专题5-数据结构
Posted zqlucky
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了专题5-数据结构相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
专题5-数据结构 2017-07-13
C++ Primer P329好好研读,stack,queue,priority_queue都是顺序容器适配器adaptor。(接受一种已有的容器类型,使其行为看起来像另一种事物一样)
| stack | 默认基于deque实现,除array和forward_list以外的容器都可以 |
| queue | 默认基于deque实现,可以构造于list和deque之上,但是不能基于vector进行构造 |
| priority_queue | 默认基于vector实现,最大堆max-heap,可以基于vetor和deque,但是不能基于list(需要随机访问能力) |
1、基础知识
1.1、stack栈
| s.pop() | 删除栈顶元素 | O(1) |
| s.push() | 压入元素 | O(1) |
| s.top() | 返回首元素,但是不删除 | O(1) |
| s.swap(stack) | 交换两个栈的内容 |
C++ primer P330
queue模板类的定义在<queue>头文件中。记住队列没有top()函数,使用front(),总是记错。
与stack模板类很相似,queue模板类也需要两个模板参数,一个是元素类型,一个容器类型,元素类型是必要的,容器类型是可选的,默认为deque类型。
定义queue对象的示例代码如下:
queue<int> q1; queue<double> q2;
queue的基本操作有:
| q.push(x) | 入队,将x接到队列的末端 | 时间复杂度是O(1) |
| q.pop() | 出队,弹出队列的第一个元素,注意,并不会返回被弹出元素的值 | 时间复杂度是O(1) |
| q.front() | 访问队首元素,即最早被压入队列的元素 | 时间复杂度是O(1) |
| q.back() | 访问队尾元素,即最后被压入队列的元素 | 时间复杂度是O(1) |
| q.empty() | 判断队列空 | |
| q.size() | 访问队列中的元素个数 |
队列经常用于BFS,之前总结过BFS要利用queue + unordered_map实现,还有就是二叉树的层次遍历。
1.3、priority_queue
主要操作是:pop(),top(),push()。pop,push都是O(logk),top是O(1)的。
左边是队头,右边是队尾,默认是最大堆即返回的top是目前最大的元素,默认是less<>,实现是x < y,因为有个建堆的过程,所以不能以平常的大小来比较。
STL里面容器默认用的是 vector. 比较方式默认用 operator< , 所以如果你把后面俩个参 缺省的话,优先队列就是大顶堆,队头元素最大。
priority_queue利用一个最大堆完成,最大堆是一个以vector表现的完全二叉树,所以缺省情况下它的底部容器是vector。,queue以底部容器完成其所有的工作,具有这种“修改某物接口,形成另一种风貌”之性质者,称为adapter(适配器)。
priority_queue 对于基本类型的使用方法相对简单。他的模板声明带有三个参数,priority_queue<Type, Container, Functional>,Type 为数据类型, Container 为保存数据的容器,Functional 为元素比较方式。
Container 必须是用数组实现的容器,比如 vector, deque 但不能用 list。STL里面默认用的是 vector. 比较方式默认用 operator< , 所以如果你把后面俩个参数缺省的话,优先队列就是大顶堆,队头元素最大。
如果要用到小顶堆,则一般要把模板的三个参数都带进去。
使用方法:
头文件:
声明方式:
1、普通方法:
//通过操作,按照元素从大到小的顺序出队
2、自定义优先级:
struct cmp { bool operator()(int x, int y) { return x > y; } };
{
int x, y;
friend bool operator < (node a, node b)
{
return a.x > b.x; //结构体中,x小的优先级高
}
};
priority_queue<node>q;//定义方法
//在该结构中,y为值, x为优先级。
//通过自定义operator<操作符来比较元素中的优先级。
//在重载”<”时,最好不要重载”>”,可能会发生编译错误
#include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std; int main(){ priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > q; for( int i= 0; i< 10; ++i ) q.push( rand() ); while( !q.empty() ){ cout << q.top() << endl; q.pop(); } getchar(); return 0; }
**对于自定义类型,则必须自己重载 operator< 或者自己写仿函数**
1)重载 operator<(自己联想一下每次弹出最小元素的queue形式,{3,2,1}所以必须是返回a.x> b.x;)sort默认是小于排序,从大到小排序,所以重载的时候需要operator<。只有自定义类类型才能重写操作符:
bool operator>( Node left, Node right ){ if( left.x== right.x )
return left.y> right.y; return left.x> right.x; }
写仿函数注意有模板的时候才需要greater<int>写这种形式是为了将模板里面的T变为int,如果没用模板,直接写greater。
struct greater{ bool operator() (const int &a, const int &b) { return a > b; } }; //用的时候直接使用geater template<typename T> struct greater{ bool operator() (const T &a, const T &b) { return a > b; } }; //用的时候使用greater<int>,匹配模板

