NOIP模拟题 2017.7.3 - 模拟 - 贪心 - 记忆化搜索
Posted 阿波罗2003
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了NOIP模拟题 2017.7.3 - 模拟 - 贪心 - 记忆化搜索相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

直接暴力模拟,注意判数据结构为空时的取出操作。
Code
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<ctime> 4 #include<cctype> 5 #include<cstring> 6 #include<cstdlib> 7 #include<fstream> 8 #include<sstream> 9 #include<algorithm> 10 #include<map> 11 #include<set> 12 #include<stack> 13 #include<queue> 14 #include<vector> 15 #include<stack> 16 using namespace std; 17 typedef bool boolean; 18 const signed int inf = (signed)((1u << 31) - 1); 19 #define smin(a, b) a = min(a, b) 20 #define smax(a, b) a = max(a, b) 21 #define max3(a, b, c) max(a, max(b, c)) 22 #define min3(a, b, c) min(a, min(b, c)) 23 template<typename T> 24 inline boolean readInteger(T& u){ 25 char x; 26 int aFlag = 1; 27 while(!isdigit((x = getchar())) && x != \'-\' && x != -1); 28 if(x == -1) { 29 ungetc(x, stdin); 30 return false; 31 } 32 if(x == \'-\'){ 33 x = getchar(); 34 aFlag = -1; 35 } 36 for(u = x - \'0\'; isdigit((x = getchar())); u = (u << 1) + (u << 3) + x - \'0\'); 37 ungetc(x, stdin); 38 u *= aFlag; 39 return true; 40 } 41 42 int n; 43 stack<int> s; 44 queue<int> q; 45 priority_queue<int> que; 46 boolean prob[3] = {true, true, true}; 47 48 inline void solve() { 49 int opt, a, x; 50 readInteger(n); 51 while(n--) { 52 readInteger(opt); 53 readInteger(a); 54 if(opt == 1) { 55 if(prob[0]) s.push(a); 56 if(prob[1]) q.push(a); 57 if(prob[2]) que.push(a); 58 } else { 59 if(prob[0]) { 60 if(s.empty()) prob[0] = false; 61 else { 62 x = s.top();s.pop(); 63 if(x != a) prob[0] = false; 64 } 65 } 66 if(prob[1]) { 67 if(q.empty()) prob[1] = false; 68 else { 69 x = q.front();q.pop(); 70 if(x != a) prob[1] = false; 71 } 72 } 73 if(prob[2]) { 74 if(que.empty()) prob[2] = false; 75 else { 76 x = que.top();que.pop(); 77 if(x != a) prob[2] = false; 78 } 79 } 80 } 81 } 82 puts(prob[0] ? "YES" : "No"); 83 puts(prob[1] ? "YES" : "No"); 84 puts(prob[2] ? "YES" : "No"); 85 } 86 87 int main() { 88 freopen("qu.in", "r", stdin); 89 freopen("qu.out", "w", stdout); 90 solve(); 91 return 0; 92 }

考虑只有两个任务的时候,只有两种情况,它们的答案分别是 和
和 。又因为
。又因为 ,所以有
,所以有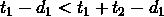 ,
, ,所以它们的谁更优取决于
,所以它们的谁更优取决于 。即d值的大小。
。即d值的大小。
现在考虑多个任务的时候,先随便安排一种执行任务的顺序,如果存在有关d值的逆序对,那么说明当前这个顺序一定不优,我们可以通过交换相邻的一对逆序对使得结果更优。最优时即不存在有关d的逆序对吗,即按d值排序再计算答案就好了。
Code
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<ctime> 4 #include<cctype> 5 #include<cstring> 6 #include<cstdlib> 7 #include<fstream> 8 #include<sstream> 9 #include<algorithm> 10 #include<map> 11 #include<set> 12 #include<stack> 13 #include<queue> 14 #include<vector> 15 #include<stack> 16 using namespace std; 17 typedef bool boolean; 18 const signed int inf = (signed)((1u << 31) - 1); 19 #define smin(a, b) a = min(a, b) 20 #define smax(a, b) a = max(a, b) 21 #define max3(a, b, c) max(a, max(b, c)) 22 #define min3(a, b, c) min(a, min(b, c)) 23 template<typename T> 24 inline boolean readInteger(T& u){ 25 char x; 26 int aFlag = 1; 27 while(!isdigit((x = getchar())) && x != \'-\' && x != -1); 28 if(x == -1) { 29 ungetc(x, stdin); 30 return false; 31 } 32 if(x == \'-\'){ 33 x = getchar(); 34 aFlag = -1; 35 } 36 for(u = x - \'0\'; isdigit((x = getchar())); u = (u << 1) + (u << 3) + x - \'0\'); 37 ungetc(x, stdin); 38 u *= aFlag; 39 return true; 40 } 41 42 typedef class Task { 43 public: 44 int t; 45 int d; 46 47 Task(int t = 0, int d = 0):t(t), d(d) { } 48 49 boolean operator < (Task b) const { 50 if(d != b.d) return d < b.d; 51 return t < b.t; 52 } 53 }Task; 54 55 int n; 56 Task* ts; 57 58 inline void init() { 59 readInteger(n); 60 ts = new Task[(const int)(n + 1)]; 61 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { 62 readInteger(ts[i].t); 63 readInteger(ts[i].d); 64 } 65 } 66 67 int res = 0; 68 inline void solve() { 69 sort(ts + 1, ts + n + 1); 70 int fin = 0; 71 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { 72 fin += ts[i].t; 73 smax(res, max(0, fin - ts[i].d)); 74 } 75 printf("%d\\n", res); 76 } 77 78 int main() { 79 freopen("ming.in", "r", stdin); 80 freopen("ming.out", "w", stdout); 81 init(); 82 solve(); 83 return 0; 84 }

先说一下70分做法(由于数据比较水,所以暴力基本上可以过7个点)吧。
- 暴力建图,然后用树归去统计。每到一个点,先统计它所在的子树的大小。然后用当前子树大小乘它和这个新树的大小再乘它到父节点的那条边的权(乘法原理)。累加起来就是答案。
- 这种做法不用建图,首先可以直接求的几个量:连接两棵树的边对答案的贡献,两边的树内部的路径对答案的贡献。现在我们希望求得经过这条边的路径对答案的贡献。根据人生的哲理和组合计数上的经验,我们可以轻松得到这个长度等于左边所有到左边连接点的路径距离总和乘右边节点数,对于右边同理。现在想要快速在O(n)的时间内处理掉这个路径长度总和又不建树,就可以按边一直分下去(类似于边分治吧)。
我先画一幅图:
显然在子树b内,可以求出其中的点到点d的距离和,在子树a内也可以用一样的方法求出其中的点到点p的距离,随后是不是还差了点什么?好像子树b内的路径没有延伸到点p。因为树上的路径是唯一的,我们只需要补上路径d-c-p的长度乘子树b内节点数就可以求答案。
我在考试的时候用的是方法1。
Code

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<ctime> 4 #include<cctype> 5 #include<cstring> 6 #include<cstdlib> 7 #include<fstream> 8 #include<sstream> 9 #include<algorithm> 10 #include<map> 11 #include<set> 12 #include<stack> 13 #include<queue> 14 #include<vector> 15 #include<stack> 16 using namespace std; 17 typedef bool boolean; 18 const signed int inf = (signed)((1u << 31) - 1); 19 #define smin(a, b) a = min(a, b) 20 #define smax(a, b) a = max(a, b) 21 #define max3(a, b, c) max(a, max(b, c)) 22 #define min3(a, b, c) min(a, min(b, c)) 23 template<typename T> 24 inline boolean readInteger(T& u){ 25 char x; 26 int aFlag = 1; 27 while(!isdigit((x = getchar())) && x != \'-\' && x != -1); 28 if(x == -1) { 29 ungetc(x, stdin); 30 return false; 31 } 32 if(x == \'-\'){ 33 x = getchar(); 34 aFlag = -1; 35 } 36 for(u = x - \'0\'; isdigit((x = getchar())); u = (u << 1) + (u << 3) + x - \'0\'); 37 ungetc(x, stdin); 38 u *= aFlag; 39 return true; 40 } 41 42 ///map template starts 43 typedef class Edge{ 44 public: 45 int end; 46 int next; 47 int w; 48 Edge(const int end = 0, const int next = 0, const int w = 0):end(end), next(next), w(w){} 49 }Edge; 50 51 typedef class MapManager{ 52 public: 53 int ce; 54 int *h; 55 Edge *edge; 56 MapManager(){} 57 MapManager(int points, int limit):ce(0){ 58 h = new int[(const int)(points + 1)]; 59 edge = new Edge[(const int)(limit + 1)]; 60 memset(h, 0, sizeof(int) * (points + 1)); 61 } 62 inline void addEdge(int from, int end, int w){ 63 edge[++ce] = Edge(end, h[from], w); 64 h[from] = ce; 65 } 66 inline void addDoubleEdge(int from, int end, int w){ 67 addEdge(from, end, w); 68 addEdge(end, from, w); 69 } 70 Edge& operator [] (int pos) { 71 return edge[pos]; 72 } 73 }MapManager; 74 #define