OI常用读入方式效率测试
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了OI常用读入方式效率测试相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
我来填坑了。
这次我用自己写的测试读入的程序来分别测试cin(不关闭流同步),scanf和读入优化的效率差别。
我们分别对三个阶段的数据量n进行测试,通过时间比对来观察性能的差异。
- n = 102时
- n = 104时
- n = 105时
为了保证测试准确并且减小偶然误差,本次测试的所有数据均为随机数。
对于每一个数据量连续测试五组不同的随机数,取平均值作为参考。
随机数生成器:
1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<ctime> 3 #include<cstdlib> 4 #define random(x) (rand()%x) 5 const int n = 100; 6 int main(){ 7 freopen("testdata.in","w",stdout); 8 srand((unsigned int)time(0)); 9 for (int i = 0;i < n;i++) 10 printf("%d\\n",random(RAND_MAX)*random(RAND_MAX)); 11 return 0; 12 }
一号选手cin:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<ctime> 4 using namespace std; 5 const int n = 100; 6 int x; 7 int main(){ 8 freopen("testdata.in","r",stdin); 9 clock_t st,ed; 10 st = clock(); 11 for (int i = 0;i < n;i++) 12 cin >> x; 13 ed = clock(); 14 printf("%fseconds",(double)(ed-st)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC); 15 return 0; 16 }
二号选手scanf:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<ctime> 4 using namespace std; 5 const int n = 100; 6 int x; 7 int main(){ 8 freopen("testdata.in","r",stdin); 9 clock_t st,ed; 10 st = clock(); 11 for (int i = 0;i < n;i++) 12 scanf("%d",&x); 13 ed = clock(); 14 printf("%fseconds",(double)(ed-st)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC); 15 return 0; 16 }
三号选手读入优化:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<ctime> 4 using namespace std; 5 const int n = 100; 6 int x; 7 inline int read(){ 8 int num = 0; 9 char c; 10 bool flag = false; 11 while ((c = getchar()) == \' \' || c == \'\\n\' || c == \'\\r\'); 12 if (c == \'-\') flag = true; 13 else 14 num = c - \'0\'; 15 while (isdigit(c = getchar())) 16 num = num * 10 + c - \'0\'; 17 return (flag ? -1 : 1) * num; 18 } 19 20 int main(){ 21 freopen("testdata.in","r",stdin); 22 clock_t st,ed; 23 st = clock(); 24 for (int i = 0;i < n;i++) 25 x = read(); 26 ed = clock(); 27 printf("%fseconds",(double)(ed-st)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC); 28 return 0; 29 }
进行测试。结果如下表
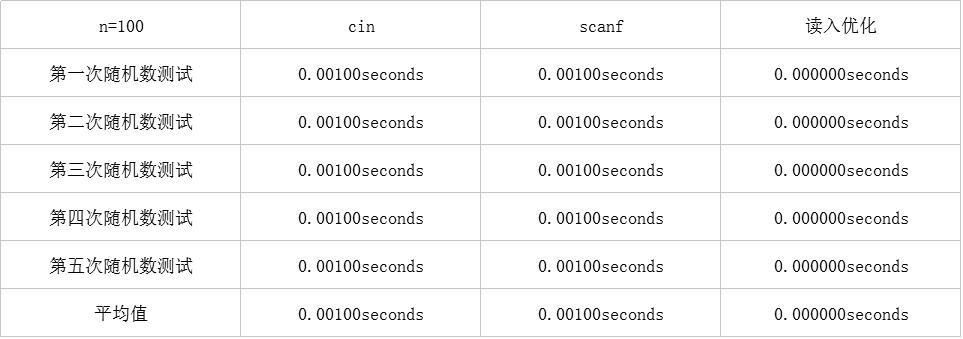
在n = 100的数据量下,表现的都还不错,那么n = 10^4的时候将会如何呢?
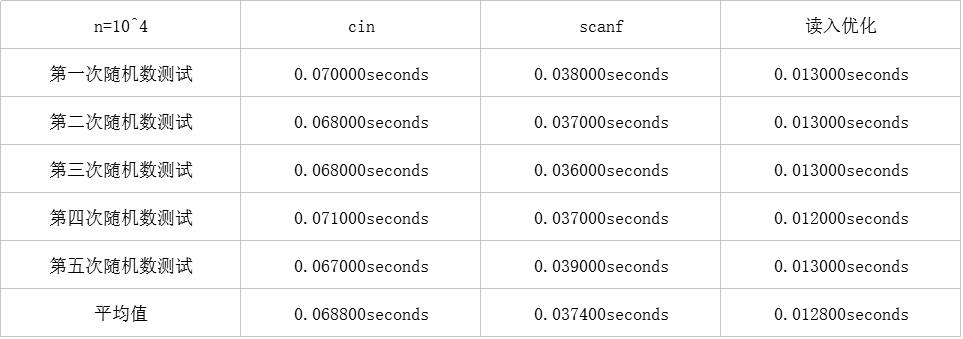
虽然这样的时间差肉眼很难分辨,但是差距还是的确存在的。
读入优化占据上风,拿到了平均0.0128s的成绩。scanf也不甘示弱,平均读入时间有0.0374s。但cin就比较惨了,只有0.0688s。
很清楚的可以看出,三种读入方式已经开始有了差别。
那么在数据量较大的10^5,三种读入方式会有怎样的表现呢?
测试发现
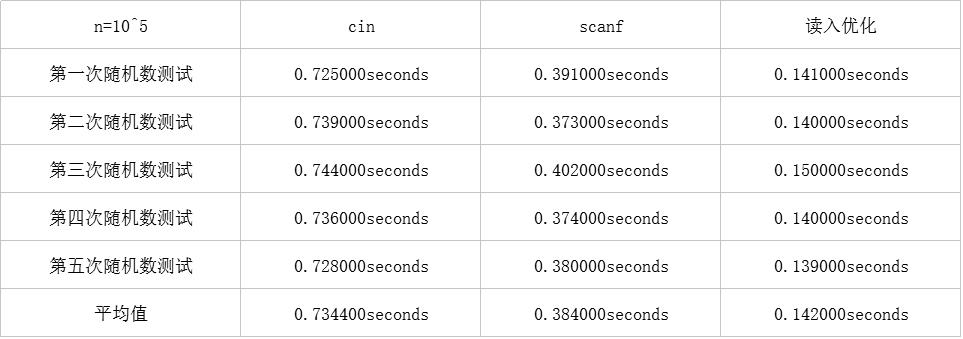
至此,三种读入方式的速度差异已见分晓。
scanf平均0.384s,比读入优化的0.142s慢了一些。
cin这个时候已经gg了,0.7344s,如果是单点时限1s的题,光读入就会耗掉超过七成的时间。如果算法不够优,可能就会TLE。
即使数据量很大,读入优化也是还能保证到能在很短时间内读取大量数据,所以可以说是当之无愧的“黑科技”了。
今天比较晚了,本来还想简要提一下scanf和cin 的原理并且分析速度慢的原因的,看来只能放在以后了。
明天更新夏令营Day4知识点整理。
以上是关于OI常用读入方式效率测试的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章