#include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std; struct Node{ int x, y; Node( int a= 0, int b= 0 ): x(a), y(b) {} }; bool operator<( Node a, Node b ){ if( a.x== b.x ) return a.y> b.y; return a.x> b.x; } int main(){ priority_queue<Node> q; for( int i= 0; i< 10; ++i ) q.push( Node( rand(), rand() ) ); while( !q.empty() ){ cout << q.top().x << \' \' << q.top().y << endl; q.pop(); } getchar(); return 0; }
2)自己写仿函数
自定义类型重载 operator< 后,声明对象时就可以只带一个模板参数。但此时不能像基本类型这样声明priority_queue<Node, vector<Node>, greater<Node> >;原因是 greater<Node> 没有定义,如果想用这种方法定义
则可以按如下方式:
记住调用的时候格式为:priority_queue<Node, vector<Node>, cmp> q;
struct cmp{ bool operator() ( Node a, Node b ){ if( a.x== b.x ) { return a.y> b.y; } return a.x> b.x; } };

#include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std; struct Node{ int x, y; Node( int a= 0, int b= 0 ): x(a), y(b) {} }; struct cmp{ bool operator() ( Node a, Node b ){ if( a.x== b.x ) return a.y> b.y; return a.x> b.x; } }; int main(){ priority_queue<Node, vector<Node>, cmp> q; for( int i= 0; i< 10; ++i ) q.push( Node( rand(), rand() ) ); while( !q.empty() ){ cout << q.top().x << \' \' << q.top().y << endl; q.pop(); } getchar(); return 0; }
不懂的话看下面的例子:

