矩阵乘法
Posted yiyiyizqy
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了矩阵乘法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
矩阵乘法
矩阵的定义:
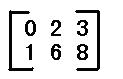


如图,三个都为矩阵。
矩阵相乘最重要的方法是一般矩阵乘积。它只有在第一个矩阵的列数(column)和第二个矩阵的行数(row)相同时才有意义[1] 。一般单指矩阵乘积时,指的便是一般矩阵乘积。一个m×n的矩阵就是m×n个数排成m行n列的一个数阵。由于它把许多数据紧凑的集中到了一起,所以有时候可以简便地表示一些复杂的模型。
矩阵乘法的基本运算:
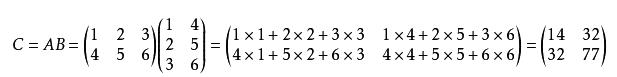
矩阵乘法满足结合律但不满足交换律!!!
快速幂:
快速幂即求一个数的xy次方,那么就把y一直除以2,当y==1时,return x。如果y是偶数时便直接把得到的结果相乘,否则把得到结果相乘之余还要再加一个x。
矩阵乘法的应用 poj 3070:
Fibonacc
Description
In the Fibonacci integer sequence, F0 = 0, F1 = 1, and Fn = Fn − 1 + Fn − 2 for n ≥ 2. For example, the first ten terms of the Fibonacci sequence are:
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, …
An alternative formula for the Fibonacci sequence is

Given an integer n, your goal is to compute the last 4 digits of Fn.
Input
The input test file will contain multiple test cases. Each test case consists of a single line containing n (where 0 ≤ n ≤ 1,000,000,000). The end-of-file is denoted by a single line containing the number −1.
Output
For each test case, print the last four digits of Fn. If the last four digits of Fn are all zeros, print ‘0’; otherwise, omit any leading zeros (i.e., print Fn mod 10000).
Sample Input
0
9
999999999
1000000000
-1
Sample Output
0
34
626
6875
Hint
As a reminder, matrix multiplication is associative, and the product of two 2 × 2 matrices is given by
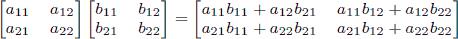
Also, note that raising any 2 × 2 matrix to the 0th power gives the identity matrix:

其实就是斐波那契数,但唯一不同的是,数据量增加到109,所以就不是普通的斐波那契数了。
当我们观察斐波那契数列时
0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55 89……
假设把1 2看作一个矩阵,那要怎样才能得到2 3呢?假设a=1,b=2。我们发现,得到后面的2 3,newa=b,而newb=a+b。说明a和b对newb是有贡献的,那么,要怎样才能使【1 2】矩阵对【2 3】矩阵有所贡献,应该乘一个什么样的矩阵呢。
可以得出,需要这样的一个矩阵
0 1
1 1 a[0][0]=0 a[0][1]=1 a[1][0]=1 a[1][1]=1
因为a是对newa没有贡献的,所以第0行第0列为0,b有贡献,所以第1行第0列为1。而a与b同时对newb有贡献,所以第一列都为1。
同样的,只要一直乘这个矩阵,便可以得出所有的f[i]。
而求出目标值,则用到上面提到的快速幂,同理可得。
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> using namespace std; const int mod=10000; int n; struct qy { int a[2][2]; }; qy juzhen(qy x,qy y)//矩阵乘法 { qy nans; nans.a[0][0]= nans.a[0][1]= nans.a[1][1]= nans.a[1][0]=0; for(int i=0;i<2;i++) { for(int j=0;j<2;j++) { for(int k=0;k<2;k++) { nans.a[i][j]=(nans.a[i][j]+ x.a[i][k] * y.a[k][j]%mod)%mod; } // cout<<nans.a[i][j]<<" "; } } return nans; } qy run(int y)//快速幂 { qy now; now.a[0][0]=0,now.a[0][1]=1,now.a[1][0]=1,now.a[1][1]=1; if(y==1) return now; if(y==2) return juzhen(now,now); qy news,news2; news=run(y/2); news2=juzhen(news,news); if(y%2==1) return juzhen( news2 ,now ); else return news2; } int main() { while(1) { cin>>n; if(n==-1) break; if(n==0) cout<<0<<endl; else if(n==1||n==2) cout<<1<<endl; else if(n==3) cout<<2<<endl; else { int times=n-3; qy wyy,ans; wyy.a[0][0]=1, wyy.a[0][1]=2, wyy.a[1][1]=0, wyy.a[1][0]=0; ans=juzhen( wyy,run(times) ); //注意矩阵不满足交换律 cout<<ans.a[0][1]<<endl; } } return 0; }
以上是关于矩阵乘法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章