java基础之集合List-ArrayListLinkedListVector的差别
Posted phlsheji
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了java基础之集合List-ArrayListLinkedListVector的差别相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
PS:本篇博客主要參考jdk的底层源代码。而非自己动手写代码。
请问ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector的差别
①ArrayList底层实际上是採用数组实现的(而且该数组的类型的Object类型的)
②假设jdk6,採用Array.copyOf()方法来生成一个新的数组,假设是jdk5,採用的是System.arraycopy()方法(当加入的数据量大于数组的长度时候)
③List list = newArrayList()时,底层会生成一个长度为10的数组来存放对象
④ArrayList、Vector底层都是採用数组实现的
⑤对于ArrayList。方法都不是同步的,对于Vector。大部分public方法都是同步的
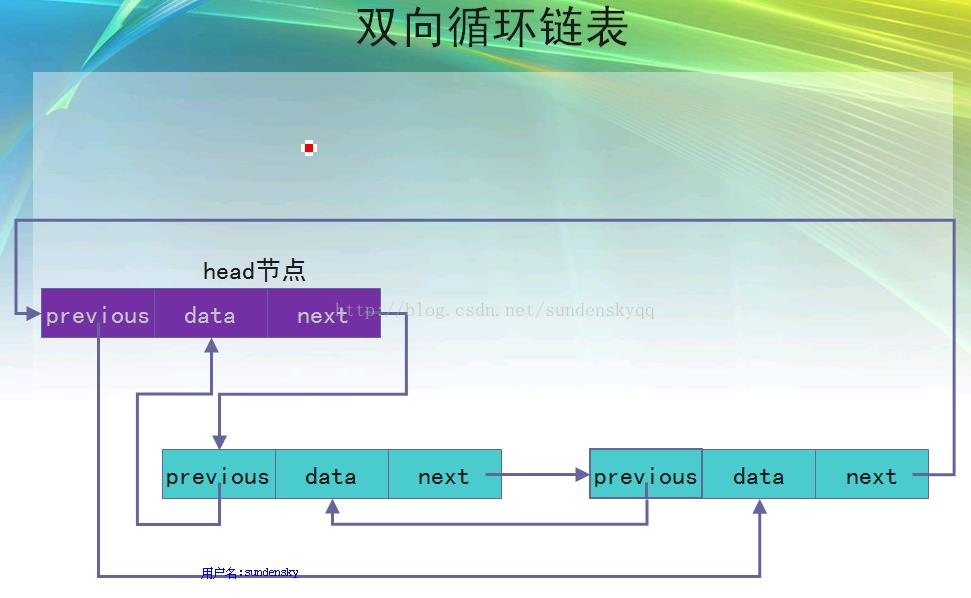
⑥LinkedList採用双向循环链表
⑦对于ArrayList,查询速度非常快,添加和删除(非最后一个节点)操作非常慢(本质上由数组的特性决定的)
⑧对于LinkedList,查询速度很慢,添加和删除操作很快(本质上是由双向循环链表决定的)
private transient Object elementData[];
public ArrayList(int i) {
if (i < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException((new StringBuilder())
.append("Illegal Capacity: ").append(i).toString());
} else {
elementData = new Object[i];
return;
}
}
public ArrayList() {
this(10);
}2、LinkList默认构造方法 (包含相关代码)
public LinkedList() {
header = new Entry(null, null, null);
size = 0;
header.next = header.previous = header;
}
private static class Entry {
Object element;
Entry next;
Entry previous;
Entry(Object obj, Entry entry1, Entry entry2) {
element = obj;
next = entry1;
previous = entry2;
}
}
private transient Entry header;
private transient int size;3、Vector默认构造方法(包含相关代码)
public Vector(int i, int j) {
if (i < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException((new StringBuilder())
.append("Illegal Capacity: ").append(i).toString());
} else {
elementData = new Object[i];
capacityIncrement = j;
return;
}
}
public Vector(int i) {
this(i, 0);
}
public Vector() {
this(10);
}
protected Object elementData[];
protected int capacityIncrement;以上是关于java基础之集合List-ArrayListLinkedListVector的差别的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章