Using Single-Row Functions to Customize Output使用单行函数自定义输出
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Using Single-Row Functions to Customize Output使用单行函数自定义输出相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
DUAL is a public table that you can use to view results from functions and calculations.
SQL> select * from DUAL;
D
-
X
SQL> desc DUAL;
Name Null? Type
----------------------------------------- -------- ----------------------------
DUMMY VARCHAR2(1)
SQL>
The DUAL table is owned by the user SYS and can be accessed by all users.
It contains one column, DUMMY, and one row with the value X.
Using Single-Row Functions to Customize Output
Oracle SQL supplies a rich library of in-built functions which can be employed for various tasks. The essential capabilities of a functions can be the case conversion of strings, in-string or substring operations, mathematical computations on numeric data, and date operations on date type values. SQL Functions optionally take arguments from the user and mandatorily return a value.
- Describe various types of functions available in SQL
- Use character, number, and date functions in SELECT statements
字符、数字、日期函数
1、SQL Functions
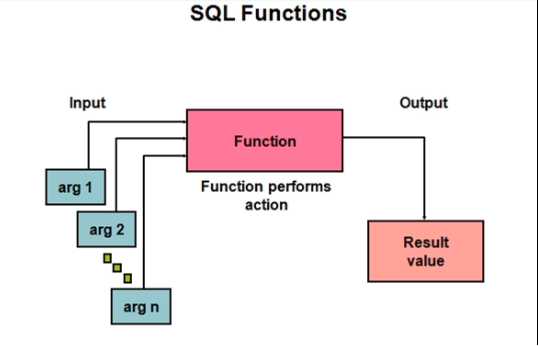
Functions are a very powerful feature of SQL. They can be used to do the following:
|
Perform calculations on data |
执行数据计算 |
|
Modify individual data items |
修改单独的数据项 |
|
Manipulate output for groups of rows |
操纵行组的输出 |
|
Format dates and numbers for display |
格式化日期和数字进行显示 |
|
Convert column data types |
转换列数据类型 |
SQL functions sometimes take arguments and always return a value.
SQL有时候接收参数并总是返回一个值.
2、Two Types of SQL Function:
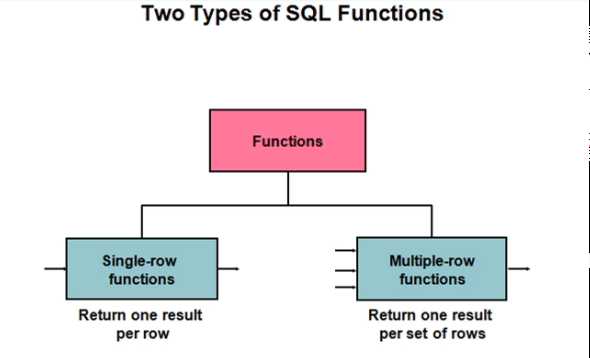
|
Single-row functions |
单行函数 These functions operate on single rows only and return one result per row. 单行函数只操作单个行并为每一行返回一个结果. - Single row functions are the one who work on single row and return one output per row. For example, length and case conversion functions are single row functions. |
|
Multiple-row functions |
多行函数 - Multiple row functions work upon group of rows and return one result for the complete set of rows. They are also known as Group Functions. |
3、Single-row functions单行函数
Single row functions
Single row functions can be character functions, numeric functions, date functions, and conversion functions. Note that these functions are used to manipulate data items. These functions require one or more input arguments and operate on each row, thereby returning one output value for each row. Argument can be a column, literal or an expression. Single row functions can be used in SELECT statement, WHERE and ORDER BY clause.
Single-row functions are used to manipulate data items. They accept one or more arguments and return one value for each row that is returned by the query.
(1)特点
|
Manipulate data items |
操作数据项 |
|
Accept arguments and return one value |
接收参数并返回一个值 |
|
Act on each row that is returned |
每一行进行操作 |
|
Return one result per row |
每一行返回一个值 |
|
Many modify the data type |
单行函数可以修改数据类型 |
|
Can be nested |
单行函数可以嵌套 |
|
Accept arguments that can be a column or an expression An argument can be one of the following:
|
函数接收的参数可以是列名或者表达式
|
(2)、语法
Function_name [(arg1,arg2….)]
