【豆科基因组】大豆适应性位点GWAS分析[转载]
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了【豆科基因组】大豆适应性位点GWAS分析[转载]相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A本文利用99085个高质量SNP 通过STRUCTURE,PCA和neighbour-joining tree的群体结构分析将地方品种分为三个亚群,这些亚群表现出地理上的遗传分化。利用纬度相差10°的两个位置(北京、武汉)收集的表型数据,鉴定了17个与开花时间性状相关的SNP(TAS),包括一个稳定的基因位点Chr12:5914898和以前未检测到的在开花基因E1和E2附近的候选基因。利用与地方种收集地点相关的已公布数据,鉴定出与三个生物气候学变量(温度,日长和降水)相关的27个SNP。在12个生物气候TASs的连锁不平衡(LD)区域内检测到一系列候选开花基因。其中9个TASs在开花时间上表现出显著差异。在44个开花和生物气候TASs中,有38个检测到了驯化、地方品种多样化和适应过程中的选择信号。
测序材料 :2368个种质材料,包括112个野生种(选自中韩俄日,代表广泛的生态地理范围),和2256个地方种(可代表核心种质的表型多样性和地理分布的中国主要的地方种)
测序平台: Life Technologies’ Ion Proton Systems
数据量: 0.75T
筛选后的97个野生种和1938个地方品种(地方种据其地理分布及种植季节类型分为7类);414个核心地方种质
开花时间表型鉴定材料: 2256个地方种,分别种于7月武汉(30.5°N, 114.3°E)、6月北京(40.1°N, 116.7°E),各两次重复;414份核心种质种于广西(2009-2011年)的南宁(7月中),北京(2011-2012)的昌平(5月初,春季型)、顺义(6月末,夏季型),三年2~3次重复。
地理和气候变量: 利用已知数据获得不同品种的经纬度及海拔的坐标,利用坐标在生物气候网站BioClim ( http://www.worldclim.org/bioclim,version 1.4)查询其对应的生物气候变量:年温度变化范围(TAR)及年降水量(AP),最大日光长度(MDL)的计量以表型鉴定为准。
群体结构分析方法 :
群体结构:软件STRUCTURE
Neighbor-joining tree:APE(V3.2)
PCA:PLINK(V1.9)
Qst-Fst比较:Pstat (V1.2)
LD:PLINK (V1.9)
参考基因组:*Glycine max *Wm82.a2.v1
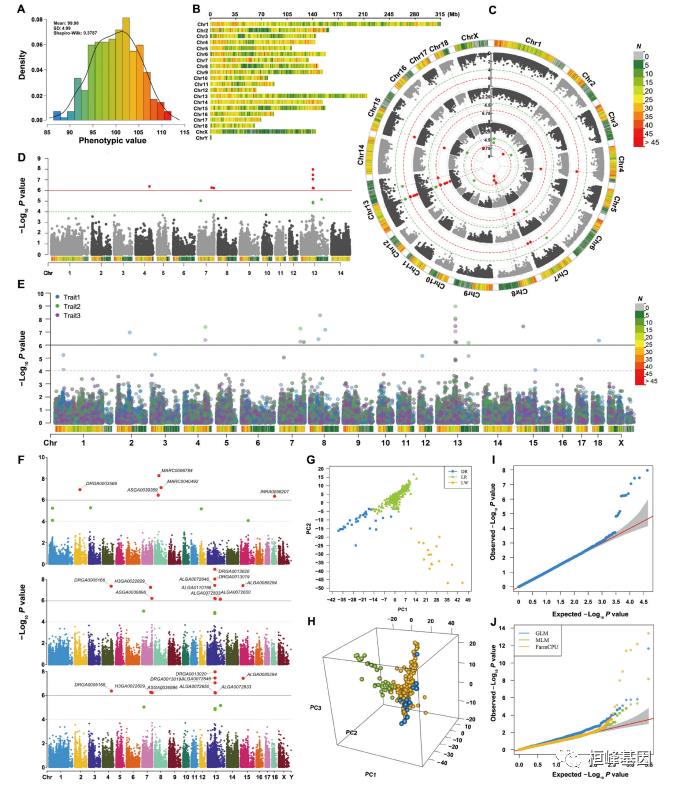
图1 不同基因型种质的地理分布和大豆基因组的特性。
A:7种生态型:东北春季型(NESp),北方春季型(NSp),黄淮春季型(HSp),黄淮夏季型(HSu),南方春季型(SSp),南方夏季型(SSu) )和南方秋季型(SAu)。
B:20条大豆染色体上共获得99085个SNP。最外圈:大豆20条染色体,灰色为染色体杂合区域,黑色为染色体臂。a:基因密度 b:SNP密度 c-f依次为:野生种、SR、HR、NR的遗传多样性。
多态性、群体结构和多样性
对2035个种质材料进行群体结构分析,共鉴定出1类野生型(wild),三类地方种的亚群(北方种NR,黄淮种HR,南方种SR),和一类混合基因组种质(mixed)。对群体分化程度的鉴定表明,虽然地方种比野生种的数量大20倍,但地方种仍比野生种存在更多的LD(图2D), SNPs更少,多样性也更少(表S5)。选择性清除分析(Fst)的比较结果表明HR和SR之间遗传分化程度最大(0.164),其次是NR与SR(0.136),NR与HR之间差异最小(0.077)。
图2群体结构和连锁不平衡分析
A:样本按生态类型和采集地点的纬度排列
B:对1938个地方种和97个野生种的群体结构分析(K=4)
C:根据99085个SNPs对2035个种质的PCA分析
D:LD衰减距离,landrace代表混合地方种
生物气候变量和开花时间的变化
不同地理位置上开花时间与生物气候变量呈现显著的相关性(图S4),两个地方的每个种质的开花时间也显著相关(图S5)。这些结果表明,虽然可以根据环境因素(不同地点)推测其开花时间,但是同一地点的不同品种间开花时间应主要受遗传因素控制。
图s4 北京和武汉不同气候变量与开花时间的相关性比较
图s5 北京和武汉三个大豆地方种群开花时间的变化
开花时间的GWAS分析
利用GWAS鉴定与开花时间相关的基因,共关联到18个相关位点,代表17个TASs,同时在武汉和北京的Chr12:5914898位置关联到同一个位点。对414份核心种质材料在其余三个地点的GWAS分析,进一步验证了该结果。
图3 地方种开花时间性状相关位点(TASs)的鉴定分析
ABEFG:五个地点开花时间的GWAS分析的曼哈顿图,北京、武汉所用材料为1938个地方种,昌平、顺义、南宁三个地点所用材料为414个核心种质。
灰色水平线表示1%阈值线
红色垂直线表示两个克隆的开花时间基因 E1 、 E2 的基因组位置。
CDHIJ:每个地方种携带早开花位点的TASs数量与开花时间的相关性
生物气候因素的GWAS分析
文中利用GWAS分析鉴定了与三个生物气候变量(温度/TAR,日长/MDL,降水/AP)的适应性相关的基因座,共鉴定到29个显著关联位点,对应27个独特的TASs(图S9)。其中两个SNPs(Chr02:6487107和Chr15:23361474)均分别与MDL和TAR相关。
图s9 大豆地方种与生物气候因素相关的GWAS分析
大豆驯化过程中选择信号的检测以及适应过程中地方品种的多样化
研究比较了地方种和野生种之间的Fst和等位基因频率比较,评估了这些生物气候TASs和开花时间的遗传分化间的关系。17个开花时间TASs和27个生物气候TASs的大部分均在驯化过程中存在强选择。在44个TASs中,有11个同时在驯化、地方种多样化和适应性中经历了选择,有3个仅在驯化过程中经历了选择,24个仅在地方种多样化和适应性中经历了选择,有6个没有表现出被选择。这些分析结果说明了自然和人工选择对特定环境适应性的作用及生物气候变量对大豆地方种之间遗传变异模式的影响。
开花候选基因/QTL的鉴定
E1 、 E2 基因是已知影响开花的基因。文中鉴定到的三个TASs(Chr06:19873100,Chr06:20003061和Chr06:20355903)位于Chr06上 E1 基因附近,且对开花时间的影响不同,在不同的地区表现出不同的表型变异,其地理分布也表现出不同的模式。说明在 E1 附近可能存在一个或多个以前未检测到的开花时间相关基因。
在E2基因附近检测到两个强关联位点Chr10:45520960和Chr10:45521328,通过对携带不同基因型的不同亚群之间表型鉴定,检测到开花时间的显著差异,表明 Glyma.10G224500 是开花时间的相关候选基因。
利用北京和武汉两地点的实测开花时间数据,通过GWAS鉴定了第12号染色体上的两个开花时间TASs(Chr12:5470311和Chr12:5914898)。Chr12:5470311位点与拟南芥开花基因同源且与一开花时间相关TAS连锁;Chr12:5914898位于编码Cyclic Nucleotide-gated Ion Channel 15-Related蛋白的基因 Glyma.12G076800 的内含子上;经表型(图4C,D)及Fst和等位基因频率分析鉴定(图4E)表明两位点均参与了开花时间的调控。
图4 开花时间位点Chr12:5470311和Chr12:5914898的鉴定
绘图之全基因组关联分析可视化(GWAS)
点击关注,桓峰基因
桓峰基因
生物信息分析,SCI文章撰写及生物信息基础知识学习:R语言学习,perl基础编程,linux系统命令,Python遇见更好的你