#include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<string> #include <cstdio> #include<queue> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; struct cmp { bool operator()(int a,int b) { return a > b; } }; struct node { int x; int y; }; bool operator<(node a, node b) { return a.x > b.y; } ostream& operator<<(ostream& os,const node&a) { os << a.x << " " << a.y<< endl; return os; } bool operator<<(node a, node b) { return a.x > b.y; } int main() { //priority_queue<int> q; priority_queue<node> q; for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) { node a; cin >> a.x; cin >> a.y; q.push(a); } cout << q.top() << endl; system("pause"); }
1.4、Hash哈希
参考链接:1)解决哈希表的冲突-开放地址法和链地址法 ;
2)哈希表的C实现(一);
3)哈希函数。
基本概念:
哈希表(Hash Table,也叫散列表),是根据关键码值 (Key-Value) 而直接进行访问的数据结构。也就是说,它通过把关键码值映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,以加快查找的速度。哈希表的实现主要需要解决两个问题,哈希函数和冲突解决。
哈希函数:
哈希函数也叫散列函数,它对不同的输出值得到一个固定长度的消息摘要。理想的哈希函数对于不同的输入应该产生不同的结构,同时散列结果应当具有同一性(输出值尽量均匀)和雪崩效应(微小的输入值变化使得输出值发生巨大的变化)。
冲突解决:
现实中的哈希函数不是完美的,当两个不同的输入值对应一个输出值时,就会产生“碰撞”,这个时候便需要解决冲突。常见的冲突解决方法有开放定址法,链地址法,建立公共溢出区等。实际的哈希表实现中,使用最多的是链地址法。
- 开放定址法
这个方法的基本思想是:当发生地址冲突时,按照某种方法继续探测哈希表中的其他存储单元,直到找到空位置为止。这个过程可用下式描述:
H i ( key ) = ( H ( key )+ d i ) mod m ( i = 1,2,…… , k ( k ≤ m – 1))
其中: H ( key ) 为关键字 key 的直接哈希地址, m 为哈希表的长度, di 为每次再探测时的地址增量。
采用这种方法时,首先计算出元素的直接哈希地址 H ( key ) ,如果该存储单元已被其他元素占用,则继续查看地址为 H ( key ) + d 2 的存储单元,如此重复直至找到某个存储单元为空时,将关键字为 key 的数据元素存放到该单元。
增量 d 可以有不同的取法,并根据其取法有不同的称呼:
( 1 ) d i = 1 , 2 , 3 , …… 线性探测再散列;
( 2 ) d i = 1^2 ,- 1^2 , 2^2 ,- 2^2 , k^2, -k^2…… 二次探测再散列;
( 3 ) d i = 伪随机序列 伪随机再散列;
这种方法删除非常麻烦。
- 链地址法
链地址法解决冲突的做法是:如果哈希表空间为 0 ~ m - 1 ,设置一个由 m 个指针分量组成的一维数组 ST[ m ], 凡哈希地址为 i 的数据元素都插入到头指针为 ST[ i ] 的链表中。这种 方法有点近似于邻接表的基本思想,且这种方法适合于冲突比较严重的情况。 实际中使用的比较多。
基本操作:
| 插入 | 时间复杂度O(1) |
| 删除 | 时间复杂度O(1) |
| 查找 | 时间复杂度O(1) |
哈希函数:
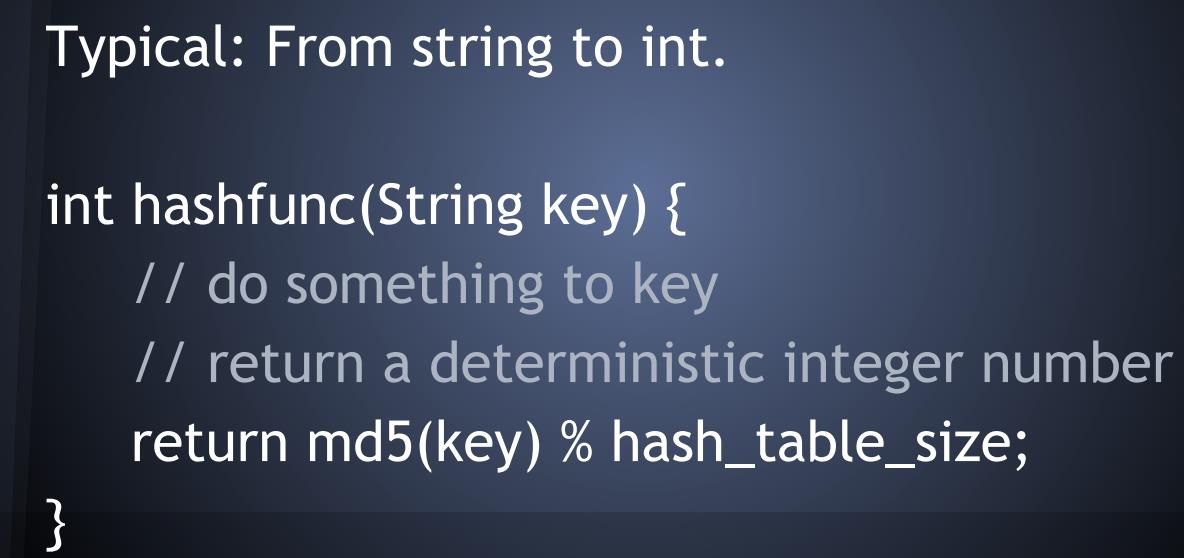