m_begin(g, i) (g).h[(i)] 75 ///map template ends 76 77 const int moder = 1e9 + 7; 78 79 int n; 80 MapManager *g; 81 int* siz; 82 int s[100005]; // The size of node i. 83 int fs[100005]; // The length of a edge which connects node i and its father node. 84 85 inline int mod_plus(int a, int b) { 86 int ret = a + b; 87 while(ret >= moder) ret -= moder; 88 return ret; 89 } 90 91 inline void init() { 92 readInteger(n); 93 g = new MapManager[(const int)(n + 1)]; 94 siz = new int[(const int)(n + 1)]; 95 siz[0] = 1; 96 g[0] = MapManager(1, 0); 97 } 98 99 int cnt = 0; 100 inline void mknewtree(int a, int b, int c, int d, int l) { // Make a new tree following the recipe within O(n). 101 cnt++; 102 siz[cnt] = siz[a] + siz[b]; 103 g[cnt] = MapManager(siz[cnt], siz[cnt] << 1); 104 for(int i = 0; i < siz[a]; i++) 105 for(int j = m_begin(g[a], i); j; j = g[a][j].next) 106 g[cnt].addEdge(i, g[a][j].end, g[a][j].w); 107 for(int i = 0; i < siz[b]; i++) 108 for(int j = m_begin(g[b], i); j; j = g[b][j].next) 109 g[cnt].addEdge(i + siz[a], g[b][j].end + siz[a], g[b][j].w); 110 g[cnt].addDoubleEdge(c, d + siz[a], l); 111 } 112 113 int res = 0; 114 void calcLength(int node, int fa) { 115 s[node] = 1; 116 for(int i = m_begin(g[cnt], node); i; i = g[cnt][i].next) { 117 int& e = g[cnt][i].end; 118 if(e == fa) continue; 119 fs[e] = g[cnt][i].w; 120 calcLength(e, node); 121 s[node] += s[e]; 122 } 123 res = mod_plus(res ,(s[node] * 1LL * (siz[cnt] - s[node]) * fs[node]) % moder); 124 } 125 126 inline void solve() { 127 int a, b, c, d, l; 128 while(n--) { 129 readInteger(a); 130 readInteger(b); 131 readInteger(c); 132 readInteger(d); 133 readInteger(l); 134 mknewtree(a, b, c, d, l); 135 res = 0, fs[0] = 0; 136 calcLength(0, -1); 137 printf("%d\\n", res); 138 } 139 } 140 141 int main() { 142 freopen("zi.in", "r", stdin); 143 freopen("zi.out", "w", stdout); 144 init(); 145 solve(); 146 return 0; 147 }
方法1似乎无法优化了,但是方法2很有搞头,因为不用建树。你可以试试人工模拟几组数据,然后你会惊讶地发现真正的状态数并不多,大概也就O(m2)吧,对于树上任意两点的距离,也就顶多连接点的组合,而这些点的(不同树上的总共)个数都是O(m)的。而考虑树上一棵树到其任意一点的距离总和,也就是到的都是连接点,数量也不多。因此2个map强势登场一堆记忆化加上直接把这道题水掉了。。
如果还不清楚就结合代码看吧。
Code
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<ctime> 4 #include<cctype> 5 #include<cstring> 6 #include<cstdlib> 7 #include<fstream> 8 #include<sstream> 9 #include<algorithm> 10 #include<map> 11 #include<set> 12 #include<stack> 13 #include<queue> 14 #include<vector> 15 #include<stack> 16 #ifndef WIN32 17 #define Auto "%lld" 18 #else 19 #define Auto "%I64d" 20 #endif 21 using namespace std; 22 typedef bool boolean; 23 const signed int inf = (signed)((1u << 31) - 1); 24 #define smin(a, b) a = min(a, b) 25 #define smax(a, b) a = max(a, b) 26 #define max3(a, b, c) max(a, max(b, c)) 27 #define min3(a, b, c) min(a, min(b, c)) 28 template<typename T> 29 inline boolean readInteger(T& u){ 30 char x; 31 int aFlag = 1; 32 while(!isdigit((x = getchar())) && x != \'-\' && x != -1); 33 if(x == -1) { 34 ungetc(x, stdin); 35 return false; 36 } 37 if(x == \'-\'){ 38 x = getchar(); 39 aFlag = -1; 40 } 41 for(u = x - \'0\'; isdigit((x = getchar())); u = (u << 1) + (u << 3) + x - \'0\'); 42 以上是关于NOIP模拟题 2017.7.3 - 模拟 - 贪心 - 记忆化搜索的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