134篇原创内容
公众号
桓峰基因公众号推出基于基因组数据生信分析教程并配有视频在线教程,目前整理出来的教程目录如下:
DNA 1. Germline Mutation Vs. Somatic Mutation 傻傻分不清楚
DNA 2. SCI 文章中基因组变异分析神器之 maftools
DNA 3. SCI 文章中基因组变异分析神器之 maftools
DNA 4. SCI 文章中基因组的突变信号(maftools)
DNA 5. 基因组变异文件VCF格式详解
DNA 6. 基因组变异之绘制精美瀑布图(ComplexHeatmap)
DNA 7. 基因组拷贝数变异分析及可视化 (GISTIC2.0)
DNA 8. 癌症的突变异质性及寻找新的癌症驱动基因(MutSigCV)
DNA 9. 揭秘肿瘤异质性与TMB, MSI之间的相关性
DNA 10. 识别癌症驱动基因 (OncodriveCLUST)
DNA 11. 识别肿瘤蛋白质三维结构上突变热点(HotSpot3D)
DNA 12. SCI 文章绘图之全基因组关联分析可视化(GWAS)
这期介绍一下GWAS分析的可视化软件包CMplot,对于研究SNP全体分析,家系遗传等方向的非常实用,给自己的文章添点色彩感。

我们来看看这个软件包能做的事情,GWAS可视化算是很OK了,记得这方面的分析可以考虑使用了!
前言
全基因组关联分析(GWAS)是在某一特定人群中研究遗传突变和表型之间的相关性。GWAS的理论基础是连锁不平衡定律(linkage disequilibrium,LD),既假设观察到的SNP与真正的致病突变(causal variant)之间存在很强的LD全基因组关联分析(Genome wide association study,GWAS)是对多个个体在全基因组范围的遗传变异(标记)多态性进行检测,获得基因型,进而将基因型与可观测的性状,即表型,进行群体水平的统计学分析,根据统计量或显著性 p 值筛选出最有可能影响该性状的遗传变异(标记),挖掘与性状变异相关的基因。因此,GWAS分析需要准备的文件主要有:基因型数据和表型数据。
表型数据统计分析方法包括:
-
逻辑回归(表型数据为二元)
-
线性回归(表型数据为连续性变量)
-
表型数据正态分析(如果不是正态分布,需转换处理为正态分布)
-
表型数据均值、中值、最大值、最小值
-
影响因子对表型的影响分析
基因型数据一般是测序下机数据经SNP calling、基因型填补等后拿到的.vcf文件,后续根据研究者的要求和条件进行质控(Quality control),群体结构分层及亲缘关系/PCA等处理。
软件安装
我们使用CMplot软件包来实现GWAS绘制Manhattan图
if (!require(CMplot)) install.packages("CMplot")
library("CMplot")
参数说明
这个CMplot函数的参数还是蛮多的,毕竟是绘制这种复杂的图像,这也是避免不了的事情,我们大概解释一下参数。
Usage CMplot(Pmap, col=c(“#4197d8”, “#f8c120”, “#413496”, “#495226”, “#d60b6f”, “#e66519”, “#d581b7”, “#83d3ad”, “#7c162c”, “#26755d”), bin.size=1e6, bin.range=NULL, bin.legend.num=10, pch=19, type=“p”, band=1, H=1.5, ylim=NULL, cex.axis=1, lwd.axis=1.5, cex.lab=1.5, plot.type=“b”, multracks=FALSE, points.alpha=100L, cex=c(0.5,1,1), r=0.3, outward=FALSE, ylab=expression(-log[10](italic§)), ylab.pos=3, xticks.pos=1, mar = c(3,6,3,3), threshold = NULL, threshold.col=“red”, threshold.lwd=1, threshold.lty=2, amplify= TRUE, signal.cex = 1.5, signal.pch = 19, signal.col=NULL, signal.line=2, highlight=NULL, highlight.cex=1, highlight.pch=19, highlight.type=“p”, highlight.col=“red”, highlight.text=NULL, highlight.text.col=“black”, highlight.text.cex=1, highlight.text.xadj=NULL, highlight.text.yadj=NULL, highlight.text.font=3, chr.labels=NULL, chr.border=FALSE, chr.labels.angle=0, chr.den.col=“black”, chr.pos.max=FALSE, cir.band=1, cir.chr=TRUE, cir.chr.h=1.5, cir.legend=TRUE, cir.legend.cex=0.6, cir.legend.col=“black”, LOG10=TRUE, box=FALSE, conf.int=TRUE, conf.int.col=NULL, file.output=TRUE, file=c(“jpg”,“pdf”,“tiff”), dpi=300, height=NULL, width=NULL, memo=“”, main=“”, main.cex=1.5, main.font=2, trait.legend.ncol=NULL, verbose=TRUE)
参数细节如下:
Pmap 输入数据文件
col 设置颜色,可以是vector or matrix
当vector数量少于染色体数目时,循环利用;也可以对每一个性状的每一条染色体进行设置
bin.size 设置SNP密度图中的窗口大小
bin.max bin中SNP数量的阈值,当大于阈值时染色体bin颜色为同一颜色
cex 设置绘制点的大小
pch 设置绘制点的形状,同plot中的"pch"
band 设置染色体之间的间隔,当为0时染色体间无空隙,默认为1
cir.band 设置不同circle的空隙,默认为1
H 性状circle的高度设置,默认1
ylim 设置y轴的范围同plot中的"ylim"
cex.axis 设置坐标轴字体和标签字体的大小
bin.size 设置SNP密度图中的窗口大小
cex.axis 设置坐标轴字体和标签字体的大小
plot.type 设置不同的绘图类型,可以设定为 “d”, “c”, “m”, “q” or “b”
“d” 表示 SNP density plot “c” 表示 circle-Manhattan plot
“m” 表示 Manhattan plot “q” 表示 Q-Q plot
“b” 表示 circle-Manhattan, Manhattan and Q-Q plots一起绘制
plot.type=c(“m”,“q”) 表示Manhattan plot和Q-Q plot一起绘制
multracks 设置是否需要绘制多个track
cex 绘制点的大小,可是为单个数值或向量(对应同一绘图中不同的plot)
r 设置圈的半径大小
xlab 设置x轴标签
ylab 设置y轴标签
outward 设置点的朝向是否向外
threshold 设置阈值并添加阈值线
threshold.col 设置阈值线的颜色
threshold.lwd 设置阈值线的宽度
threshold.lty 设置阈值线的类型
