
如果栈S2不为空,将S2栈顶元素弹出至输出序列
如果一个1~n的排列P可以通过一系列操作使得输出序列为1,2,…,(n-1),n,Tom就称P是一个“可双栈排序排列”。例如(1,3,2,4)就是一个“可双栈排序序列”,而(2,3,4,1)不是。下图描述了一个将(1,3,2,4)排序的操作序列:<a,c,c,b,a,d,d,b>
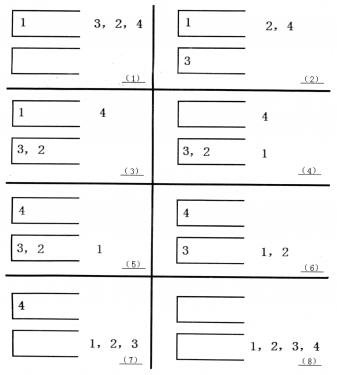
当然,这样的操作序列有可能有几个,对于上例(1,3,2,4),<a,c,c,b,a,d,d,b>是另外一个可行的操作序列。Tom希望知道其中字典序最小的操作序列是什么。
输入输出格式
输入格式:
输入文件twostack.in的第一行是一个整数n。
第二行有n个用空格隔开的正整数,构成一个1~n的排列。
输出格式:
输出文件twostack.out共一行,如果输入的排列不是“可双栈排序排列”,输出数字0;否则输出字典序最小的操作序列,每两个操作之间用空格隔开,行尾没有空格。
输入输出样例
【输入样例1】 4 1 3 2 4 【输入样例2】 4 2 3 4 1 【输入样例3】 3 2 3 1
【输出样例1】 a b a a b b a b 【输出样例2】 0 【输出样例3】 a c a b b d
说明
30%的数据满足: n<=10
50%的数据满足: n<=50
100%的数据满足: n<=1000
先考虑单个栈排序
只有当 i<j<k 而a[k]<a[i]<a[j] 时 无法排序
其他情况皆可按顺序输出
那么放在两个站中
我们可以把以上的 i 和 j 放在两个栈中 也就是双栈排序
对于不在一个栈中的 i 和 j 我们要先预处理 将 i 和 j 连一条边
a[k]=min(a[j],a[j+1],....a[n])
我们枚举 k 的 复杂度太大 O(n^3) n=1000 无法承受
就采用动规的思想 预处理 k 可以降到O(n^2)左右
就转化成了图匹配问题
建好图就跑染色 对于不在一个栈中的点染不同的颜色 若一个点两个颜色都染过 则无解
最小字典序模拟一遍就好了

1 #include <cstdlib>
2 #include <cctype>
3 #include <cstdio>
4 #include <stack>
5
6 const int MAXN=2010;
7
8 int n;
9
10 int a[MAXN],k[MAXN],col[MAXN];
11
12 std::stack<int> s,b;
13
14 struct node {
15 int to;
16 int next;
17 node(){}
18 node(int to,int next):to(to),next(next) {}
19 };
20 node e[MAXN<<1];
21
22 int head[MAXN],tot;
23
24 inline void read(int&x) {
25 int f=1;register char c=getchar();
26 for(x=0;!isdigit(c);c==‘-‘&&(f=-1),c=getchar());
27 for(;isdigit(c);x=x*10+c-48,c=getchar());
28 x=x*f;
29 }
30
31 inline void add(int x,int y) {
32 e[++tot]=node(y,head[x]);
33 head[x]=tot;
34 e[++tot]=node(x,head[y]);
35 head[y]=tot;
36 }
37
38 inline int min(int a,int b) {return a<b?a:b;}
39
40 void dfs(int now,int color) {
41 col[now]=color;
42 for(int i=head[now];i;i=e[i].next) {
43 int v=e[i].to;
44 if(col[v]==color) {
45 printf("0\n");
46 exit(0);
47 }
48 if(!col[v]) dfs(v,3-color);
49 }
50 }
51
52 int hh() {
53 freopen("twostack.in","r",stdin);
54 freopen("twostack.out","w",stdout);
55 read(n);
56 if(n==8) {printf("0\n");return 0;}//COGS 有一组数据少了一个数 就CHEAT过了...
57 for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) read(a[i]);
58 k[n+1]=0x7fffffff;
59 for(int i=n;i;--i) k[i]=min(k[i+1],a[i]);
60 for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
61 for(int j=i+1;j<=n;++j)
62 if(k[j+1]<a[i]&&a[i]<a[j])
63 add(i,j);
64 for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) if(!col[i]) dfs(i,1);
65 int now=1,cnt=1;
66 while(true) {
67 if(now>n) break;
68 if(col[cnt]==1&&(s.empty()||s.top()>a[cnt])) {
69 s.push(a[cnt]);
70 printf("a ");
71 ++cnt;
72 continue;
73 }
74 if(!s.empty()&&s.top()==now) {
75 s.pop();
76 printf("b ");
77 ++now;
78 continue;
79 }
80 if(col[cnt]==2&&(b.empty()||b.top()>a[cnt])) {
81 b.push(a[cnt]);
82 printf("c ");
83 ++cnt;
84 continue;
85 }
86 if(!b.empty()&&b.top()==now) {
87 b.pop();
88 printf("d ");
89 ++now;
90 continue;
91 }
92 }
93 return 0;
94 }
95
96 int sb=hh();
97 int main(int argc,char**argv) {;}
以上是关于NOIP2008 双栈排序的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
