『cs231n』作业2选讲_通过代码理解卷积层&池化层
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了『cs231n』作业2选讲_通过代码理解卷积层&池化层相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
卷积层
卷积层向前传播示意图:
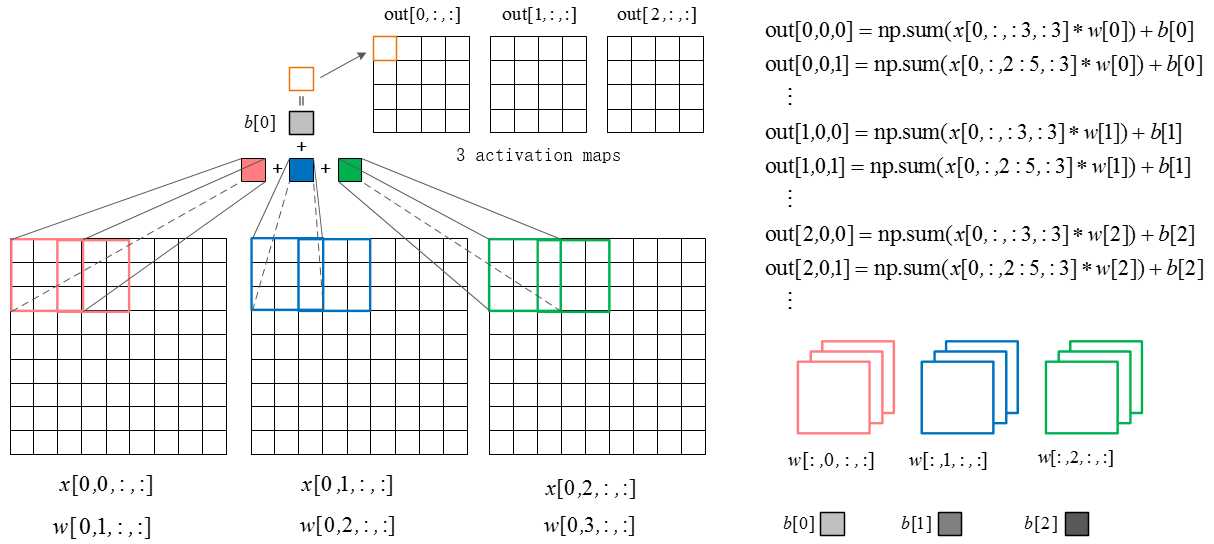
def conv_forward_naive(x, w, b, conv_param):
"""
A naive implementation of the forward pass for a convolutional layer.
The input consists of N data points, each with C channels, height H and width
W. We convolve each input with F different filters, where each filter spans
all C channels and has height HH and width HH.
Input:
- x: Input data of shape (N, C, H, W)
- w: Filter weights of shape (F, C, HH, WW)
- b: Biases, of shape (F,)
- conv_param: A dictionary with the following keys:
- ‘stride‘: The number of pixels between adjacent receptive fields in the
horizontal and vertical directions.
- ‘pad‘: The number of pixels that will be used to zero-pad the input.
Returns a tuple of:
- out: Output data, of shape (N, F, H‘, W‘) where H‘ and W‘ are given by
H‘ = 1 + (H + 2 * pad - HH) / stride
W‘ = 1 + (W + 2 * pad - WW) / stride
- cache: (x, w, b, conv_param)
"""
out = None
#############################################################################
# TODO: Implement the convolutional forward pass. #
# Hint: you can use the function np.pad for padding. #
############################################################################
pad = conv_param[‘pad‘]
stride = conv_param[‘stride‘]
N, C, H, W = x.shape
F, _, HH, WW = w.shape
H0 = 1 + (H + 2 * pad - HH) / stride
W0 = 1 + (W + 2 * pad - WW) / stride
x_pad = np.pad(x, ((0,0),(0,0),(pad,pad),(pad,pad)),‘constant‘) # 填充后的输入
out = np.zeros((N,F,H0,W0)) # 初始化的输出
# 以输出的每一个像素点为单位写出其前传表达式
for n in range(N):
for f in range(F):
for h0 in range(H0):
for w0 in range(W0):
out[n,f,h0,w0] = np.sum(x_pad[n,:,h0*stride:HH+h0*stride,w0*stride:WW+w0*stride] * w[f]) + b[f]
#############################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
#############################################################################
cache = (x, w, b, conv_param)
return out, cache
卷积层反向传播示意图:
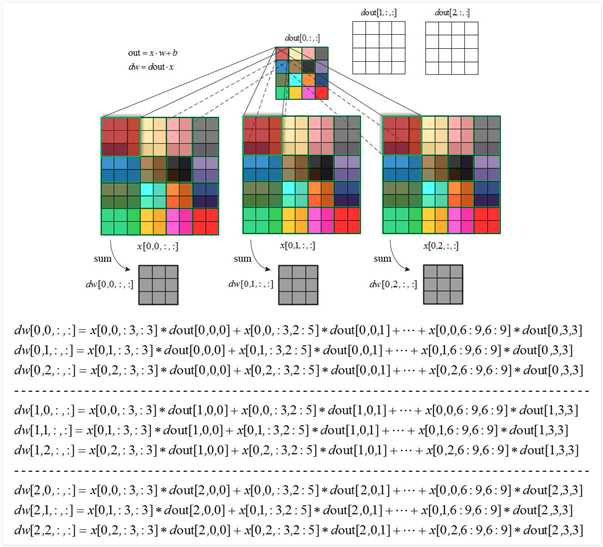
def conv_backward_naive(dout, cache):
"""
A naive implementation of the backward pass for a convolutional layer.