amplify 设置是否放大显著的点
chr.labels 设置染色体的标签
signal.cex 设置显著点的大小
signal.pch 设置显著点的形状
signal.col 设置显著点的颜色
singal.line 设置显著线的宽度
chr.den.col 设置SNP密度图的颜色
cir.band 设置环状曼哈顿图中不同染色体之间的间隔
cir.chr 设置是否显示染色体的边界
cir.chr.h 设置染色体边界的高度
chr.den.col SNP密度的颜色,可以为字符,向量或空
cir.legend 设置是否显示图例
cir.legend.cex 设置图例字体的大小
cir.legend.col 设置图例的颜色
LOG10 设置是否对p-value取log10对数
box 曼哈顿是否绘制方框
conf.int.col 设置QQ图中置信区间的颜色
file.output 设置是否输出图片
file 设置输出图片的格式,可以设定为"jpg", “pdf”, “tiff”
dpi 设置输出图片的分辨度
memo 设置输出图片文件的名字
数据读取
我们这里选择使用软件包自带的两个数据集,方便大家理解。
Genotyped by pig 60k chip Description This dataset gives the results of Genome-wide association study of 3 traits, individuals were genotyped by pig 60K chip. Format A dataframe containing 3 traits’ Pvalue
data(pig60K) #calculated p-values by MLM
head(pig60K)
## SNP Chromosome Position trait1 trait2 trait3
## 1 ALGA0000009 1 52297 0.7738187 0.51194318 0.51194318
## 2 ALGA0000014 1 79763 0.7738187 0.51194318 0.51194318
## 3 ALGA0000021 1 209568 0.7583016 0.98405289 0.98405289
## 4 ALGA0000022 1 292758 0.7200305 0.48887140 0.48887140
## 5 ALGA0000046 1 747831 0.9736840 0.22096836 0.22096836
## 6 ALGA0000047 1 761957 0.9174565 0.05753712 0.05753712
Genotyped by Bovine50K chip Description This dataset gives the effects of all SNPs using rrBLUP algorithm for 3 traits, individuals were genotyped by Bovine50K chip. Format A dataframe containing 3 traits’ SNPs effects
data(cattle50K) #calculated SNP effects by rrblup
head(cattle50K)
## SNP chr pos Somatic cell score Milk yield Fat percentage
## 1 SNP1 1 59082 0.000244361 0.000484255 0.001379210
## 2 SNP2 1 118164 0.000532272 0.000039800 0.000598951
## 3 SNP3 1 177246 0.001633058 0.000311645 0.000279427
## 4 SNP4 1 236328 0.001412865 0.000909370 0.001040161
## 5 SNP5 1 295410 0.000090700 0.002202973 0.000351394
## 6 SNP6 1 354493 0.000110681 0.000342628 0.000105792
实例操作
这里的例子都是来之文档说明,我就当一次搬运工,有需要使用自己数据分析的,搞不定可以找桓峰基因,我们随时在线等!话不多说,上代码就可以了。
使用例子:https://github.com/YinLiLin/CMplot
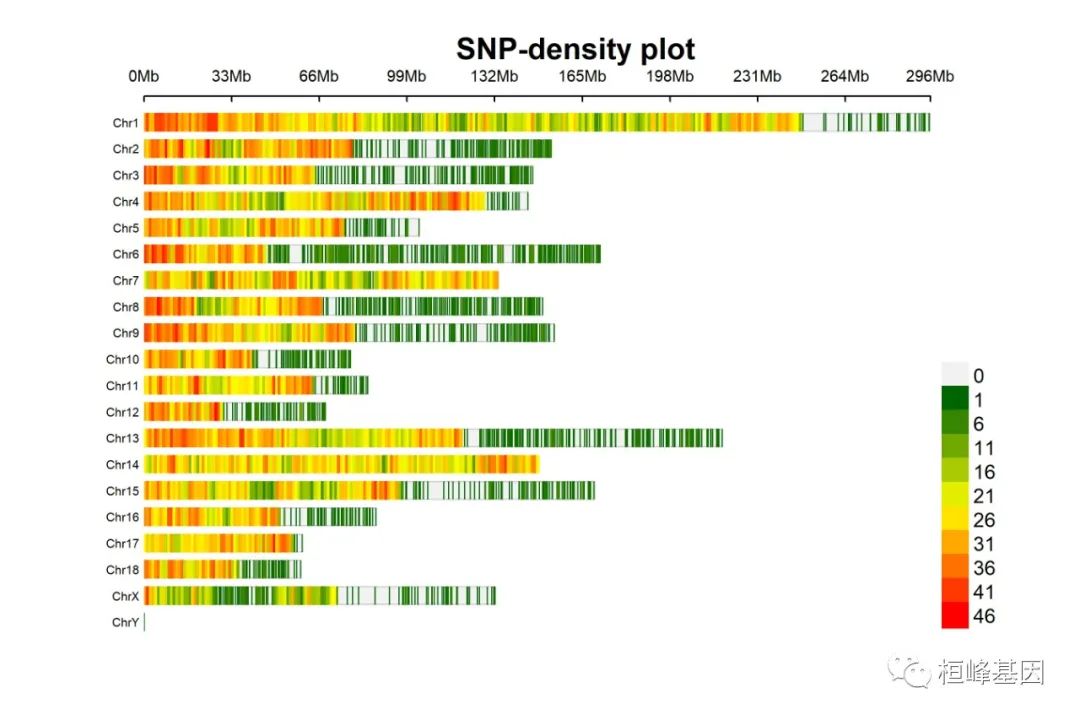
1. SNP-density plot
绘制SNP密度图
CMplot(pig60K, type = "p", plot.type = "d", bin.size = 1e+06, chr.den.col = c("darkgreen",
"yellow", "red"), file = "jpg", memo = "", dpi = 300, main = "SNP-density plot",
file.output = TRUE, verbose = TRUE, width = 9, height = 6)
## SNP-Density Plotting.
## Plots are stored in: F:/demo script/基因组分析系列/CMplot
2. Circular-Manhattan plot
绘制圆形Manhattan图
(1) Genome-wide association study(GWAS)
CMplot(pig60K, type = "p", plot.type = "c", chr.labels = paste("Chr", c(1:18, "X",
"Y"), sep = ""), r = 0.4, cir.legend = TRUE, outward = FALSE, cir.legend.col = "black",
cir.chr.h = 1.3, chr.den.col = "black", file = "jpg", memo = "", dpi = 300, file.output = TRUE,
verbose = TRUE, width = 10, height = 10)
## Circular-Manhattan Plotting trait1.
## Circular-Manhattan Plotting trait2.
## Circular-Manhattan Plotting trait3.
## Plots are stored in: F:/demo script/基因组分析系列/CMplot

添加色带的Manhattan图
CMplot(pig60K, type = "p", plot.type = "c", r = 0.4, col = c("grey30", "grey60"),
chr.labels = paste("Chr", c(1:18, "X", "Y"), sep = ""), threshold = c(1e-06,
1e-04), cir.chr.h = 1.5, amplify = TRUE, threshold.lty = c(1, 2), threshold.col = c("red",
"blue"), signal.line = 1, signal.col = c("red", "green"), chr.den.col = c("darkgreen",
"yellow", "red"), bin.size = 1e+06, outward = FALSE, file = "jpg", memo = "",
dpi = 300, file.output = TRUE, verbose = TRUE, width = 10, height = 10)
