2017.7.17-2017.7.23
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了2017.7.17-2017.7.23相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
本周任务:
1.CS61B往后四个lecture
2. lab3&hw3
7.17
√lecture7:继承和测试
对应的reading完成,包括HFJ第七章习题,有些用eclipse试了一下结果。
晚上szw给我讲解了多态性和习题,让我先不要用eclipse,教我装了一个sublime text。
7.18
今天不打算看lecture 看算法书
下午看完了3.2的二叉查找树 我为什么要从3.2开始看起呢 因为我看完了才发现原来这本书不是CS61B的指定用书(手动微笑) 于是我按照CS61B用的算法书的要求看的
感觉自己好像要更喜欢看算法书。。除了HFJ的java书总是看的很累。。
晚上做lab3
lab3打卡 先说一件非常蠢的事 我复制SList的代码没复制全,进去真的满眼红叉叉,我还心累的想:这尼玛是个找bug的lab啊
然后就开始狂加程序。。。。。。
后来发现。。。好像别人做得都很轻松的样子啊。。一看发现代码没有复制全。。。
Lab3
/* SList.java */
/**
* The SList class is a singly-linked implementation of the linked list
* abstraction. SLists are mutable data structures, which can grow at either
* end.
*
* @author Kathy Yelick and Jonathan Shewchuk
**/
public class SList {
private SListNode head;
private int size;
private SListNode tail;
/**
* SList() constructs an empty list.
**/
public SList() {
size = 0;
head = null;
}
/**
* isEmpty() indicates whether the list is empty.
* @return true if the list is empty, false otherwise.
**/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
/**
* length() returns the length of this list.
* @return the length of this list.
**/
public int length() {
return size;
}
/**
* insertFront() inserts item "obj" at the beginning of this list.
* @param obj the item to be inserted.
**/
public void insertFront(Object obj) {
head = new SListNode(obj, head);
if(tail==null) {
tail=head;//when SList is empty
}
size++;
}
/**
* insertEnd() inserts item "obj" at the end of this list.
* @param obj the item to be inserted.
**/
public void insertEnd(Object obj) {
if (tail==null) {
tail=new SListNode(obj);
head=tail;
}else {
tail.next=new SListNode(obj);
tail=tail.next;
}
// if (head == null) {
// head = new SListNode(obj);
// } else {
// SListNode node = head;
// while (node.next != null) {
// node = node.next;
// }
// node.next = new SListNode(obj);
// }
size++;
}
/**
* nth() returns the item at the specified position. If position < 1 or
* position > this.length(), null is returned. Otherwise, the item at
* position "position" is returned. The list does not change.
* @param position the desired position, from 1 to length(), in the list.
* @return the item at the given position in the list.
**/
public Object nth(int position) {
SListNode currentNode;
if ((position < 1) || (head == null)) {
return null;
} else {
currentNode = head;
while (position > 1) {
currentNode = currentNode.next;
if (currentNode == null) {
return null;
}
position--;
}
return currentNode.item;
}
}
/**
* toString() converts the list to a String.
* @return a String representation of the list.
**/
public String toString() {
int i;
Object obj;
String result = "[ ";
SListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
obj = cur.item;
result = result + obj.toString() + " ";
cur = cur.next;
}
result = result + "]";
return result;
}
/**
* main() runs test cases on the SList class. Prints summary
* information on basic operations and halts with an error (and a stack
* trace) if any of the tests fail.
**/
public static void main (String[] args) {
// Fill in your solution for Part I here.
SList s=new SList();
s.insertEnd(6);
s.insertEnd(9);
s.insertEnd(12);
System.out.println(s.toString());
s.insertFront(3);
s.insertEnd(15);
System.out.println(s.toString());
testEmpty();
testAfterInsertFront();
testAfterInsertEnd();
}
/**
* testEmpty() tests toString(), isEmpty(), length(), insertFront(), and
* insertEnd() on an empty list. Prints summary information of the tests
* and halts the program if errors are detected.