1.5 堆heap

heap可以使用动态数组vector实现,下标从1开始,root就是vec[i],左儿子是2*i,右儿子是2*i+1,插入删除使用siftup,siftdown操作不断进行调整。删除将最下面的一个元素调整到root,如果是最小堆,就按照儿子大于父亲的调整策略进行调整,插入就是插入到最后一个位置,在按照上述策略进行调整。堆的最值放在vector中的第一个位置。
建立堆的时间复杂度是O(N)的,
T(n) = 2*T(n/2) + O(lg n)
它的解是 T(n) = O(n)
链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/20729324/answer/132711265
函数说明:
std::make_heap将[start, end)范围进行堆排序,默认使用less<int>, 即最大元素放在第一个。
std::pop_heap将front(即第一个最大元素)移动到end的前部,同时将剩下的元素重新构造成(堆排序)一个新的heap,并没有删除该元素。
std::push_heap对刚插入的(尾部)元素做堆排序。(新加入的元素一定放在最下一层作为叶节点,并填补在由左至右的第一个孔哥哥,也就是插入到vector中的end前)。
std::sort_heap将一个堆做排序,最终成为一个有序的系列,可以看到sort_heap时,必须先是一个堆(两个特性:1、最大元素在第一个 2、添加或者删除元素以对数时间),因此必须先做一次make_heap.
其中使用仿函数来指定最大堆和最小堆,less是最大堆,greater是最小堆,默认是最大堆。
2、leetcode题目实战
2.1 155. Min Stack
https://leetcode.com/problems/min-stack/#/description
思路:使用两个栈,一个栈存正常数据,另一个栈记录每个元素对应的最小值是多少,这题细节,压入MinStack的时候,一定要使用if_else,minStack为空的时候要单独考虑,top()操作是返回stack中的数据。

class MinStack { public: /** initialize your data structure here. */ stack<int> s; stack<int> minStack; MinStack() { } void push(int x) { s.push(x); if(minStack.empty()){ minStack.push(x); } else{//总是忘记加上else,只有非空的时候才能这样 minStack.push(min(x,minStack.top())); } } void pop() { if(!s.empty()){ s.pop(); } if(!minStack.empty()){ minStack.pop(); } return; } int top() {//这里的top返回的是当前元素,不是需要返回最小值 if(!s.empty()){ return s.top(); } return 0; } int getMin() { if(!minStack.empty()){ return minStack.top(); } return 0; } }; /** * Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such: * MinStack obj = new MinStack(); * obj.push(x); * obj.pop(); * int param_3 = obj.top(); * int param_4 = obj.getMin(); */
2.2 232. Implement Queue using Stacks
https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/#/description
思路:这题自己思路不清晰,要理顺。使用两个栈oldStack和newStack,其中newStack总是存储目前压入的元素,在pop和front操作前,如果oldStack中有元素,就直接弹出oldStack的元素,只有oldStack为空的时候,才将newStack中的元素弹出压入到oldStack中。

class MyQueue { public: /** Initialize your data structure here. */ stack<int> newStack,oldStack;//newStack总是存储最新压入的元素 MyQueue() { } /** Push element x to the back of queue. */ void push(int x) { newStack.push(x); } /** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */ int pop() { if(oldStack.empty()){ while(!newStack.empty()){ oldStack.push(newStack.top()); newStack.pop(); } } int tmp = oldStack.top(); oldStack.pop(); return tmp; } /** Get the front element. */ int peek() { if(oldStack.empty()){ while(!newStack.empty()){ oldStack.push(newStack.top()); newStack.pop(); } } return oldStack.top(); } /** Returns whether the queue is empty. */ bool empty() { return newStack.empty() && oldStack.empty(); } }; /** * Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such: * MyQueue obj = new MyQueue(); * obj.push(x); * int param_2 = obj.pop(); * int param_3 = obj.peek(); * bool param_4 = obj.empty(); */
2.3 225. Implement Stack using Queues
https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-stack-using-queues/#/description
思路:这题有一个非常简单巧妙无敌的方法,除了push操作其他操作都和queue正常操作一样,使用一个队列就可以实现,将新元素压入queue,然后弹出一个front,再压入到queue中,这样就可以按照stack的顺序保存元素了。