## Circular-Manhattan Plotting trait1.
## Circular-Manhattan Plotting trait2.
## Circular-Manhattan Plotting trait3.
## Plots are stored in: F:/demo script/基因组分析系列/CMplot

(2) Genomic Selection/Prediction(GS/GP)
基因组选择或者预测
CMplot(cattle50K, type = "p", plot.type = "c", LOG10 = FALSE, outward = TRUE, col = matrix(c("#4DAF4A",
NA, NA, "dodgerblue4", "deepskyblue", NA, "dodgerblue1", "olivedrab3", "darkgoldenrod1"),
nrow = 3, byrow = TRUE), chr.labels = paste("Chr", c(1:29), sep = ""), threshold = NULL,
r = 1.2, cir.chr.h = 1.5, cir.legend.cex = 0.5, cir.band = 1, file = "jpg", memo = "",
dpi = 300, chr.den.col = "black", file.output = TRUE, verbose = TRUE, width = 10,
height = 10)
## Circular-Manhattan Plotting Somatic cell score.
## Circular-Manhattan Plotting Milk yield.
## Circular-Manhattan Plotting Fat percentage.
## Plots are stored in: F:/demo script/基因组分析系列/CMplot

3. Single_track Rectangular-Manhattan plot
1. Genome-wide association study(GWAS)
CMplot(pig60K, type = "p", plot.type = "m", LOG10 = TRUE, threshold = NULL, file = "jpg",
memo = "", dpi = 300, file.output = TRUE, verbose = TRUE, width = 14, height = 6,
chr.labels.angle = 45)
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting trait1.
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting trait2.
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting trait3.
## Plots are stored in: F:/demo script/基因组分析系列/CMplot


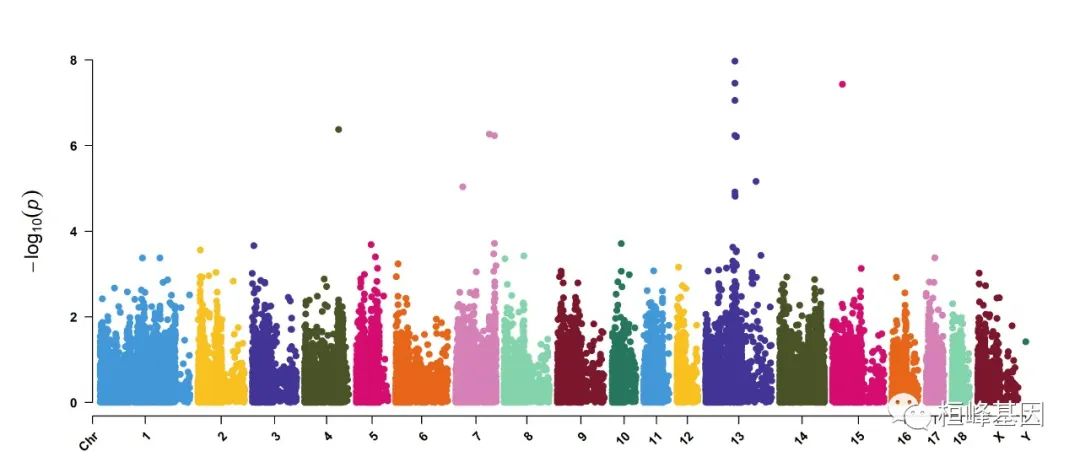
2. Amplify signals on pch, cex and col
CMplot(pig60K, plot.type="m", col=c("grey30","grey60"), LOG10=TRUE, ylim=c(2,12), threshold=c(1e-6,1e-4),
threshold.lty=c(1,2), threshold.lwd=c(1,1), threshold.col=c("black","grey"), amplify=TRUE,
chr.den.col=NULL, signal.col=c("red","green"), signal.cex=c(1.5,1.5),signal.pch=c(19,19),
file="jpg",memo="",dpi=300,file.output=TRUE,verbose=TRUE,width=14,height=6)
3. Attach chromosome density on the bottom of Manhattan plot
CMplot(pig60K, plot.type = "m", LOG10 = TRUE, ylim = NULL, threshold = c(1e-06, 1e-04),
threshold.lty = c(1, 2), threshold.lwd = c(1, 1), threshold.col = c("black",
"grey"), amplify = TRUE, bin.size = 1e+06, chr.den.col = c("darkgreen", "yellow",
"red"), signal.col = c("red", "green"), signal.cex = c(1.5, 1.5), signal.pch = c(19,
19), file = "jpg", memo = "", dpi = 300, file.output = TRUE, verbose = TRUE,
width = 14, height = 6)
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting trait1.
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting trait2.
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting trait3.
## Plots are stored in: F:/demo script/基因组分析系列/CMplot



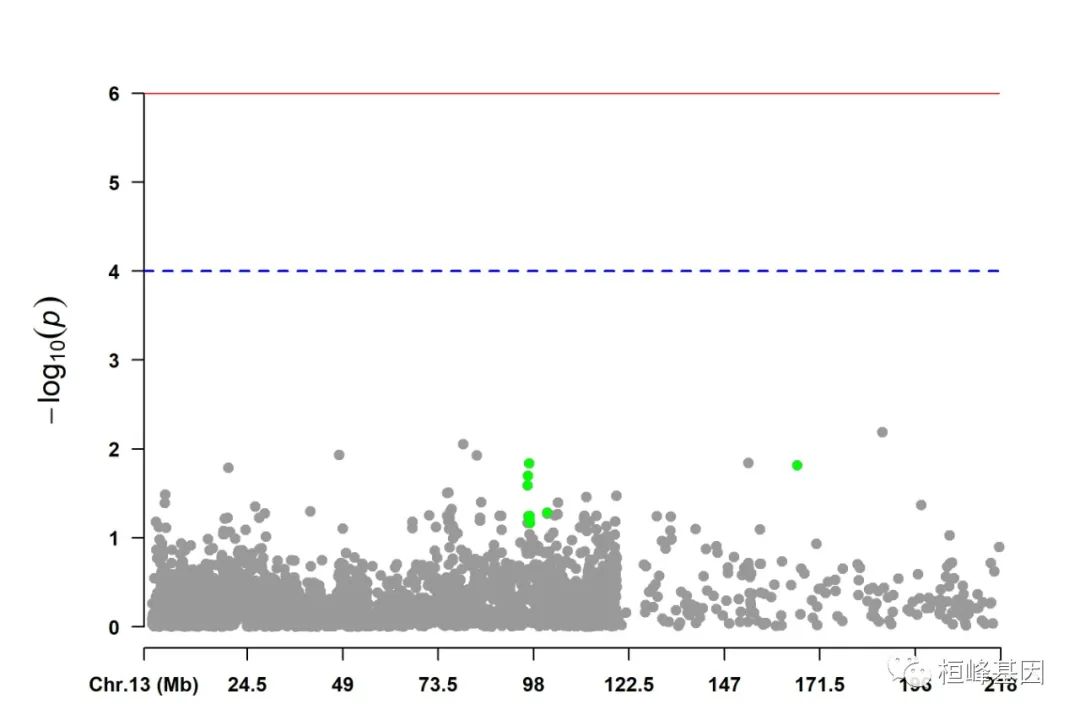
4. Highlight a group of SNPs on pch, cex, type, and col
signal <- pig60K$Position[which.min(pig60K$trait2)]
SNPs <- pig60K$SNP[pig60K$Chromosome == 13 & pig60K$Position < (signal + 1e+06) &
pig60K$Position > (signal - 1e+06)]
CMplot(pig60K, plot.type = "m", LOG10 = TRUE, col = c("grey30", "grey60"), highlight = SNPs,
highlight.col = "green", highlight.cex = 1, highlight.pch = 19, file = "jpg",
memo = "", chr.border = TRUE, dpi = 300, file.output = TRUE, verbose = TRUE,
width = 14, height = 6)
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting trait1.