**/
private static void testEmpty() {
SList lst1 = new SList();
SList lst2 = new SList();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Here is a list after construction: "
+ lst1.toString());
TestHelper.verify(lst1.toString().equals("[ ]"),
"toString on newly constructed list failed");
System.out.println("isEmpty() should be true. It is: " +
lst1.isEmpty());
TestHelper.verify(lst1.isEmpty() == true,
"isEmpty() on newly constructed list failed");
System.out.println("length() should be 0. It is: " +
lst1.length());
TestHelper.verify(lst1.length() == 0,
"length on newly constructed list failed");
lst1.insertFront(new Integer(3));
System.out.println("Here is a list after insertFront(3) to an empty list: "
+ lst1.toString());
TestHelper.verify(lst1.toString().equals("[ 3 ]"),
"InsertFront on empty list failed");
lst2.insertEnd(new Integer(5));
System.out.println("Here is a list after insertEnd(5) on an empty list: "
+ lst2.toString());
TestHelper.verify(lst2.toString().equals("[ 5 ]"),
"insertEnd on empty list failed");
}
/**
* testAfterInsertFront() tests toString(), isEmpty(), length(),
* insertFront(), and insertEnd() after insertFront(). Prints summary
* information of the tests and halts the program if errors are detected.
**/
private static void testAfterInsertFront() {
SList lst1 = new SList();
lst1.insertFront(new Integer(3));
lst1.insertFront(new Integer(2));
lst1.insertFront(new Integer(1));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Here is a list after insertFront 3, 2, 1: "
+ lst1.toString());
TestHelper.verify(lst1.toString().equals("[ 1 2 3 ]"),
"InsertFronts on non-empty list failed");
System.out.println("isEmpty() should be false. It is: " +
lst1.isEmpty());
TestHelper.verify(lst1.isEmpty() == false,
"isEmpty() after insertFront failed");
System.out.println("length() should be 3. It is: " +
lst1.length());
TestHelper.verify(lst1.length() == 3,
"length() after insertFront failed");
lst1.insertEnd(new Integer(4));
System.out.println("Here is the same list after insertEnd(4): "
+ lst1.toString());
TestHelper.verify(lst1.toString().equals("[ 1 2 3 4 ]"),
"insertEnd on non-empty list failed");
}
/**
* testAfterInsertEnd() tests toString(), isEmpty(), length(),
* insertFront(), and insertEnd() after insertEnd(). Prints summary
* information of the tests and halts the program if errors are detected.
**/
private static void testAfterInsertEnd() {
SList lst1 = new SList();
lst1.insertEnd(new Integer(6));
lst1.insertEnd(new Integer(7));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Here is a list after insertEnd 6, 7: "
+ lst1.toString());
System.out.println("isEmpty() should be false. It is: " +
lst1.isEmpty());
TestHelper.verify(lst1.isEmpty() == false,
"isEmpty() after insertEnd failed");
System.out.println("length() should be 2. It is: " +
lst1.length());
TestHelper.verify(lst1.length() == 2,
"length() after insertEndfailed");
lst1.insertFront(new Integer(5));
System.out.println("Here is the same list after insertFront(5): "
+ lst1.toString());
TestHelper.verify(lst1.toString().equals("[ 5 6 7 ]"),
"insertFront after insertEnd failed");
}
}
运行结果:
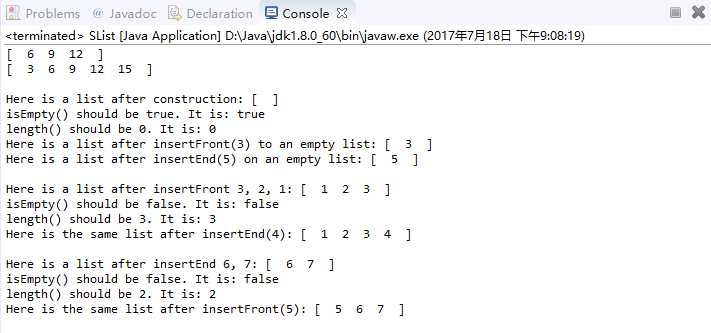
注意!!
