C++:类中两个易被忽略的默认函数
Posted Tom文星
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C++:类中两个易被忽略的默认函数相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
C++的自定义类中有六个默认的函数,即如果用户没有显式定义这些函数时,C++编译器会类中生成这些函数的默认形式。除了大家所熟知的构造函数、拷贝构造函数、赋值函数和析构函数外,C++为自定义类 还提供了两个容易被人忽视的默认函数——取地址函数和对常对象的取地址函数。
一、取地址函数
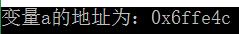
在C++中可以通过取地址运算符&求得变量的地址,如:
1 int a=10; 2 cout<<"变量a的地址为:"<<&a<<endl;
那么对于自定义类的对象是否可以通过取地址运算符&求得对象在内存中的地址呢?我们先来看个例子:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<string> 3 using namespace std; 4 class Student{ 5 public: 6 Student(){ 7 cout<<"调用无参数的构造函数"<<endl; 8 } 9 Student(string name,int age):Name(name),Age(age){ 10 cout<<"调用有参数的构造函数"<<endl; 11 } 12 Student(const Student& stu){ 13 cout<<"调用拷贝构造函数"<<endl; 14 Name=stu.Name; 15 Age=stu.Age; 16 } 17 Student& operator=(const Student& stu){ 18 cout<<"调用赋值函数"<<endl; 19 if(this!=&stu){ 20 Name=stu.Name; 21 Age=stu.Age; 22 } 23 return *this; 24 } 25 ~Student(){ 26 cout<<"调用析构函数"<<endl; 27 } 28 private: 29 string Name; 30 int Age; 31 }; 32 int main(){ 33 Student stu("Tomwenxing",23); 34 cout<<"对象stu的地址为:"<<&stu<<endl;//成功:运行对对象stu进行取地址操作 35 return 0; 36 }

由上面的例子可知,C++允许通过取地址运算符&求得对象在内存中的地址,而这个功能就是依靠类中的取地址函数实现的。和赋值函数相似,类中的取地址函数是通过对取地址运算符&进行重载来实现的,如果用户在编写类时没有显式地定义类的取地址函数,那么C++编译器将会在类中生成一个默认的取地址函数。
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<string> 3 using namespace std; 4 class Student{ 5 public: 6 Student(){ 7 cout<<"调用无参数的构造函数"<<endl; 8 } 9 Student(string name,int age):Name(name),Age(age){ 10 cout<<"调用有参数的构造函数"<<endl; 11 } 12 Student(const Student& stu){ 13 cout<<"调用拷贝构造函数"<<endl; 14 Name=stu.Name; 15 Age=stu.Age; 16 } 17 Student& operator=(const Student& stu){ 18 cout<<"调用赋值函数"<<endl; 19 if(this!=&stu){ 20 Name=stu.Name; 21 Age=stu.Age; 22 } 23 return *this; 24 } 25 Student* operator&(){ //取地址函数 26 cout<<"调用取地址函数"<<endl; 27 return this; 28 } 29 ~Student(){ 30 cout<<"调用析构函数"<<endl; 31 } 32 private: 33 string Name; 34 int Age; 35 }; 36 int main(){ 37 Student stu("Tomwenxing",23); 38 cout<<"对象stu的地址为:"<<&stu<<endl;//成功:运行对对象stu进行取地址操作,该语句相当于stu.operator&(); 39 return 0; 40 }

二、对常对象的取地址函数
还是上面的例子,这次我们队常对象进行取地址操作,看看会发生什么:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<string> 3 using namespace std; 4 class Student{ 5 public: 6 Student(){ 7 cout<<"调用无参数的构造函数"<<endl; 8 } 9 Student(string name,int age):Name(name),Age(age){ 10 cout<<"调用有参数的构造函数"<<endl; 11 } 12 Student(const Student& stu){ 13 cout<<"调用拷贝构造函数"<<endl; 14 Name=stu.Name; 15 Age=stu.Age; 16 } 17 Student& operator=(const Student& stu){ 18 cout<<"调用赋值函数"<<endl; 19 if(this!=&stu){ 20 Name=stu.Name; 21 Age=stu.Age; 22 } 23 return *this; 24 } 25 Student* operator&(){ 26 cout<<"调用取地址函数"<<endl; 27 return this; 28 } 29 ~Student(){ 30 cout<<"调用析构函数"<<endl; 31 } 32 private: 33 string Name; 34 int Age; 35 }; 36 int main(){ 37 const Student stu("Tomwenxing",23); 38 cout<<"对象stu的地址为:"<<&stu<<endl;//成功:运行对对象stu进行取地址操作 39 return 0; 40 }

通过上面的例子我们发现,在对常对象stu进行取地址操作时,对象并没有调用类中的取地址函数,这是因为类中还有一个默认的函数,其功能是对常对象进行取地址操作。和取地址函数相同,对常对象的取地址函数也是通过对取地址运算符&重载来实现的,同样如果用户在编写类时没有显式地定义类的对常对象的取地址函数,那么C++编译器将会在类中生成一个默认的对常对象的取地址函数:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<string> 3 using namespace std; 4 class Student{ 5 public: 6 Student(){ 7 cout<<"调用无参数的构造函数"<<endl; 8 } 9 Student(string name,int age):Name(name),Age(age){ 10 cout<<"调用有参数的构造函数"<<endl; 11 } 12 Student(const Student& stu){ 13 cout<<"调用拷贝构造函数"<<endl; 14 Name=stu.Name; 15 Age=stu.Age; 16 } 17 Student& operator=(const Student& stu){ 18 cout<<"调用赋值函数"<<endl; 19 if(this!=&stu){ 20 Name=stu.Name; 21 Age=stu.Age; 22 } 23 return *this; 24 } 25 Student* operator&(){ 26 cout<<"调用取地址函数"<<endl; 27 return this; 28 } 29 const Student* operator&() const{ 30 cout<<"调用对常对象的取地址函数"<<endl; 31 return this; 32 } 33 ~Student(){ 34 cout<<"调用析构函数"<<endl; 35 } 36 private: 37 string Name; 38 int Age; 39 }; 40 int main(){ 41 const Student stu("Tomwenxing",23); 42 cout<<"对象stu的地址为:"<<&stu<<endl;//成功:运行对常对象stu进行取地址操作 43 return 0; 44 }

特别注意:两个const的作用
• 第一个const要求函数返回的指针是常量,如果返回的是非常量则报错
• 第二个const修饰this指针,使该对象的this指针是一个指针常量,从而能够被该函数成功返回。
以上是关于C++:类中两个易被忽略的默认函数的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章