4是需要压入的元素,{1,2,3}是已经压入的元素,然后将123弹出压入重新压入queue,就形成了{1‘,2‘,3’,4};

class MyStack { public: /** Initialize your data structure here. */ queue<int> q; MyStack() { } /** Push element x onto stack. */ void push(int x) { q.push(x); for(int i = 0;i < q.size() - 1;++i){ q.push(q.front()); q.pop(); } } /** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */ int pop() { int tmp = q.front(); q.pop(); return tmp; } /** Get the top element. */ int top() { return q.front(); } /** Returns whether the stack is empty. */ bool empty() { return q.empty(); } }; /** * Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such: * MyStack obj = new MyStack(); * obj.push(x); * int param_2 = obj.pop(); * int param_3 = obj.top(); * bool param_4 = obj.empty(); */
2.4 84. Largest Rectangle in Histogram
https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/#/description
思路:参照李二娃的文章,这题思路很重要,注意:单调栈适合只要弹出元素就可以开始计算的情况。
1)heights.push_back(0);是为了后面将栈中所有元素弹出。记住变量一定要在定义的时候初始化,不然后面比较的时候就会出错。stack里面存储的是索引值。
while循环里面的条件记住栈为空的时候,直接将当前元素压栈,当前元素大于栈顶元素的时候也是直接压栈,所以就得到循环的退出条件:
!s.empty() && heights[i] < heights[s.top()]

2)另外一个细节需要注意的是,弹栈过程中面积的计算。在求出高度后弹出一个元素,保证栈顶元素是小于当前元素高度的,这样求宽度的时候才能得到,
int h = heights[s.top()]; s.pop();//栈中存储的都是比目前索引小的元素 int w = s.empty() ? i : (i - s.top() - 1);
第二步非常关键一定要理解,再求宽度之前弹出一个元素。而且栈的首元素一定是最小的那个值,最后栈为空的时候一定是目前长度乘上高度。而且访问栈之前一定啊哟判断它是否为空。
h[t] * (stack.isEmpty() ? i : i - stack.peek() - 1)
h[t]是刚刚弹出的栈顶端元素。此时的面积计算是h[t]和前面的“上流社会”能围成的最大面积。这时候要注意哦,栈内索引指向的元素都是比h[t]小的,如果h[t]是目前最小的,那么栈内就是空哦。而在目前栈顶元素和h[t]之间(不包括h[t]和栈顶元素),都是大于他们两者的。如下图所示:
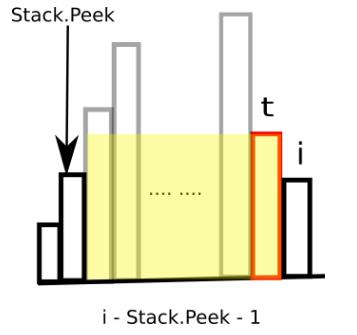

class Solution { public: int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& height) { if(height.size() == 0){ return 0; } int Max = 0; stack<int> s; vector<int> heights{height}; heights.push_back(0); for(int i = 0;i < heights.size();++i){ while(!s.empty() && heights[i] < heights[s.top()]){ int h = heights[s.top()]; s.pop();//栈中存储的都是比目前索引小的元素 int w = s.empty() ? i : (i - s.top() - 1); Max = max(Max,h * w); } s.push(i); } return Max; } };
2.5 max tree(这题不是leetcode上的题目)
题目描述:
Given an integer array with no duplicates. A max tree building on this array is defined as follow: - The root is the maximum number in the array. - The left subtree and right subtree are the max trees of the subarray divided by the root number. - Construct the max tree by the given array. Example Given [2, 5, 6, 0, 3, 1], the max tree constructed by this array is: 6 / \\ 5 3 / / \\ 2 0 1 Challenge O(n) time and memory.
思路:使用一个栈,下一个压栈元素比栈顶元素大的时候,就将栈顶元素置为当前元素的左孩子,如果当前节点小于栈顶元素,那么就将当前节点置为栈顶元素的右孩子。
解题思路
如果是自顶向下,按照 Max Tree 的定义构造,那么时间复杂度至少是 O(nlogn) 。查找最大值的时间复杂度是 O(n) ,如果最大值刚好可以将数组分为两部分,那么复杂度递归关系如下 T(n) = 2 * T(n / 2) + O(n) 。最坏的情况是数组是降序/升序,时间复杂度为 O(n^2) 。
考虑自底向上的方法。对一个数,考察其父亲结点是谁,它是左儿子还是右儿子。对于数 i,寻找左边第一个比它大的数 x ,和右边第一个比它大的数 y ,如果 x > y 那么 i 是 y 的左儿子,否则是 i是 x 的右儿子。可以用反证法证明。
具体实现使用一个降序栈。
- 将数组按从左到右顺序迭代,当处理一个新的结点
curt时,所有在栈中的结点全部都在其左边,因此需要判断curt和栈中结点的关系( 是curt的左儿子或者左父亲)。 - 当栈顶结点值大于当前结点值时,将当前结点设为栈顶结点的右儿子,进栈;当栈顶结点值小于当前结点值时,出栈,将其设置为当前结点的左儿子。
- 重复以上步骤,并返回栈底元素,即为最大数(根结点)。

