L007- linux系统优化进阶课堂小节
Posted 别动那颗白菜
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了L007- linux系统优化进阶课堂小节相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
首先把这节课所讲的大概引锁一下,然后下面详细列举。
1.填加普通用户,通过sudo管理。
2.更改默认的SSH服务端口及禁止root用户远程连接。
3.定时自动更新服务器时间
4.关闭防火墙(iptables)
5.调整文件描述符的数量
6.linux内核参数优化/etc/sysctl.conf, sysctl -p生效
7.更改字符集,支持中文,但建议还是用英文字符集,不然会有乱码问题,特殊情况除外。
8.锁定关键系统文件
9.清空/etc/issue,去除系统及内核版本登录前的屏幕显示,防止黑客了解系统版本。
10.在使用普通用户出现命令找不到的情况可以更改$PTAH环境变量
11.查看网络参数以及端口
12.检查磁盘
以上,是L007本堂课的内容。
1.增加普通用户,通过sudo管理
useradd [name] //增加普通用户
1 [[email protected] ~]# useradd blog 2 [[email protected] ~]# passwd blog 3 Changing password for user blog. 4 New password: 5 BAD PASSWORD: it is too simplistic/systematic 6 BAD PASSWORD: is too simple 7 Retype new password: 8 passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
visudo //管理sudo
1 [[email protected] ~]# visudo 2 ## Sudoers allows particular users to run various commands as 3 ## the root user, without needing the root password. 4 ## 5 ## Examples are provided at the bottom of the file for collections 6 ## of related commands, which can then be delegated out to particular 7 ## users or groups. 8 ## 9 ## This file must be edited with the ‘visudo‘ command. 10 11 ## Host Aliases 12 ## Groups of machines. You may prefer to use hostnames (perhaps using 13 ## wildcards for entire domains) or IP addresses instead. 14 "/etc/sudoers.tmp" 119L, 4040C
进入visudo文件后,根据下面的这个格式写入文件可以管理普通用户权限
1 命令:visudo 2 配置文件 3 user MACHINE= COMMANDS 4 root ALL=(ALL) ALL 5 oldboy ALL=(ALL) /usr/sbin/useradd 6 用户 机器=(授权哪个角色的权利) /usr/sbin/useradd 7 %用户组 机器=(授权哪个角色的权利) /usr/sbin/useradd 8 多个命令用逗号分隔
然后用sudo -l来查看当前用户都开通了什么权限
1 [[email protected] ~]# sudo -l 2 Matching Defaults entries for root on this host: 3 requiretty, !visiblepw, always_set_home, env_reset, 4 env_keep="COLORS DISPLAY HOSTNAME HISTSIZE INPUTRC KDEDIR 5 LS_COLORS", env_keep+="MAIL PS1 PS2 QTDIR USERNAME LANG 6 LC_ADDRESS LC_CTYPE", env_keep+="LC_COLLATE LC_IDENTIFICATION 7 LC_MEASUREMENT LC_MESSAGES", env_keep+="LC_MONETARY LC_NAME 8 LC_NUMERIC LC_PAPER LC_TELEPHONE", env_keep+="LC_TIME LC_ALL 9 LANGUAGE LINGUAS _XKB_CHARSET XAUTHORITY", 10 secure_path=/sbin\:/bin\:/usr/sbin\:/usr/bin 11 12 User root may run the following commands on this host: 13 (ALL) ALL
之所以要这么做事因为远程连接状态下,尽量不要使用root,权限大,当然安全隐患也就多,所以尽量以普通用户登录,如果需要使用root,可以在普通用户下输入su - 或者su - root。
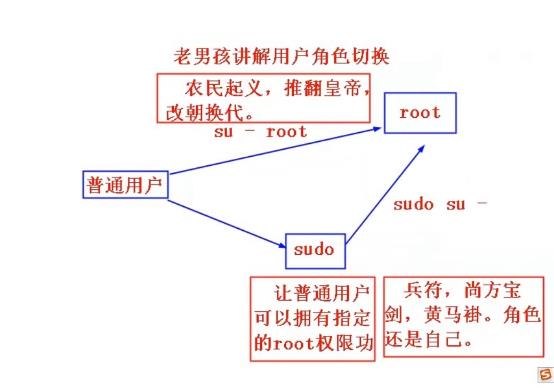
2.更改默认的SSH服务端口及禁止root用户远程连接。
ssh的默认端口为22,因为是默认,所以是十分不安全的,所以我们要更换一个端口和禁止root用户来提升系统的安全性。
1 [[email protected] ~]# vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config //ssh配置文件 2 # $OpenBSD: sshd_config,v 1.80 2008/07/02 02:24:18 djm Exp $ 3 4 # This is the sshd server system-wide configuration file. See 5 # sshd_config(5) for more information. 6 7 # This sshd was compiled with PATH=/usr/local/bin:/bin:/usr/bin 8 9 # The strategy used for options in the default sshd_config shipped wit 10 h 11 # OpenSSH is to specify options with their default value where 12 # possible, but leave them commented. Uncommented options change a 13 # default value. 14 "/etc/ssh/sshd_config" 146L, 4044C