一开始有一处报错但是test的结果却没错,也可以运行:
找了很久,以为在insertEnd那里,后来发现是在insertFront那里!没有考虑一开始SList就是空的情况(即tail==null)
报错结果:
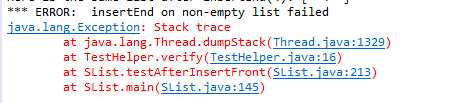
之后加上:
if(tail==null) {
tail=head;
}
就没有报错了。。
奇怪。。那为什么报错是insertEnd那里failed呢?
7.19
完成lecture8 主要是讲abstract,interface接口和package的
完成对应的reading任务
7.20
HW3:
完整代码:
Homework3:

/* Homework3.java */ public class Homework3 { /** * smoosh() takes an array of ints. On completion the array contains * the same numbers, but wherever the array had two or more consecutive * duplicate numbers, they are replaced by one copy of the number. Hence, * after smoosh() is done, no two consecutive numbers in the array are the * same. * * Any unused elements at the end of the array are set to -1. * * For example, if the input array is [ 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 3 3 3 1 1 0 ], * it reads [ 0 1 0 3 1 0 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 ] after smoosh() * completes. * * @param ints the input array. **/ public static void smoosh(int[] ints) { int j=1; int[] Tempt=new int[ints.length]; for(int k=0;k<ints.length;k++) { Tempt[k]=-1; } Tempt[0]=ints[0]; for(int i=1;i<ints.length;i++) { if(ints[i]!=ints[i-1]) { Tempt[j]=ints[i]; }else continue; j++; } for(int i=0;i<ints.length;i++) { ints[i]=Tempt[i]; } // Fill in your solution here. (Ours is fourteen lines long, not counting // blank lines or lines already present in this file.) } /** * stringInts() converts an array of ints to a String. * @return a String representation of the array. **/ private static String stringInts(int[] ints) { String s = "[ "; for (int i = 0; i < ints.length; i++) { s = s + Integer.toString(ints[i]) + " "; } return s + "]"; } /** * main() runs test cases on your smoosh and squish methods. Prints summary * information on basic operations and halts with an error (and a stack * trace) if any of the tests fail. **/ public static void main(String[] args) { String result; int i; System.out.println("Let‘s smoosh arrays!\\n"); int[] test1 = {3, 7, 7, 7, 4, 5, 5, 2, 0, 8, 8, 8, 8, 5}; System.out.println("smooshing " + stringInts(test1) + ":"); smoosh(test1); result = stringInts(test1); System.out.println(result); TestHelper.verify(result.equals( "[ 3 7 4 5 2 0 8 5 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 ]"), "BAD SMOOSH!!! No cookie."); int[] test2 = {6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 3, 6, 3, 6, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3}; System.out.println("smooshing " + stringInts(test2) + ":"); smoosh(test2); result = stringInts(test2); System.out.println(result); TestHelper.verify(result.equals( "[ 6 3 6 3 6 3 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 ]"), "BAD SMOOSH!!! No cookie."); int[] test3 = {4, 4, 4, 4, 4}; System.out.println("smooshing " + stringInts(test3) + ":"); smoosh(test3); result = stringInts(test3); System.out.println(result); TestHelper.verify(result.equals("[ 4 -1 -1 -1 -1 ]"), "BAD SMOOSH!!! No cookie."); int[] test4 = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}; System.out.println("smooshing " + stringInts(test4) + ":"); smoosh(test4); result = stringInts(test4); System.out.println(result); TestHelper.verify(result.equals("[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 ]"), "BAD SMOOSH!!! No cookie."); System.out.println("\\nLet‘s squish linked lists!