Inputs:
- dout: Upstream derivatives.
- cache: A tuple of (x, w, b, conv_param) as in conv_forward_naive
Returns a tuple of:
- dx: Gradient with respect to x
- dw: Gradient with respect to w
- db: Gradient with respect to b
"""
dx, dw, db = None, None, None
#############################################################################
# TODO: Implement the convolutional backward pass. #
#############################################################################
x, w, b, conv_param = cache
pad = conv_param[‘pad‘]
stride = conv_param[‘stride‘]
N, C, H, W = x.shape
F, _, HH, WW = w.shape
_, _, H0, W0 = out.shape
x_pad = np.pad(x, [(0,0), (0,0), (pad,pad), (pad,pad)], ‘constant‘)
dx, dw = np.zeros_like(x), np.zeros_like(w)
dx_pad = np.pad(dx, [(0,0), (0,0), (pad,pad), (pad,pad)], ‘constant‘)
# 计算b的梯度(F,)
db = np.sum(dout, axis=(0,2,3)) # dout:(N,F,H0,W0)
# 以每一个dout点为基准计算其两个输入矩阵x(:,:,窗,窗)和w(f)的梯度,注意由于这两个矩阵都是多次参与运算,所以都是累加的关系
for n in range(N):
for f in range(F):
for h0 in range(H0):
for w0 in range(W0):
x_win = x_pad[n,:,h0*stride:h0*stride+HH,w0*stride:w0*stride+WW]
dw[f] += x_win * dout[n,f,h0,w0]
dx_pad[n,:,h0*stride:h0*stride+HH,w0*stride:w0*stride+WW] += w[f] * dout[n,f,h0,w0]
dx = dx_pad[:,:,pad:pad+H,pad:pad+W]
#############################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
#############################################################################
return dx, dw, db
池化层(亦下采样层)
池化层向前传播:
和卷积层类似,但是更简单一点,只要在对应feature map的原输入上取个窗口然后池化之即可,
def max_pool_forward_naive(x, pool_param):
HH, WW = pool_param[‘pool_height‘], pool_param[‘pool_width‘]
s = pool_param[‘stride‘]
N, C, H, W = x.shape
H_new = 1 + (H - HH) / s
W_new = 1 + (W - WW) / s
out = np.zeros((N, C, H_new, W_new))
for i in xrange(N):
for j in xrange(C):
for k in xrange(H_new):
for l in xrange(W_new):
window = x[i, j, k*s:HH+k*s, l*s:WW+l*s]
out[i, j, k, l] = np.max(window)
cache = (x, pool_param)
return out, cache
池化层反向传播:
反向传播的时候也是还原窗口,除最大值处继承上层梯度外(也就是说本层梯度为零),其他位置置零。
池化层没有过滤器,只有dx梯度,且x的窗口不像卷积层会重叠,所以不用累加,
def max_pool_backward_naive(dout, cache):
x, pool_param = cache
HH, WW = pool_param[‘pool_height‘], pool_param[‘pool_width‘]
s = pool_param[‘stride‘]
N, C, H, W = x.shape
H_new = 1 + (H - HH) / s
W_new = 1 + (W - WW) / s
dx = np.zeros_like(x)
for i in xrange(N):
for j in xrange(C):
for k in xrange(H_new):
for l in xrange(W_new):
window = x[i, j, k*s:HH+k*s, l*s:WW+l*s]
m = np.max(window)
dx[i, j, k*s:HH+k*s, l*s:WW+l*s] = (window == m) * dout[i, j, k, l]
return dx
以上是关于『cs231n』作业2选讲_通过代码理解卷积层&池化层的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章