struct TreeNode{ int val; TreeNode* left; TreeNode* right; TreeNode(int x):val(x),left(NULL),right(NULL){} }; class solution{ public: TreeNode* maxTree(vector<int> A){ if(A.size() == 0){ return NULL; } stack<TreeNode*> s; for(int i = 0;i < A.size();++i){ TreeNode* curN = new TreeNode(A[i]); while(!s.empty() && curN -> val > s.top() -> val){ curN -> left = s.top(); s.pop(); } if(!s.empty()){ stack.top() -> right = curN; } s.push(curN); } int len = s.size(); while(len > 1){ s.pop(); --len; } return s.top(); } };
2.6 rehashing重哈希
http://www.lintcode.com/zh-cn/problem/rehashing/
思路:思路其实很简单,就是按照链表法,每个原数组中的元素按照哈希函数进行计算,压入到新的vector中,如果有冲突,就用一个链表组成单链表,使用链表的插入操作即可。
注意每次取出来的元素可能是一个链表,所以取出元素后,需要循环遍历,直到该元素为空为止。
主要是这题目的细节:
1)对比前面拷贝带有随机指针链表,克隆图这两道题,只要是这种有指针的,必须要new一个原来的对象,不然指针指向的还是原来的节点,就不是复制得到一个新节点了;
2)刚开始的时候我没有新建一个变量,使用的是result[idx],这样结果是错的,记住数组中存的是每个单链表的表头,result[idx]是一个指针,如果不新建变量,那么随着while操作,就会指向最后一个元素,为node前面一个元素。所以这里必须新建dummy,dummy是对原数组指针的拷贝,原数组的指针仍然指向原区域。
3)数组初始化为空可以直接全为NULL。
4)新建new的时候,直接赋整数值即可,至于next的操作,后面else会进行处理。
ListNode* dummy = result[idx]; //这里必须要使用一个dummy,因为数组中的元素必须是链表的索引 while( dummy -> next != NULL){ dummy = dummy -> next; } dummy -> next = new ListNode(node -> val);

/** * Definition of ListNode * class ListNode { * public: * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int val) { * this->val = val; * this->next = NULL; * } * } */ class Solution { public: /** * @param hashTable: A list of The first node of linked list * @return: A list of The first node of linked list which have twice size */ int hashcode(int key, int capacity) { if(key < 0){ return (key % capacity + capacity ) % capacity; } return key % capacity; } vector<ListNode*> rehashing(vector<ListNode*> hashTable) { // write your code here if(hashTable.size() == 0){ return {}; } int size = 2 * hashTable.size(); vector<ListNode*> result(size,NULL); for(auto node : hashTable){ if(node == NULL){ continue; } while(node != NULL){ int key = node -> val; int capacity = size; int idx = hashcode(key,capacity); // ListNode* dummy = ; if(result[idx] == NULL){ result[idx] = new ListNode(node -> val); } else{ ListNode* dummy = result[idx]; //这里必须要使用一个dummy,因为数组中的元素必须是链表的索引 while( dummy -> next != NULL){ dummy = dummy -> next; } dummy -> next = new ListNode(node -> val); } node = node -> next; } } return result; } };
2.7 LRU Cache
https://leetcode.com/problems/lru-cache/#/description
思路:
1)题目需要LRU的意思是最近使用的,本题需要自己定义一个数据类型node,可以使用class,也可以使用struct,class里面记得加上public。定义构造函数。
