CentOS6和CentOS7区别
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了CentOS6和CentOS7区别相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
区别1:网卡名称eth0和enp5s0
传统上,Linux的网络接口名称为eth0、eth1…,但这些名称并不一定符合实际的硬件插槽等,这可
能会导致不同的网络配置错误(例如,由无意的接口改名引起的禁止接口)。基于MAC地址的udev规
则在虚拟化的环境中并不有用,这里的MAC地址如端口数量一样无常。
CentOS6/RHEL6引入了一致和可预测的网络设备命名网络接口的方法。这些特性可以唯一地确定网络
接口的名称以使定位和区分设备更容易,并且在这样一种方式下,无论是否重启机器、过了多少时间、
或者改变硬件,其名字都是持久不变的。然而,这种命名规则并不是默认在CentOS/RHEL6上开启。
从CentOS7/RHEL7起,这种可预见的命名规则变成了默认。根据这一规则,接口名称被自动基于固件,
拓扑结构和位置信息来确定。现在,即使添加或移除网络设备,接口名称仍然保持固定,而无需重新
枚举,和坏掉的硬件可以无缝替换。
区别2:网络配置相关命令
ip:yum -y install iproute
CentOS7主推使用ip、ss命令。
ifconfig:yum -y install net-tools
setup:yum -y install setuptool 废弃命令
安装好之后,你会发现里面什么都没有,这只是一个图形工具。我们需要
用到的网络服务,防火墙,系统服务等需要另外再安装。
安装好setup tools工具之后,我们需要安装工具组件如ntsysv(系统服
务),system-config-networktui(网络服务),iptables(防火墙配置)
等。只需要部分的也可以只安装需要的也行。
nmtui:替代setup命令
区别3:主机名等配置文件
修改主机名
hostname CentOS7 临时生效
编辑/etc/hostname 主机名的配置文件变了
hostnamectl set-hostname CentOS7 #→方法2,本质还是改配置文件。
修改字符集
localectl set-locale. UTF-8
编辑/etc/locale.conf
cat /etc/redhat-release 查看系统版本号
cat /etc/os-release 所有支持systemd系统的统一发行版名称和版本号文件。
区别4:兼容的 /etc/rc.local
# Please note that you must run ‘chmod +x/etc/rc.d/rc.local‘ to ensure
# that this script will be executed duringboot.
区别5:运行级别Runlevel
Runlevel
[[email protected] ~]# cat /etc/inittab
# inittab is no longer used when usingsystemd.
当前启动级别
[[email protected] ~]# systemctl get-default
multi-user.target
设置启动级别
systemctl set-default multi-user.target
systemd一统天下
看看从前的runlevel都变成什么样了?
ls -lh/usr/lib/systemd/system/runlevel*.target
所有可用的单元文件存放在/usr/lib/systemd/system/和
/etc/systemd/system/目录(后者优先级更高)。
ll -h /etc/systemd/system/default.target
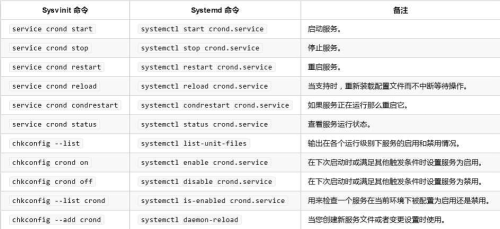
区别6:管理服务
chkconfig
service
/etc/init.d/
systemctl:融合service和chkconfig的功能于一体,兼容SysV和LSB的启动脚
本,而且够在进程启动过程中更有效地引导加载服务。。
systemctl start crond.service和systemctlstart crond效果一样。
启动时间优化
systemd-analyze time
systemd-analyze blame
systemd-analyze plot > bootime.svg
本文出自 “李松阳” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://lsy666.blog.51cto.com/11729318/1945918
以上是关于CentOS6和CentOS7区别的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章