\\n"); int[] test5 = {3, 7, 7, 7, 4, 5, 5, 2, 0, 8, 8, 8, 8, 5}; SList list5 = new SList(); for (i = 0; i < test5.length; i++) { list5.insertEnd(new Integer(test5[i])); } System.out.println("squishing " + list5.toString() + ":"); list5.squish(); result = list5.toString(); System.out.println(result); TestHelper.verify(result.equals("[ 3 7 4 5 2 0 8 5 ]"), "BAD SQUISH!!! No biscuit."); int[] test6 = {6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 3, 6, 3, 6, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3}; SList list6 = new SList(); for (i = 0; i < test6.length; i++) { list6.insertEnd(new Integer(test6[i])); } System.out.println("squishing " + list6.toString() + ":"); list6.squish(); result = list6.toString(); System.out.println(result); TestHelper.verify(result.equals("[ 6 3 6 3 6 3 ]"), "BAD SQUISH!!! No biscuit."); int[] test7 = {4, 4, 4, 4, 4}; SList list7 = new SList(); for (i = 0; i < test7.length; i++) { list7.insertEnd(new Integer(test7[i])); } System.out.println("squishing " + list7.toString() + ":"); list7.squish(); result = list7.toString(); System.out.println(result); TestHelper.verify(result.equals("[ 4 ]"), "BAD SQUISH!!! No biscuit."); int[] test8 = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}; SList list8 = new SList(); for (i = 0; i < test8.length; i++) { list8.insertEnd(new Integer(test8[i])); } System.out.println("squishing " + list8.toString() + ":"); list8.squish(); result = list8.toString(); System.out.println(result); TestHelper.verify(result.equals("[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 ]"), "BAD SQUISH!!! No biscuit."); SList list9 = new SList(); System.out.println("squishing " + list9.toString() + ":"); list9.squish(); result = list9.toString(); System.out.println(result); TestHelper.verify(result.equals("[ ]"), "BAD SQUISH!!! No biscuit."); System.out.println("\\nLet‘s twin linked lists!\\n"); System.out.println("twinning " + list6.toString() + ":"); list6.twin(); result = list6.toString(); System.out.println(result); TestHelper.verify(result.equals( "[ 6 6 3 3 6 6 3 3 6 6 3 3 ]"), "BAD TWIN!!! No gravy."); System.out.println("twinning " + list7.toString() + ":"); list7.twin(); result = list7.toString(); System.out.println(result); TestHelper.verify(result.equals("[ 4 4 ]"), "BAD TWIN!!! No gravy."); System.out.println("twinning " + list9.toString() + ":"); list9.twin(); result = list9.toString(); System.out.println(result); TestHelper.verify(result.equals("[ ]"), "BAD TWIN!!! No gravy."); } }
SList:

/* SList.java */ /** * The SList class is a singly-linked implementation of the linked list * abstraction. SLists are mutable data structures, which can grow at either * end. * * @author Kathy Yelick and Jonathan Shewchuk **/ public class SList { private SListNode head; private int size; /** * SList() constructs an empty list. **/ public SList() { size = 0; head = null; } /** * isEmpty() indicates whether the list is empty. * @return true if the list is empty, false otherwise. **/ public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; } /** * length() returns the length of this list. * @return the length of this list. **/ public int length() { return size; } /** * insertFront() inserts item "obj" at the beginning of this list. * @param obj the item to be inserted. **/ public void insertFront(Object obj) { head = new SListNode(obj, head); size++; } /** * insertEnd() inserts item "obj" at the end of this list. * @param obj the item to be inserted. **/ public void insertEnd(Object obj) { if (head == null) { head = new SListNode(obj); } else { SListNode node = head; while (node.next != null) { node = node.next; } node.next = new SListNode(obj); } size++; } /** * nth() returns the item at the specified position. If position < 1 or * position > this.length(), null is returned. Otherwise, the item at * position "position" is returned. The list does not change. * @param position the desired position, from 1 to length(), in