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting trait2.
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting trait3.
## Plots are stored in: F:/demo script/基因组分析系列/CMplo
SNPs <- pig60K[pig60K$trait2 < 1e-04, 1]
CMplot(pig60K, type = "h", plot.type = "m", LOG10 = TRUE, highlight = SNPs, highlight.type = "p",
highlight.col = NULL, highlight.cex = 1.2, highlight.pch = 19, file = "jpg",
memo = "", dpi = 300, file.output = TRUE, verbose = TRUE, width = 14, height = 6,
band = 0.6)
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting trait1.
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting trait2.
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting trait3.
## Plots are stored in: F:/demo script/基因组分析系列/CMplot
SNPs <- pig60K[pig60K$trait2 < 1e-04, 1]
CMplot(pig60K, type = "p", plot.type = "m", LOG10 = TRUE, highlight = SNPs, highlight.type = "h",
col = c("grey30", "grey60"), highlight.col = "darkgreen", highlight.cex = 1.2,
highlight.pch = 19, file = "jpg", dpi = 300, file.output = TRUE, verbose = TRUE,
width = 14, height = 6)
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting trait1.
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting trait2.
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting trait3.
## Plots are stored in: F:/demo script/基因组分析系列/CMplot
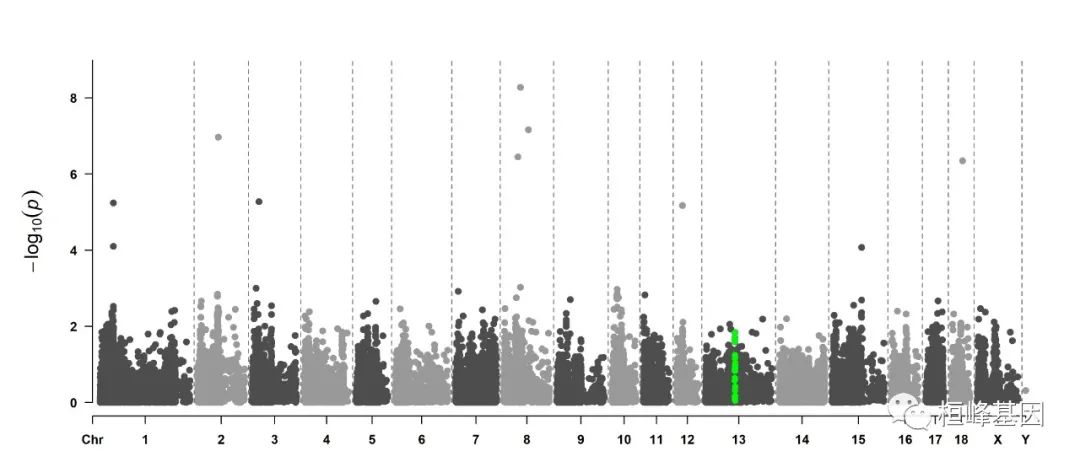
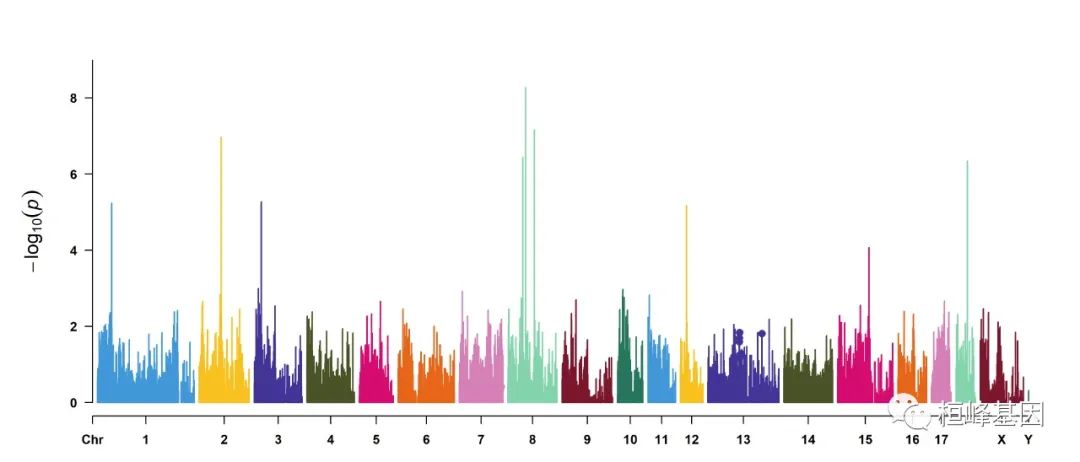
5. Visualize only one chromosome
CMplot(pig60K[pig60K$Chromosome == 13, ], plot.type = "m", LOG10 = TRUE, col = c("grey60"),
highlight = SNPs, highlight.col = "green", highlight.cex = 1, highlight.pch = 19,
file = "jpg", memo = "", threshold = c(1e-06, 1e-04), threshold.lty = c(1, 2),
threshold.lwd = c(1, 2), width = 9, height = 6, threshold.col = c("red", "blue"),
amplify = FALSE, dpi = 300, file.output = TRUE, verbose = TRUE)
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting trait1.
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting trait2.
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting trait3.
## Plots are stored in: F:/demo script/基因组分析系列/CMplot
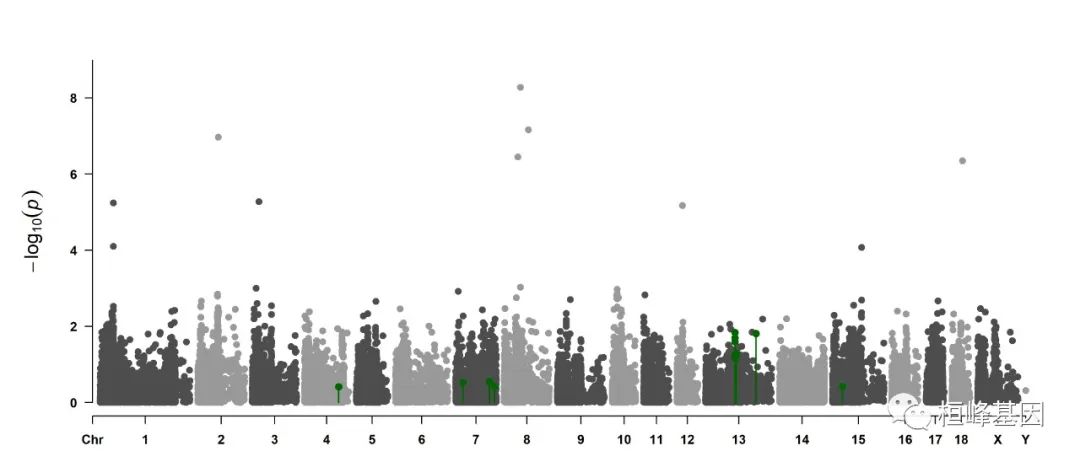
6. add genes or SNP names around the highlighted SNPs
SNPs <- pig60K[pig60K[, 5] < (0.05/nrow(pig60K)), 1]
genes <- paste("GENE", 1:length(SNPs), sep = "_")
set.seed(666666)
CMplot(pig60K[, c(1:3, 5)], plot.type = "m", LOG10 = TRUE, col = c("grey30", "grey60"),
highlight = SNPs, highlight.col = c("red", "blue", "green"), highlight.cex = 1,
highlight.pch = c(15:17), highlight.text = genes, highlight.text.col = c("red",
"blue", "green"), threshold = 0.05/nrow(pig60K), threshold.lty = 2, amplify = FALSE,
file = "jpg", memo = "", dpi = 300, file.output = TRUE, verbose = TRUE, width = 14,
height = 6)
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting trait2.