(3)、类型
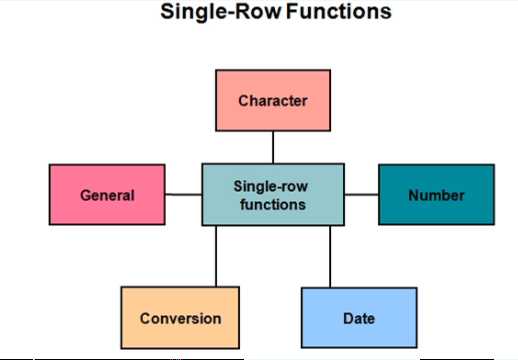
|
字符函数 character functions |
Accept character input and can return both character and number values. |
|
数字函数 number functions |
Accept numeric input and return numeric values. |
|
日期函数 date functions |
Operate on values of the DATE data type (All date functions return a value of the DATE data type except the MONTHS_BETWEEN function, which returns a number) 所有日期函数都返回一个DATE类型的值,除了MONTHS_BETWEEN函数,它返回一个数字. |
|
转换函数 Conversion function |
Convert a value from one data type to another |
|
通用函数 General function |
NVL:对空值做处理 NVL2:对空值做处理 NULLIF:对空值做处理 COALESCE CASE DECODE General functions The SELECT query below demonstrates the use of NVL function. SELECT first_name, last_name, salary, NVL (commission_pct,0) FIRST_NAME LAST_NAME SALARY NVL(COMMISSION_PCT,0)
|
(3.1)字符函数character functions
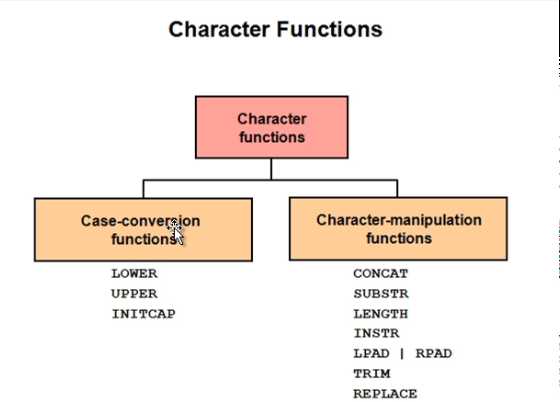
Character Functions
Single-row character functions accept character data as input and can return both character and numeric values. Character functions can be divided into the following:
|
Case-conversion functions 大小写转换函数
|
Lower转换为小写 Upper转换为大写 initcap首字母大写,其他小写
SQL> select lower(‘SQL Function‘) from dual;
LOWER(‘SQLFU ------------ sql function
SQL> select upper(‘SQL Function‘) from dual;
UPPER(‘SQLFU ------------ SQL FUNCTION
SQL> select initcap(‘sql function‘) from dual;
INITCAP(‘SQL ------------ Sql Function
SQL> select ‘The job id for ‘||UPPER(ename)||‘ is ‘||LOWER(JOB) AS "emp details" FROM scott.emp; emp details -------------------------------------- The job id for SMITH is clerk The job id for WARD is salesman
应用:有时候不知道查询的名字是大写还是小写,在匹配的时候可能找不到,就使用LOWER将名字全部转换为小写,再来匹配. SQL> select ename,job FROM emp WHERE ename=‘higgins‘; SQL> select ename,job FROM emp WHERE LOWER(ename)=‘higgins‘; Case Conversion functions The SELECT query below demonstrates the use of case conversion functions. SELECT UPPER (first_name), INITCAP (last_name), LOWER (job_id) UPPER(FIRST_NAME) INITCAP(LAST_NAME) LOWER(JOB_ |
||||||||||||||||
|
Character-manipulation functions 字符操作函数
|
CONCAT连接||操作 SUBSTR取子字符串 LENGTH求字符串的长度 INTER返回的是一个数字,查询一个子字符串在字符串中的第几个位置 LPAD左填充 RPAD右填充 TRIM去掉字符串的首尾空格或特殊字符(注意只能去掉首尾空格或字符) REPLACE搜索字符串,替换
综合应用: SELECT empid, CONCAT(first_name,last_name) NAME, jobid, LENGTH(last_name), INSTR(last_name,‘a‘) "Contains ‘a‘?" FROM emp WHERE substri(jobid,4)=‘REP‘; Character functions The SELECT query below demonstrates the use of CONCAT function to concatenate two string values. SELECT CONCAT (first_name, last_name) CONCAT(FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME) The SELECT query below demonstrates the use of SUBSTR and INSTR functions. SUBSTR function returns the portion of input string from 1st position to 5th position. INSTR function returns the numeric position of character ‘a‘ in the first name. SELECT SUBSTR (first_name,1,5), INSTR (first_name,‘a‘) SUBST INSTR(FIRST_NAME,‘A‘) The SELECT query below demonstrates the usage of LPAD and RPAD to pretty print the employee and job information. SELECT RPAD(first_name,10,‘_‘)||LPAD (job_id,15,‘_‘) RPAD(FIRST_NAME,10,‘_‘)|| |
