linux --> 获取系统启动时间
Posted 蚂蚁吃大象
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了linux --> 获取系统启动时间相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
获取系统启动时间
一、前言
时间对操作系统来说非常重要,从内核级到应用层,时间的表达方式及精度各部相同。linux内核里面用一个名为jiffes的常量来计算时间戳。应用层有time、getdaytime等函数。今天需要在应用程序获取系统的启动时间,百度了一下,通过sysinfo中的uptime可以计算出系统的启动时间。
二、sysinfo结构
sysinfo结构保持了系统启动后的信息,主要包括启动到现在的时间,可用内存空间、共享内存空间、进程的数目等。man sysinfo得到结果如下所示:
struct sysinfo { long uptime; /* Seconds since boot */ unsigned long loads[3]; /* 1, 5, and 15 minute load averages */ unsigned long totalram; /* Total usable main memory size */ unsigned long freeram; /* Available memory size */ unsigned long sharedram; /* Amount of shared memory */ unsigned long bufferram; /* Memory used by buffers */ unsigned long totalswap; /* Total swap space size */ unsigned long freeswap; /* swap space still available */ unsigned short procs; /* Number of current processes */ char _f[22]; /* Pads structure to 64 bytes */ };
三、获取系统启动时间
通过sysinfo获取系统启动到现在的秒数,用当前时间减去这个秒数即系统的启动时间。程序如下所示:
#include <stdio.h> #include <sys/sysinfo.h> #include <time.h> #include <errno.h> static int print_system_boot_time() { struct sysinfo info; time_t cur_time = 0; time_t boot_time = 0; struct tm *ptm = NULL; if (sysinfo(&info)) { fprintf(stderr, "Failed to get sysinfo, errno:%u, reason:%s\\n", errno, strerror(errno)); return -1; } time(&cur_time); if (cur_time > info.uptime) { boot_time = cur_time - info.uptime; } else { boot_time = info.uptime - cur_time; } ptm = gmtime(&boot_time); printf("System boot time: %d-%-d-%d %d:%d:%d\\n", ptm->tm_year + 1900, ptm->tm_mon + 1,
ptm->tm_mday, ptm->tm_hour, ptm->tm_min, ptm->tm_sec); return 0; } int main() { if (print_system_boot_time() != 0) { return -1; } return 0; }
测试结果如下所:
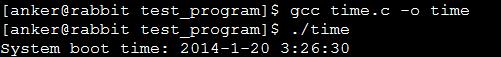
参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/Anker/p/3527609.html
以上是关于linux --> 获取系统启动时间的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章