Kotlin中equals方法与==,===
Posted 落幕夜未央
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Kotlin中equals方法与==,===相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
先看一段代码:
1 fun main(args: Array<String>) { 2 val person1 = Person(1,"liuliqianxiao") 3 val person2 = Person(1,"liuliqianxiao") 4 println(person1 == person2)//false 5 } 6 7 class Person(var id: Int, var name: String) { 8 9 }
自定义了一个类之后,天然的就能使用==运算符。这是因为Kotlin中==运算符会调用到equals函数,而equals是根类Any上定义的方法(这里我没找到Any上equals方法的实现)。
这里很容跟其他运算符重载的特性,导致一个惯性思维就是a == b就是调用的 a.equals(b),其实不然,a == b其实是如下调用过程:
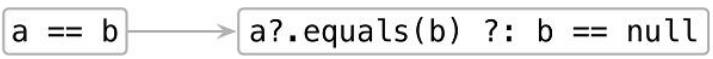
默认实现的equals也许不是我们想要的而结果,此时可以自行重写equals方法。试着给Person类实现它自己的equals,偷个懒,直接idea快捷键生成吧:
1 class Person(var id: Int, var name: String) { 2 override fun equals(other: Any?): Boolean { 3 if (this === other) return true 4 if (other?.javaClass != javaClass) return false 5 6 other as Person 7 8 if (id != other.id) return false 9 if (name != other.name) return false 10 11 return true 12 } 13 14 override fun hashCode(): Int { 15 var result = id 16 result = 31 * result + name.hashCode() 17 return result 18 } 19 }
此处ide自动生成的equals略显啰嗦,可以稍微简化下,如下代码:
1 override fun equals(other: Any?): Boolean { 2 if (this === other) return true 3 if (other !is Person) return false 4 5 return this.id == other.id && this.name == other.name 6 }
这里看到运算符重载,我们并没有加上operator关键字,这也是因为equals是在根类Any上定义的,已经加上了operator修饰符,如下:
public open operator fun equals(other: Any?): Boolean
所以子类只需要override就可以。
还有一点需要注意的是equals不能以扩展函数的形式实现。这是因为从Any继承来的equals方法优先级高于扩展函数。
在Kotlin中 ===运算符就相当于java中的==,比较的是两个引用是否相等。
!=运算符其实也是调用了equals
以上是关于Kotlin中equals方法与==,===的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章