在ssh配置文件中,填加如下:
1 ####SSHpeizhi#### 2 Port 52113 3 PermitRootLogin no 4 PermitEmptyPasswords no 5 UseDNS no 6 GSSAPIAuthentication no 7 ####SSHpeizhi#### 8 翻译: 9 ################### 10 端口:52113 11 使用root账户登录 no 12 使用空密码 no 13 用DNS认证 no 14 是否在用户退出登录后自动销毁用户凭证缓存。默认值是”yes”。仅用于SSH-2。 no 15 ##################
3.定时自动更新服务器时间
ntpdate 时间服务器命令
1 [[email protected] ~]# which ntpdate //查询ntpdate路径 2 /usr/sbin/ntpdate 3 [[email protected] ~]# /usr/sbin/ntpdate time.nist.gov //同步时间 4 26 Mar 15:26:08 ntpdate[1194]: adjust time server 216.229.0.179 offset 0.102953 sec 5 [[email protected] ~]# echo ‘*/5 * * * * /usr/sbin/stpdate time.nist.gov >/dev/null 2>&1‘ >>/var/spool/cron/root //循环更新时间 6 [[email protected] ~]# crontab -l //查询循环 7 */5 * * * * /usr/sbin/nptdate time.nist.gov >/dev/null 2>&1
4.关闭防火墙(iptables)
1 [[email protected] ~]# /etc/init.d/iptables stop //外网时需要打开防火墙
5.调整文件描述符的数量
文件描述符是一个简单的整数,用以标明每一个被进程所打开的文件和socket。第一个打开的文件是0,第二个是1,依此类推。Linux 操作系统通常给每个进程能打开的文件数量强加一个限制。更甚的是,Linux 通常有一个系统级的限制。当用完所有的文件描述符后,它不能接收用户新的连接。也就是说,用完文件描述符导致拒绝服务。所以我们要加大文件描述符。
1 [[email protected] ~]# ulimit -n //查询文件描述符的数量 2 65535 3 [[email protected] ~]# ulimit -HSn 65535 //修改最大文件描述符为65535 4 65535是最大范围,不能大于65535,调大也是为了黑客虚假空排。
大部分命令行的修改都是重启后复原的,ulimit -HSn [数量] 也一样,所以下面我们来永久改动。
1 [[email protected] ~]# echo ‘* - nofile 65535‘ >>/etc/security/limits.conf //写入文件 2 [[email protected] ~]# cat /etc/security/limits.conf //查询 3 #* soft core 0 4 #* hard rss 10000 5 #@student hard nproc 20 6 #@faculty soft nproc 20 7 #@faculty hard nproc 50 8 #ftp hard nproc 0 9 #@student - maxlogins 4 10 11 # End of file 12 * - nofile 65535
6.linux内核参数优化/etc/sysctl.conf, sysctl -p生效
内核参数文件在vi /etc/sysctl.conf
1 [[email protected] ~]# vi /etc/sysctl.conf 2 # Kernel sysctl configuration file for Red Hat Linux 3 # 4 # For binary values, 0 is disabled, 1 is enabled. See sysctl(8) and 5 # sysctl.conf(5) for more details. 6 7 # Controls IP packet forwarding 8 net.ipv4.ip_forward = 0 9 10 # Controls source route verification 11 net.ipv4.conf.default.rp_filter = 1 12 13 # Do not accept source routing 14 "/etc/sysctl.conf" 61L, 1898C
把下列参数复制到文件中。
net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 2 net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 600 net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 4000 65000 net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 16384 net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 36000 net.ipv4.route.gc_timeout = 100 net.ipv4.tcp_syn_retries = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_synack_retries = 1 net.core.somaxconn = 16384 net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 16384 net.ipv4.tcp_max_orphans = 16384
如果有防火墙,请把一下复制进去
net.nf_conntrack_max = 25000000 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max = 25000000 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established = 180 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_time_wait = 120 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_close_wait = 60 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_fin_wait = 120