|
function |
purpose |
|
LOWER(column | expression) |
Coverts alpha character values to lowercase 将字符串转换为小写字母 Coverts mixed-case or uppercase character strings to lowercase |
|
UPPER(column | expression) |
Coverts alpha character values to uppercase 将字符串转换为大写字母 Converts mixed-case or lowercase character strings to uppercase |
|
INITCAP(column | expression) |
Coverts alpha character values to uppercase for the first letter of each word; all other letters in lowercase 将字符串中每个单词首字母大写,其他小写 Converts the first letter of each word to uppercase and the remaining letters to lowercase |
|
CONCAT(column | expression) |
Concatenates the first character value to the second character value; equivalent to concatenation operator(||) 把两个字符串连接起来 |
|
SUBSTR(column | expression, m[,n]) |
Returns specified characters from character value starting at character position m, n characters long(if m is negative, the count starts from the end of the character value, if n is omitted, all characters to the end of the string are returned ) 从字符串中返回指定字符,从字符m开始,n个字符长(如果m是负数,则计数从字符值的结尾开始,如果省略n,则返回字符串结尾的所有字符) |
|
LENGTH(column | expression) |
Returns the number of characters in the expression |
|
INTER(column | expression, ‘string‘, [,m],[n]) 查找子字符串在表达式中的为位置 m为开始搜索的位置,n表示字符串第几次出现. |
Returns the numeric position of a named string. Optionally, you can provide a position m to start searching ,m 表示开始搜索的位置,and the occurrence n of the string. n表示字符串第几次出现. m and n default to 1, m,n默认都是1,meaning start the search at the beginning of the string and report the first occurrence. |
|
LPAD(column | expression, n, ‘string‘)
RPAD(column | expression, n, ‘string‘) 用一个给定的字符string来填出这个表达式/字符串,填充完以后总长度为n.
|
Returns an expression left-padded(左填充) to legth of n characters with a character expression. Returns an expression right-padded to length of n characters with a character expression. 例子:LPAD(column | expression, 5, ‘w‘) 给这个字符串左边填充w,直到填充后的字符串总长度为5 |
|
TRIM(leading|trailing|both, trim_character FROM trim_source) |
Enables you to trim(削减) leading(前导) or trailing(尾部) characters(or both) from a character string. If trim_character on trim_source is a character literal, you must enclose it in single quotation marks.
|
|
REPLACE(text, search_string, replacement_string) 在文本里搜指定字符串,将搜寻到的字符串替换为替换字符串. |
Searches a text expression for a character string and, if found, replaces it with a specified replacement string |
(3.2)数字函数number functions
- Number functions - Accepts numeric input and returns numeric values. Functions under the category are ROUND, TRUNC, and MOD.
- ROUND and TRUNC functions are used to round and truncate the number value.