## Plots are stored in: F:/demo script/基因组分析系列/CMplot

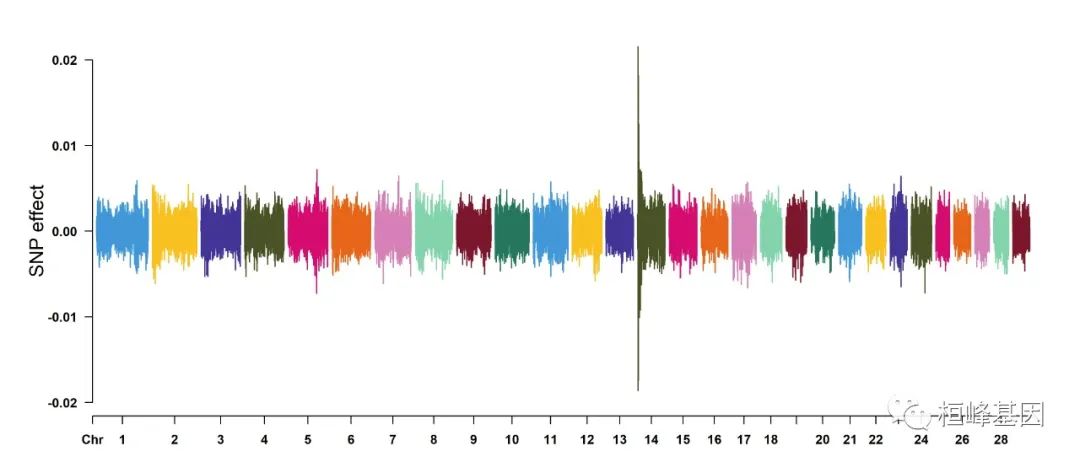
7. Genomic Selection/Prediction(GS/GP) or other none p-values
CMplot(cattle50K, plot.type = "m", band = 0.5, LOG10 = FALSE, ylab = "SNP effect",
threshold = 0.015, threshold.lty = 2, threshold.lwd = 1, threshold.col = "red",
amplify = TRUE, width = 14, height = 6, signal.col = NULL, chr.den.col = NULL,
file = "jpg", memo = "", dpi = 300, file.output = TRUE, verbose = TRUE, cex = 0.8)
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting Somatic cell score.
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting Milk yield.
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting Fat percentage.
## Plots are stored in: F:/demo script/基因组分析系列/CMplot
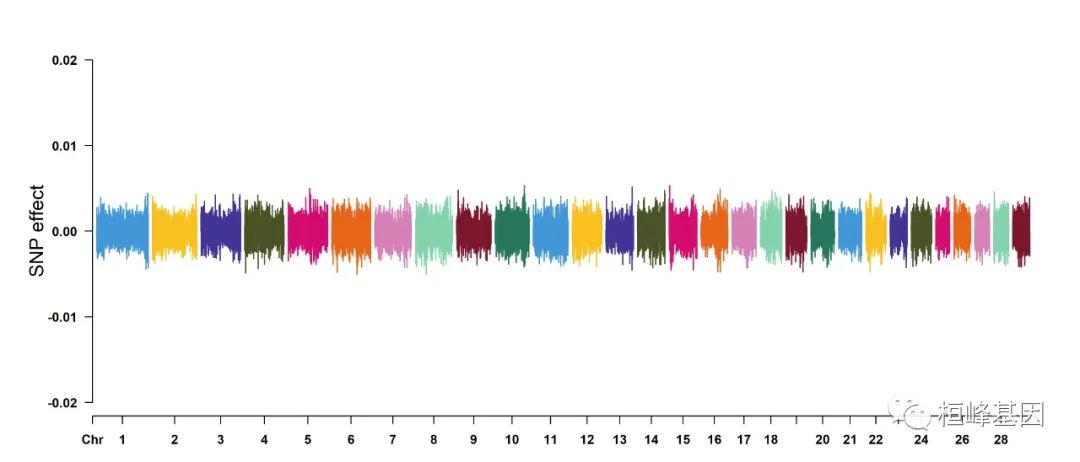
cattle50K[, 4:ncol(cattle50K)] <- apply(cattle50K[, 4:ncol(cattle50K)], 2, function(x) x *
sample(c(1, -1), length(x), rep = TRUE))
CMplot(cattle50K, type = "h", plot.type = "m", band = 0.5, LOG10 = FALSE, ylab = "SNP effect",
ylim = c(-0.02, 0.02), threshold.lty = 2, threshold.lwd = 1, threshold.col = "red",
amplify = FALSE, cex = 0.6, chr.den.col = NULL, file = "jpg", memo = "", dpi = 300,
file.output = TRUE, verbose = TRUE)
## (warning: all phenotypes will use the same ylim.)
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting Somatic cell score.
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting Milk yield.
## Rectangular-Manhattan Plotting Fat percentage.
## Plots are stored in: F:/demo script/基因组分析系列/CMplot


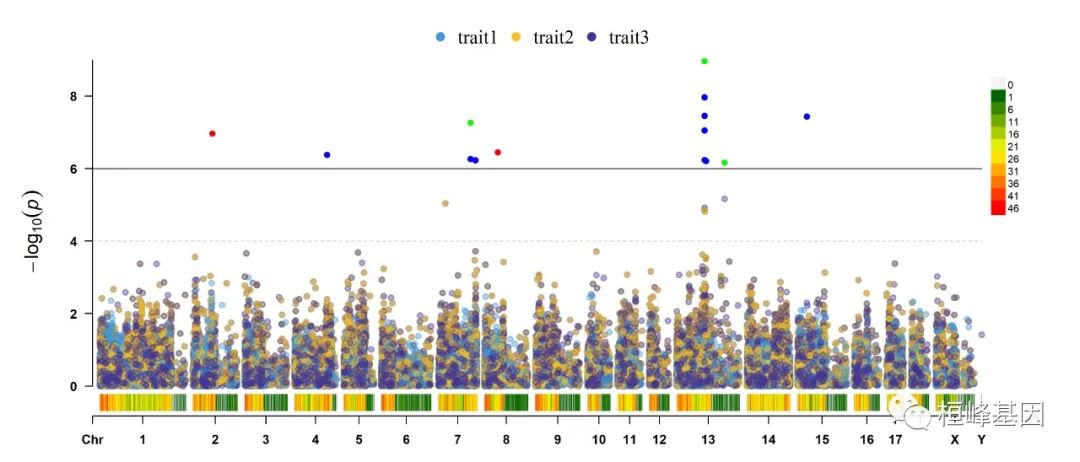
4. Multi_tracks Rectangular-Manhattan plot
SNPs <- list(pig60K$SNP[pig60K$trait1 < 1e-06], pig60K$SNP[pig60K$trait2 < 1e-06],
pig60K$SNP[pig60K$trait3 < 1e-06])
CMplot(pig60K, plot.type = "m", multracks = TRUE, threshold = c(1e-06, 1e-04), threshold.lty = c(1,
2), threshold.lwd = c(1, 1), threshold.col = c("black", "grey"), amplify = TRUE,
bin.size = 1e+06, chr.den.col = c("darkgreen", "yellow", "red"), signal.col = c("red",
"green", "blue"), signal.cex = 1, file = "jpg", memo = "", dpi = 300, file.output = TRUE,
verbose = TRUE, highlight = SNPs, highlight.text = SNPs, highlight.text.cex = 1.4)