如下为重新开始sysctl服务。如果防火墙关闭状态可能报错,偶尔也不会报错。
1 [[email protected] ~]# sysctl -p 2 net.ipv4.ip_forward = 0 3 net.ipv4.conf.default.rp_filter = 1 4 net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_source_route = 0 5 kernel.sysrq = 0 6 kernel.core_uses_pid = 1 7 net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1 8 error: "net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables" is an unknown key 9 error: "net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables" is an unknown key 10 error: "net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-arptables" is an unknown key 11 kernel.msgmnb = 65536 12 kernel.msgmax = 65536 13 kernel.shmmax = 68719476736 14 kernel.shmall = 4294967296 15 net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 2 16 net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1 17 net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 1 18 net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1 19 net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 600 20 net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 4000 65000 21 net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 16384 22 net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 36000 23 net.ipv4.route.gc_timeout = 100 24 net.ipv4.tcp_syn_retries = 1 25 net.ipv4.tcp_synack_retries = 1 26 net.core.somaxconn = 16384 27 net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 16384 28 net.ipv4.tcp_max_orphans = 16384 29 error: "net.nf_conntrack_max" is an unknown key 30 error: "net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max" is an unknown key 31 error: "net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established" is an unknown key 32 error: "net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_time_wait" is an unknown key 33 error: "net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_close_wait" is an unknown key 34 error: "net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_fin_wait" is an unknown key 35 [[email protected] ~]#
7.更改字符集,支持中文,但建议还是用英文字符集,不然会有乱码问题,特殊情况除外。
查看计算机内的字符集
1 [[email protected] ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/i18n 2 LANG="en_US.UTF-8" 3 SYSFONT="latarcyrheb-sun16"
加入中文字符集
1 [[email protected] ~]# echo ‘LANG="zh_CN,GB18030"‘ >> /etc/sysconfig/i18n
再用VI给之前的那个字符集用#注释掉。
设置好后需要执行文件才可以更新字符集
1 [[email protected] ~]# $LANG
8.锁定关键系统文件
charrt +i 锁定
charrt -i 解锁
1 [[email protected] ~]#chattr +i /etc/passwd /etc/shadow /etc/group /etc/gshadow /etc/inittab 2 锁定 用户文件 用户密码文件 用户主文件 主密码文件 开机启动文件
上锁以后这些功能就不能正常使用了,所以再使用时需要解锁
[[email protected] ~]#chattr -i /etc/passwd /etc/shadow /etc/group /etc/gshadow /etc/inittab
之所以上锁就是因为防止黑客破坏系统,但是你会上锁,黑客更会解锁,所以可以在上锁后删除chattr命令,等下次需要时再上传,或者更名
1 [[email protected] ~]# which chattr 2 /usr/bin/chattr 3 [[email protected] ~]# mv /usr/bin/chattr /usr/bin/oldboy //oldboy为自己起的一个名字 4 [[email protected] ~]# chattr -i /etc/passwd /etc/shadow /etc/group /etc/gshadow /etc/inittab //再次使用解除命令 5 -bash: /usr/bin/chattr:没有那个文件或目录 //系统提示无此命令,成功,不过此时把chattr变换城oldboy会成功。你猜猜是为什么呢?是不是很巧妙?