- MOD is used to return the remainder of the division operation between two numbers.
|
function |
result |
|
ROUND |
Rounds value to a specified decimal 四舍五入 |
|
TRUNC |
Truncates value to a specified decimal 截断一个值到一定的小数位,不管大于5小于5 |
|
MOD |
Returns remainder of division 返回一个除数的余数 |
|
function |
result |
|
ROUND(45.926,2) |
45.93 |
|
TRUNC(45.926,2) |
45.92 |
|
MOD(1600,300) |
100 |
|
function |
purpose |
|
ROUND(column | expression,n) |
Rounds (四舍五入)the column, expression, or value to n decimal places(小数位) or, if n is omitted(省略), no decimal places (if n degative, numbers to the left of decimal point are rounded.) 如果n是负数,小数点左边四舍五入 SQL> SELECT ROUND(45.923,2),ROUND(45.923,0),ROUND(45.923,-1) FROM DUAL;
ROUND(45.923,2) ROUND(45.923,0) ROUND(45.923,-1) --------------- --------------- ---------------- 45.92 46 50
|
|
TRUNC(column | expression,n) |
Truncates(截断) the column, expression, or value to n decimal places or, if n is omitted, n defaults to zero. Like the ROUND function, the TRUC function can be used with date functions. TRUNC函数也可以用作日期函数. |
|
MOD(m,n) |
Returns the remainder(余数) of m divided by n Note : The MOD function is often used to determine whether a value is odd or even. The MOD function is also the ORACLE hash function. MOD函数经常被用于判断一个值是奇数还是偶数. |
Number functions
The SELECT query below demonstrates the use of ROUND and TRUNC functions.
SELECT ROUND (1372.472,1)
FROM dual;
ROUND(1372.472,1)
-----------------
1372.5
SELECT TRUNC (72183,-2)
FROM dual;
TRUNC(72183,-2)
---------------
72100
(3.3)日期函数date functions
- Date functions - Date arithmetic operations return date or numeric values. Functions under the category are MONTHS_BETWEEN, ADD_MONTHS, NEXT_DAY, LAST_DAY, ROUND and TRUNC.
- MONTHS_BETWEEN function returns the count of months between the two dates.
- ADD_MONTHS function add ‘n‘ number of months to an input date.
- NEXT_DAY function returns the next day of the date specified.
- LAST_DAY function returns last day of the month of the input date.
- ROUND and TRUNC functions are used to round and truncates the date value.
- The oracle database stores dates in an internal numeric format: century, year, month, day, hours, minutes ,and seconds.
数据库内部以数字格式存储日期,可表示世纪、年,月,日,时,分,秒.
- This data is stored internally as follow:
CENTYURY YEAR MONTH DAY HOUR MINUTE SECOND
19 89 06 17 17 10 43
- 当带有日期列的记录被插入到表中时,世纪信息从SYSDATE函数中获取。
- 当日期列被显示在屏幕上时,世纪部分默认不被显示.
- The default date display format is DD-MON-RR.
默认显示和输入格式是DD-MON-RR.
- Enables you to store 21st-century dates in the 20th century by specifying only the last two digits of the year
- Enables you to store 20th-century dates in the 21st century in the same way
(3.3.1)SYSDATE and CURRENT_DATE
Using the SYSDATE Function
SYSDATE is a function that returns:
- Date
- Time
SQL> select sysdate from dual;
SYSDATE
------------------
04-JUL-17
CURRENT_DATE也可以返回当前时间,但是CURRENT_DATE函数返回会话时区中的当前日期.
如:在中国访问美国的远程数据库,SYSDATE会返回美国的日期和时间;CURRENT_DATE会返回中国的日期和时间.
(3.3.2)NLS(国家语言字符支持National Language Support )
如何查看数据库使用的字符集:select * from V$NLS_PARAMETERS;
(3.3.3)RR Date Format
RR日期格式类似于YY格式,但是可使用它来指定不同的世纪.
|
Current Year |
Specified Date |
RR Format |
YY Format |
|
1995 |
27-OCT-95 |
1995 |
1995 |
|
1995 |
27-OCT-17 |
2017 |
1917 |
|
2001 |
27-OCT-17 |
2017 |
2017 |
|
2001 |
27-OCT-95 |
1995 |
2095 |
|
|
If the specified two-digit year is: |
||||||||||||||
|
0-49 |
50-99 |
||||||||||||||
|
If two digits of the current year are |
0-49 |
The return date is in the current century 当前世纪年在0-49,指定世纪年在0-49则返回当前世纪年
|
The return date is in the century before the current one 当前世纪年在0-49,指定世纪年在50-99则返回当前世纪年的前一年
|
||||||||||||
|
50-99 |
The return date is in the century after the current one 当前世纪年在50-99,指定世纪年在0-49则返回当前世纪年的后一年
|
The return date is in the current century 当前世纪年在50-99,指定世纪年在50-99,则返回当前世纪年.
|
|||||||||||||
(3.3.4)arithmetic with Dates
因为数据库把日期作为数字存储,因此可以对日期进行加减运算.