the list. * @return the item at the given position in the list. **/ public Object nth(int position) { SListNode currentNode; if ((position < 1) || (head == null)) { return null; } else { currentNode = head; while (position > 1) { currentNode = currentNode.next; if (currentNode == null) { return null; } position--; } return currentNode.item; } } /** * squish() takes this list and, wherever two or more consecutive items are * equal(), it removes duplicate nodes so that only one consecutive copy * remains. Hence, no two consecutive items in this list are equal() upon * completion of the procedure. * * After squish() executes, the list may well be shorter than when squish() * began. No extra items are added to make up for those removed. * * For example, if the input list is [ 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 3 3 3 1 1 0 ], the * output list is [ 0 1 0 3 1 0 ]. * * IMPORTANT: Be sure you use the equals() method, and not the "==" * operator, to compare items. **/ public void squish() { SListNode CurrentNode=head; while(size!=0&&CurrentNode.next!=null) { if(CurrentNode.item.equals(CurrentNode.next.item)) { CurrentNode.next=CurrentNode.next.next; }else { CurrentNode=CurrentNode.next; } } // Fill in your solution here. (Ours is eleven lines long.) } /** * twin() takes this list and doubles its length by replacing each node * with two consecutive nodes referencing the same item. * * For example, if the input list is [ 3 7 4 2 2 ], the * output list is [ 3 3 7 7 4 4 2 2 2 2 ]. * * IMPORTANT: Do not try to make new copies of the items themselves. * Just copy the references to the items. **/ public void twin() { SListNode CurrentNode; CurrentNode=head; while(CurrentNode!=null) { CurrentNode.next=new SListNode(CurrentNode.item,CurrentNode.next); if(CurrentNode.next.next==null){ break; }else{ CurrentNode=CurrentNode.next.next;} } // Fill in your solution here. (Ours is seven lines long.) } /** * toString() converts the list to a String. * @return a String representation of the list. **/ public String toString() { int i; Object obj; String result = "[ "; SListNode cur = head; while (cur != null) { obj = cur.item; result = result + obj.toString() + " "; cur = cur.next; } result = result + "]"; return result; } /** * main() runs test cases on the SList class. Prints summary * information on basic operations and halts with an error (and a stack * trace) if any of the tests fail. **/ public static void main (String[] args) { testEmpty(); testAfterInsertFront(); testAfterInsertEnd(); } /** * testEmpty() tests toString(), isEmpty(), length(), insertFront(), and * insertEnd() on an empty list. Prints summary information of the tests * and halts the program if errors are detected. **/ private static void testEmpty() { SList lst1 = new SList(); SList lst2 = new SList(); System.out.println(); System.out.println("Here is a list after construction: " + lst1.toString()); TestHelper.verify(lst1.toString().equals("[ ]"), "toString on newly constructed list failed"); System.out.println("isEmpty() should be true. It is: " + lst1.isEmpty()); TestHelper.verify(lst1.isEmpty() == true, "isEmpty() on newly constructed list failed"); System.out.println("length() should be 0. It is: " + lst1.length()); TestHelper.verify(lst1.length() == 0, "length on newly constructed list failed"); lst1.insertFront(new Integer(3)); System.out.println("Here is a list after insertFront(3) to an empty list: " + lst1.toString()); TestHelper.verify(lst1.toString().equals("[ 3 ]"), "InsertFront on empty list failed"); lst2.insertEnd(new Integer(5)); System.out.println("Here is a list after insertEnd(5) on an empty list: " + lst2.toString()); TestHelper.verify(lst2.toString().equals("[ 5 ]"), "insertEnd on empty list failed"); } /** * testAfterInsertFront() tests toString(), isEmpty(), length(), * insertFront(), and insertEnd() after insertFront(). Prints summary * information of the tests and halts the program if errors are detected. **/ private static void testAfterInsertFront() { SList lst1 = new SList(); lst1.insertFront(new Integer(3)); lst1.insertFront(new Integer(2)); lst1.insertFront(new Integer(1)); System.out.println(); System.out.println("Here is a list after insertFront 3, 2, 1: " + lst1.toString()); TestHelper.verify(lst1.toString().equals("[ 1 2 3 ]"), "InsertFronts on non-empty list failed"); System.out.println("isEmpty() should be false. It is: " + lst1.isEmpty()); TestHelper.verify(lst1.isEmpty() == false, "isEmpty() after insertFront failed"); System.out.println("length() should be 3. It is: " + lst1.length()); TestHelper.verify(lst1.length() == 3, "length() after insertFront failed"); lst1.insertEnd(new Integer(4)); System.out.println("Here is the same list after insertEnd(4): " + lst1.toString()); TestHelper.verify(lst1.toString().equals("[ 1 2 3 4 ]"), "insertEnd on non-empty list failed"); } /** * testAfterInsertEnd() tests toString(), isEmpty(), length(), * insertFront(), and insertEnd() after insertEnd(). Prints summary * information of the tests and halts the program if errors are detected. **/ private static void testAfterInsertEnd() { SList lst1 = new SList(); lst1.insertEnd(new Integer(6)); lst1.insertEnd(new Integer(7)); System.out.println(); System.out.println("Here is a list after insertEnd 6, 7: " + lst1.toString()); System.out.println("isEmpty() should be false. It is: " + lst1.isEmpty()); TestHelper.verify(lst1.isEmpty() == false, "isEmpty() after insertEnd failed"); System.out.println("length() should be 2. It is: " + lst1.length()); TestHelper.verify(lst1.length() == 2, "length() after insertEndfailed"); lst1.insertFront(new Integer(5)); System.out.println("Here is the same list after insertFront(5): " + lst1.toString()); TestHelper.verify(lst1.toString().equals("[ 5 6 7 ]"), "insertFront after insertEnd failed"); } }
运行结果:
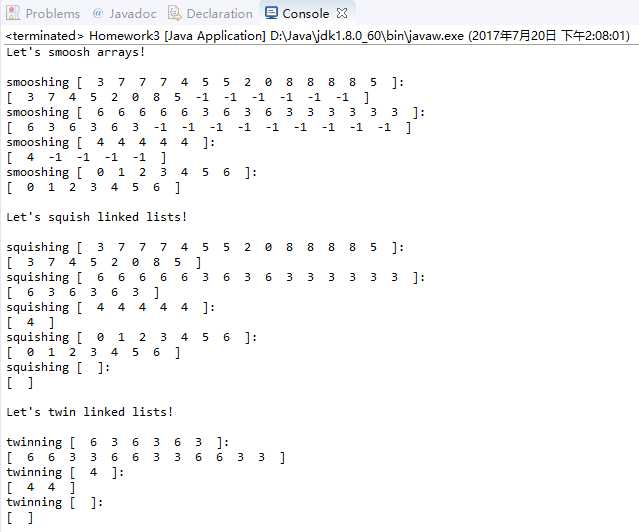
其中:
public static void smoosh(int[] ints) { int j=1; int[] Tempt=new int[ints.length]; for(int k=0;k<ints.length;k++) { Tempt[k]=-1; } Tempt[0]=ints[0]; for(int i=1;i<ints.length;i++) { if(ints[i]!=ints[i-1]) { Tempt[j]=ints[i]; }else continue; j++; } for(int i=0;i<ints.length;i++) { ints[i]=Tempt[i]; } // Fill in your solution here. (Ours is fourteen lines long, not counting // blank lines or lines already present in this file.) }
public void squish() { SListNode CurrentNode=head; while(size!=0&&CurrentNode.next!=null) { if(CurrentNode.item.equals(CurrentNode.next.item)) { CurrentNode.next=CurrentNode.next.next; }else { CurrentNode=CurrentNode.next; } } // Fill in your solution here. (Ours is eleven lines long.) }
public void twin() { SListNode CurrentNode; CurrentNode=head; while(CurrentNode!=null) { CurrentNode.next=new SListNode(CurrentNode.item,CurrentNode.next); if(CurrentNode.next.next==null){ break; }else{ CurrentNode=CurrentNode.next.next;
} } // Fill in your solution here. (Ours is seven lines long.) }
注意:1.smoosh里:要先设置一个全为-1的数组。(本来想先添加原数组的元素再添加-1)
2.squish里:while循环条件要加size!=0,比较List是不是为空,比如“[ ]”
3.twin里,和之前的两个不同,重新定义CurrentNode.next,然后把CurrenNode的内容赋给它(copy),以及指向CurrentNode下一个结点
最后要看CurrentNode是否为List里最后一个结点,如果是,跳出Loop(break)。
4. Be sure you use the equals() method, and not the "==" operator, to compare items.
以上是关于2017.7.17-2017.7.23的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