lsattr 查看某某命令是否已经加锁
1 [[email protected] ~]# lsattr /etc/passwd 2 ----i--------e- /etc/passwd //i为加锁
9.清空/etc/issue,去除系统及内核版本登录前的屏幕显示,防止黑客了解系统版本。
系统内核信息存储在issue下,使用如下命令清空
1 [[email protected] ~]# cat /etc/issue 2 CentOS release 6.5 (Final) 3 Kernel \r on an \m 4 [[email protected] ~]# > /etc/issue //清空版本
这么做主要是迷惑黑客,不让其知道版本,也就不知道版本的漏洞了。
10.在使用普通用户出现命令找不到的情况可以更改$PTAH环境变量
在使用普通用户时,可能输入一些命令却找不到,那么这时就需要输入跟命令或者是填加环境变量。
1)根命令
使用which找到命令的跟,如需使用mv,那么先which mv,查出mv的根路径/bin/mv。
2)查看$PATH,如果没有/bin的路径,可以手动加进去
[[email protected] ~]# $PATH //查看环境变量 -bash: /usr/lib64/qt-3.3/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin: No such file or directory [[email protected] ~]# PATH=/bin:$PATH //加入环境变量/oldboy/ [[email protected] ~]# $PATH -bash: /oldboy/:/usr/lib64/qt-3.3/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin: No such file or directory //看到了加进去的
但是这种情况,重启服务器后会消失(大多数都是,在命令行修改都属于临时生效,只有放在文件里才会永久更改。)
1 [[email protected] ~]# echo ‘PATH="/bin:$PATH"‘ >> /etc/profile //加入到变量文件中 2 [[email protected] ~]# source /etc/profile //source使其生效
PATH 环境变量大写,所有包含在环境变量里面的路径,都可以直接敲出来执行。
全局生效/etc/profile。 普通用户生效~/.bash_profile或者~/.bashrc
11.查看网络参数以及端口
netstat 查看网络状态 参数:lntup或an
lsof -i :port(端口) 查看端口
1 [[email protected] ~]# netstat -lntup 2 Active Internet connections (only servers) 3 Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name 4 tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:52113 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 896/sshd 5 tcp 0 0 :::52113 :::* LISTEN 896/sshd
6 [[email protected] ~]# lsof -i :52113 7 COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME 8 sshd 896 root 3u IPv4 8915 0t0 TCP *:52113 (LISTEN) 9 sshd 896 root 4u IPv6 8917 0t0 TCP *:52113 (LISTEN) 10 sshd 1107 root 3r IPv4 10070 0t0 TCP bogon:52113->bogon:51317 (ESTABLISHED) 11 sshd 1109 lichaoran 3u IPv4 10070 0t0 TCP bogon:52113->bogon:51317 (ESTABLISHED) 12 [[email protected] ~]#
12.检查磁盘
df -h 查看物理空间
1 [[email protected] ~]# df -h 2 Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on 3 /dev/sda3 8.9G 1.6G 6.9G 19% / 4 tmpfs 932M 0 932M 0% /dev/shm 5 /dev/sda1 194M 29M 155M 16% /boot
df -hi 查看物理空间以外的
1 [[email protected] ~]# df -hi 2 Filesystem Inodes IUsed IFree IUse% Mounted on 3 /dev/sda3 579K 55K 525K 10% / 4 tmpfs 233K 1 233K 1% /dev/shm 5 /dev/sda1 50K 38 50K 1% /boot
以上是关于L007- linux系统优化进阶课堂小节的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章