- Add or subtract a number to or from a date for a resultant date value.
- Subtract two dates to find the number of days between those dates.
- Add hours to a date by dividing the number of hours by 24.
|
Operation |
Result |
Description |
|
Date+number |
Date |
Adds a number of days to a date给日期加几天 |
|
Date-number |
Date |
Subtracts a number of days from a date减去几天 |
|
Date-date |
Number of days |
Subtracts one date from another两个日期相减 |
|
Date+number/24 |
Date |
Adds a number of hours to a date 加几个小时 |
(3.3.3)其他日期函数
注:数字函数ROUND和TRUNC还可以对日期做操作.
SYSDATE=‘25-JUL-03‘
|
function |
purpose |
|
ROUND(SYSDATE,‘MONTH‘)四舍五入 MONTH:日期是1-15,当前月的第一天,如期是16-31会是下个月的第1天 |
01-AUG-03 |
|
ROUND(SYSDATE,‘YEAR‘)四舍五入 YEAR:月1-6会是当前年的1月1日,月7-12会是下一年的1月1日 |
01-JAN-04 |
|
TRUNC(SYSDATE,‘MONTH‘)截断 MONTH:当前月第一天 |
01-JUL-03 |
|
TRUNC(SYSDATE,‘YEAR‘)截断 当前年的1月1日 |
01-JAN-03 |
|
MONTHS_BETWEEN(date1,date2) |
Number of months between two dates SQL> SELECT 2 MONTHS_BETWEEN(‘1-OCT-2012‘,‘10-NOV-2012‘) 3 FROM DUAL;
MONTHS_BETWEEN(‘1-OCT-2012‘,‘10-NOV-2012‘) ------------------------------------------ -1.2903226 |
|
ADD_MONTHS(date, n) |
Add calendar months to date |
|
NEXT_DAY(date, ‘char‘) char表示星期几 |
Next day of the date specified 找到date开始的下一个星期几的日期 SQL> SELECT NEXT_DAY(‘1-OCT-2012‘,‘Friday‘) FROM DUAL;
NEXT_DAY(‘1-OCT-20 ------------------ 05-OCT-12 |
|
LAST_DAY(date) |
Last day of the month 每月的最后一天 SQL> SELECT LAST_DAY(‘1-FEB-2012‘) FROM DUAL;
LAST_DAY(‘1-FEB-20 ------------------ 29-FEB-12
|
|
Months |
Days |
|
January |
31days |
|
February |
28 days in a common year and 29 days in Leap years |
|
March |
31 days |
|
April |
30 days |
|
May |
31 days |
|
June |
30 days |
|
July |
31 days |
|
August |
31 days |
|
September |
30 days |
|
October |
31 days |
|
November |
30 days |
|
December |
31 days |
Date arithmetic operations
The SELECT query below shows a date arithmetic function where difference of employee hire date and sysdate is done.
SELECT employee_id, (sysdate - hire_date) Employment_days
FROM employees
WHERE rownum < 5;
EMPLOYEE_ID EMPLOYMENT_DAYS
----------- ---------------
100 3698.61877
101 2871.61877
102 4583.61877
103 2767.61877
Date functions
The SELECT query below demonstrates the use of MONTHS_BETWEEN, ADD_MONTHS, NEXT_DAY and LAST_DAY functions.
SELECT employee_id, MONTHS_BETWEEN (sysdate, hire_date) Employment_months
FROM employees
WHERE rownum < 5;
EMPLOYEE_ID EMPLOYMENT_MONTHS
----------- -----------------
100 121.504216
101 94.3751837
102 150.633248
103 90.9558289
SELECT ADD_MONTHS (sysdate, 5), NEXT_DAY (sysdate), LAST_DAY (sysdate)
FROM dual;
ADD_MONTH NEXT_DAY( LAST_DAY(
--------- --------- ---------
01-JAN-14 05-AUG-13 31-AUG-13
以上是关于Using Single-Row Functions to Customize Output使用单行函数自定义输出的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章