## Multracks-Manhattan Plotting trait1.
## Multracks-Manhattan Plotting trait2.
## Multracks-Manhattan Plotting trait3.
## Multraits-Rectangular Plotting...(finished 13%)
## Plots are stored in: F:/demo script/基因组分析系列/CMplot
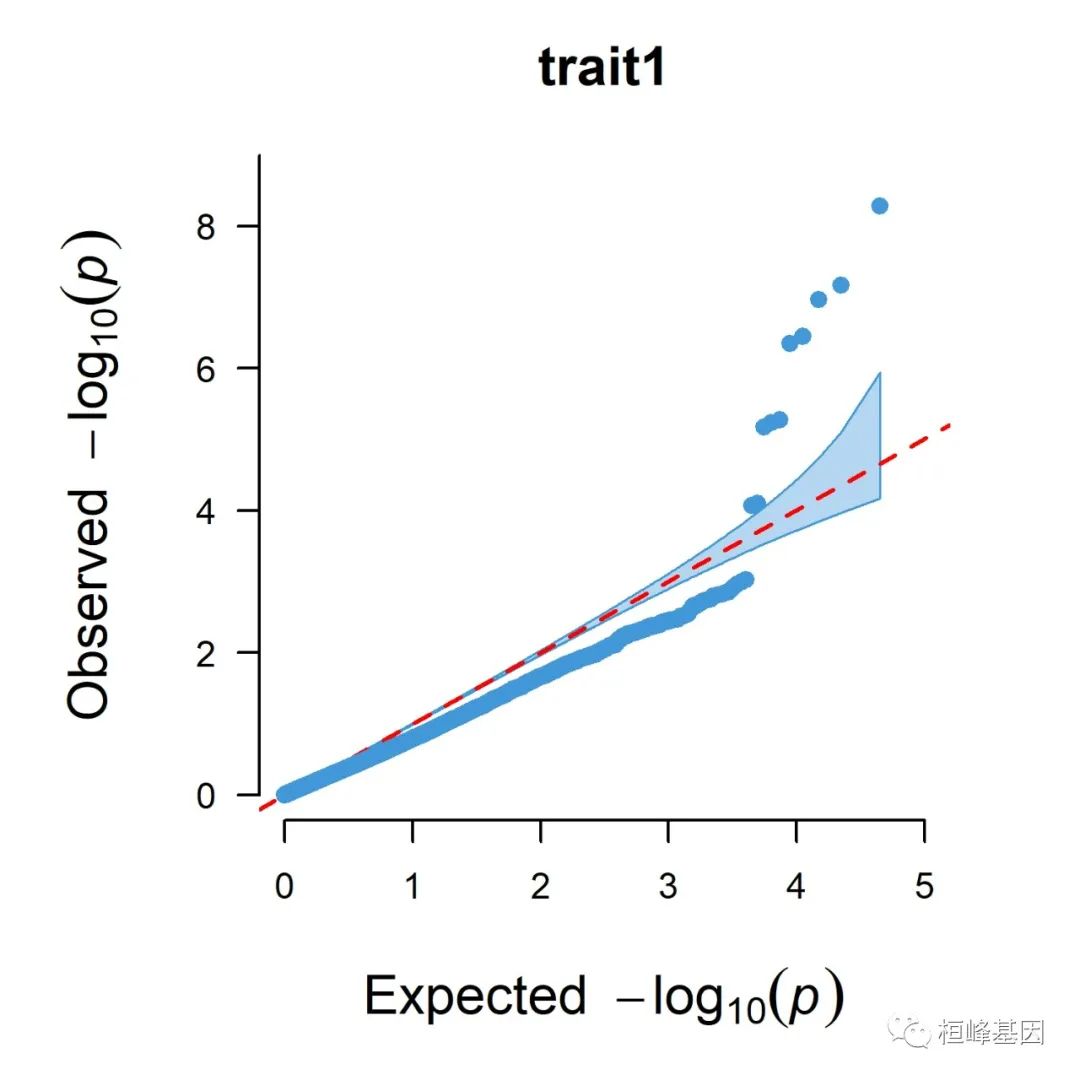
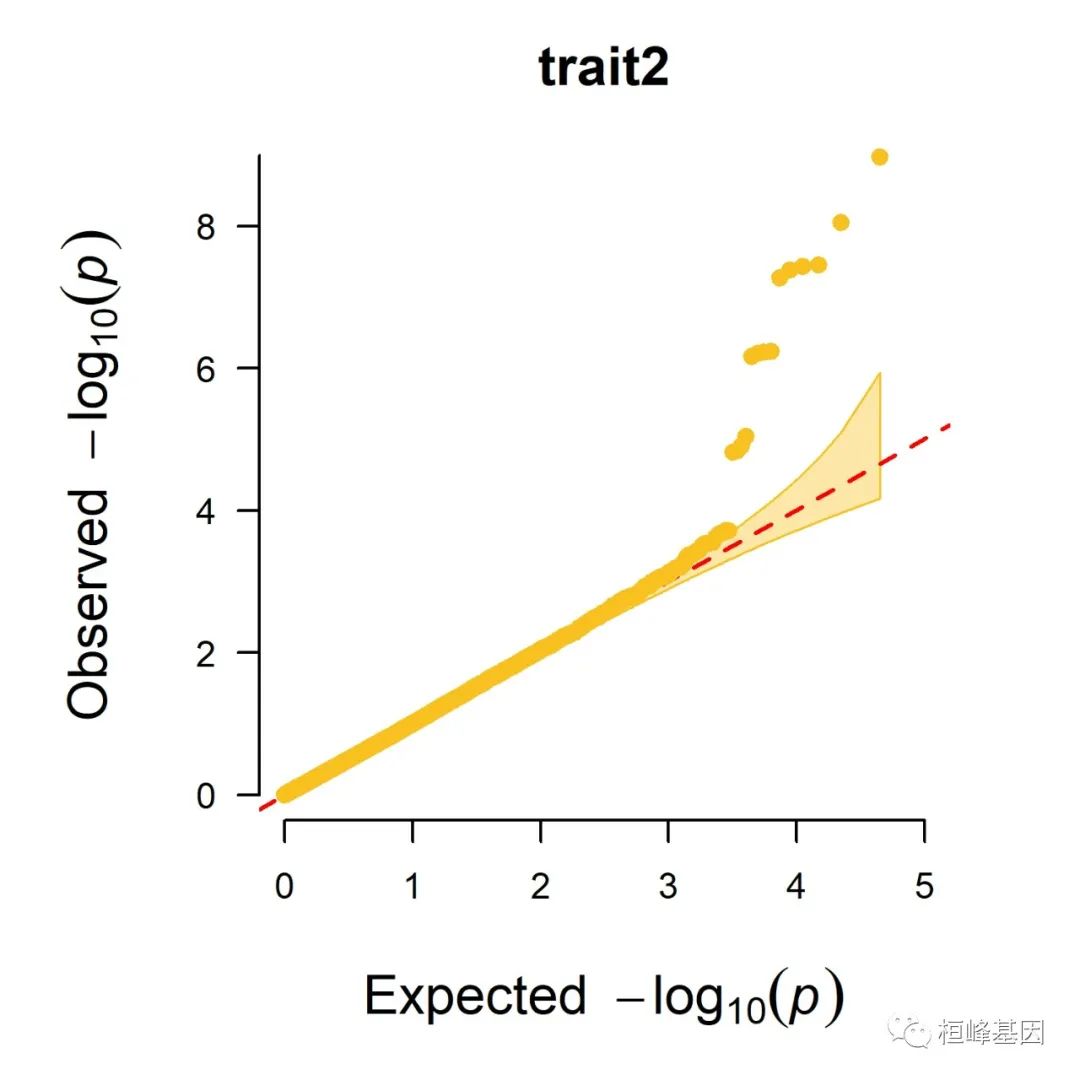
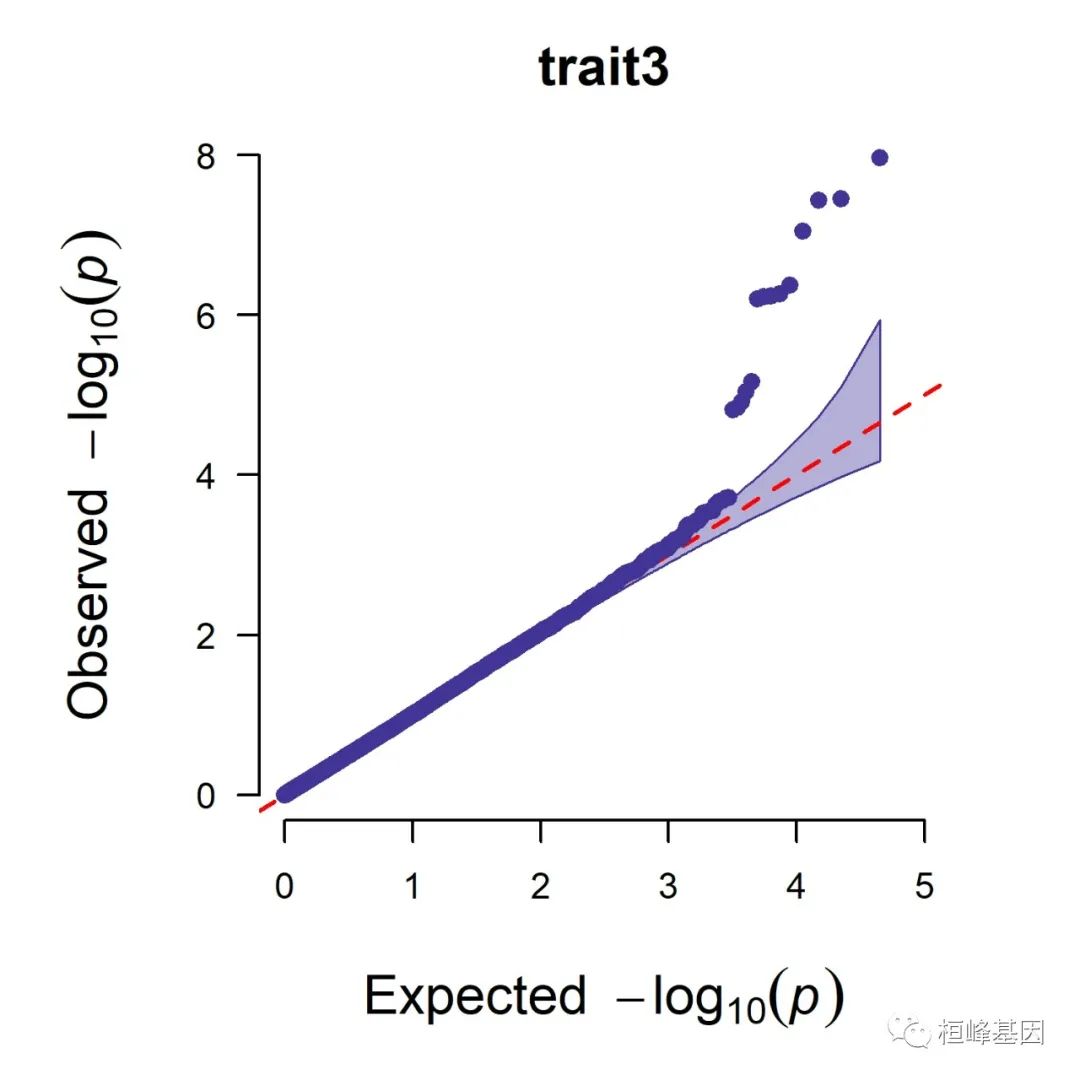
5. Q-Q plot
1. Single_track Q-Q plot
CMplot(pig60K, plot.type = "q", box = FALSE, file = "jpg", memo = "", dpi = 300,
conf.int = TRUE, conf.int.col = NULL, threshold.col = "red", threshold.lty = 2,
file.output = TRUE, verbose = TRUE, width = 5, height = 5)
## QQ Plotting trait1.
## QQ Plotting trait2.
## QQ Plotting trait3.
## Plots are stored in: F:/demo script/基因组分析系列/CMplot
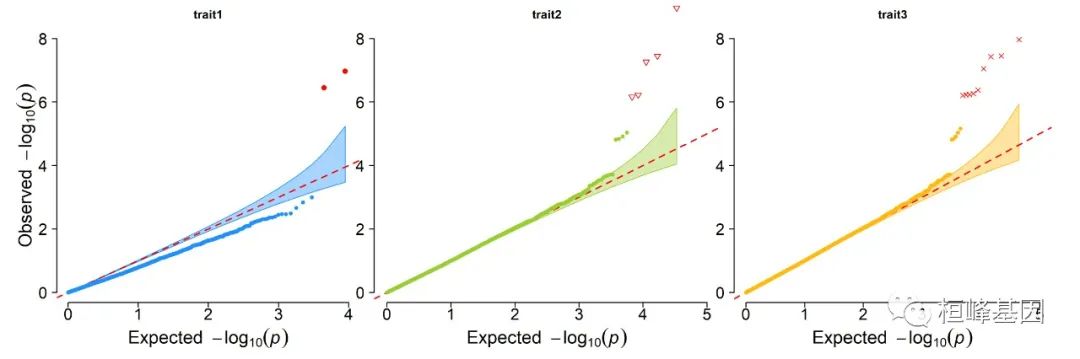
2. Multi_tracks Q-Q plot
pig60K$trait1[sample(1:nrow(pig60K), round(nrow(pig60K) * 0.8))] <- NA
pig60K$trait2[sample(1:nrow(pig60K), round(nrow(pig60K) * 0.25))] <- NA
CMplot(pig60K, plot.type = "q", col = c("dodgerblue1", "olivedrab3", "darkgoldenrod1"),
threshold = 1e-06, ylab.pos = 2, signal.pch = c(19, 6, 4), signal.cex = 1.2,
signal.col = "red", conf.int = TRUE, box = FALSE, multracks = TRUE, cex.axis = 2,
file = "jpg", memo = "", dpi = 300, file.output = TRUE, verbose = TRUE, ylim = c(0,
8), width = 5, height = 5)
## (warning: all phenotypes will use the same ylim.)
## Multracks-QQ Plotting trait1.
## Multracks-QQ Plotting trait2.
## Multracks-QQ Plotting trait3.
## Multraits-QQ Plotting trait1.
## Multraits-QQ Plotting trait2.
## Multraits-QQ Plotting trait3.
## Plots are stored in: F:/demo script/基因组分析系列/CMplot

References:
Yin, L. et al. rMVP: A Memory-efficient, Visualization-enhanced, and Parallel-accelerated tool for Genome-Wide Association Study, Genomics, Proteomics & Bioinformatics (2021), doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2020.10.007.

以上是关于【豆科基因组】大豆适应性位点GWAS分析[转载]的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章