手写数字集介绍
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了手写数字集介绍相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A 手写数字集介绍import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
#MNIST数据集
minist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(train_x, train_y), (test_x, test_y) = minist.load_data()
#训练集和测试集的长度
print("Training set:", len(train_x))
print("Testing set:", len(test_x))
#图像数据和标记数据的形状
print("train_x", train_x.shape, train_x.dtype)
print("train_y", train_y.shape, train_y.dtype)
#数据集中的第1个样本
train_x[0]
#显示图片5
plt.axis("off")
plt.imshow(train_x[0], cmap="gray")
plt.title("显示图片5")
plt.show()
#输出图片5标签
train_y[0]
#随机显示4幅手写数字图片
for i in range(4):
num = np.random.randint(1, 60000)
plt.subplot(1, 4, i+1)
plt.axis("off")
plt.imshow(train_x[num], cmap="gray")
plt.title(train_y[num])
plt.show()
基于MNIST数据集实现手写数字识别
介绍
在TensorFlow的官方入门课程中,多次用到mnist数据集。mnist数据集是一个数字手写体图片库,但它的存储格式并非常见的图片格式,所有的图片都集中保存在四个扩展名为idx*-ubyte.gz的二进制文件。
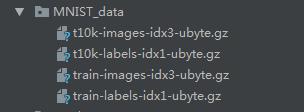
可以直接从官网进行下载
http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/

如果我们想要知道大名鼎鼎的mnist手写体数字都长什么样子,就需要从mnist数据集中导出手写体数字图片。了解这些手写体的总体形状,也有助于加深我们对TensorFlow入门课程的理解。
训练数据集
当我们下载了数据集后,需要对数据集进行训练。并保存训练的模型
#!/usr/bin/python3.5
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import tensorflow as tf
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data', one_hot=True)
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784])
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10])
def weight_variable(shape):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def conv2d(x, W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
W_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32])
b_conv1 = bias_variable([32])
x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1])
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1)
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1)
W_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64])
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64])
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)
W_fc1 = weight_variable([7 * 7 * 64, 1024])
b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024])
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1)
keep_prob = tf.placeholder("float")
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob)
W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024, 10])
b_fc2 = bias_variable([10])
y_conv = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2)
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y_conv))
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for i in range(20000):
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(50)
if i % 100 == 0:
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict=
x: batch[0], y_: batch[1], keep_prob: 1.0)
print('step %d, training accuracy %g' % (i, train_accuracy))
train_step.run(feed_dict=x: batch[0], y_: batch[1], keep_prob: 0.5)
saver.save(sess, 'WModel/model.ckpt')
print('test accuracy %g' % accuracy.eval(feed_dict=
x: mnist.test.images, y_: mnist.test.labels, keep_prob: 1.0))
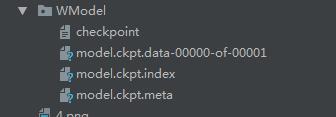
对应的模型文件如图所示
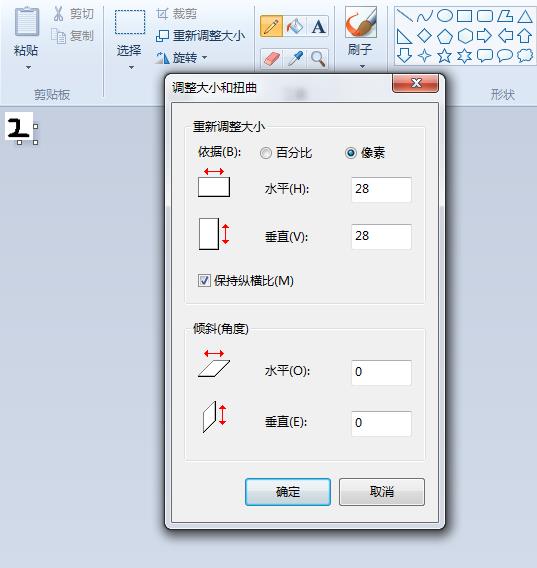
用画图手写数字
通过电脑自带画图工具,手写一个数字,像素为28,如图所示
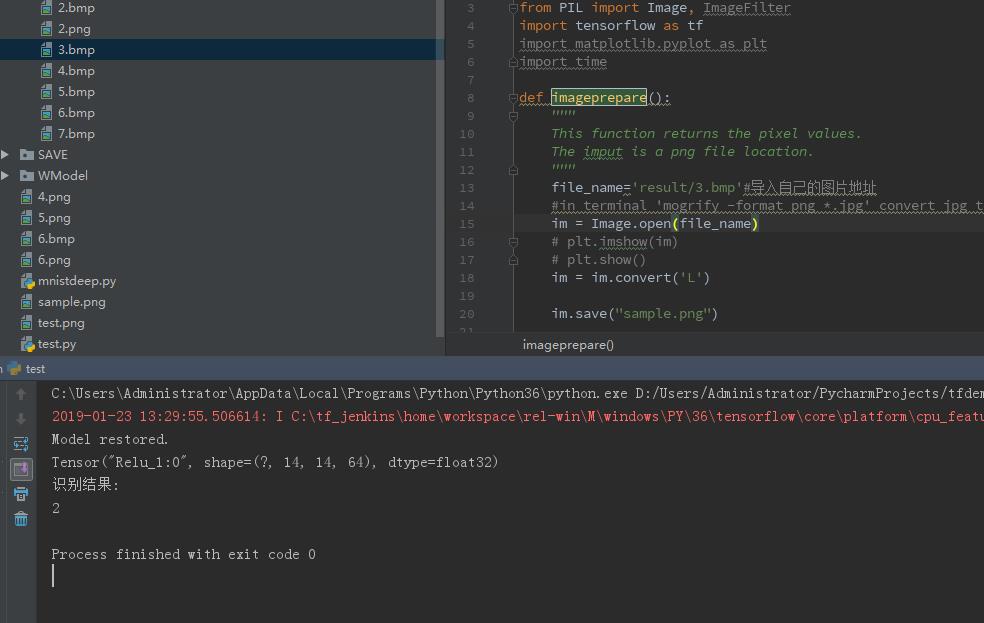
识别手写数字
把上面生成的图片保存为bmp或png
然后通过程序调用,在使用之前需要先加载前面保存的模型
#!/usr/bin/python3.5
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from PIL import Image, ImageFilter
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
def imageprepare():
"""
This function returns the pixel values.
The imput is a png file location.
"""
file_name='result/4.bmp'#导入自己的图片地址
#in terminal 'mogrify -format png *.jpg' convert jpg to png
im = Image.open(file_name)
# plt.imshow(im)
# plt.show()
im = im.convert('L')
im.save("sample.png")
tv = list(im.getdata()) #get pixel values
#normalize pixels to 0 and 1. 0 is pure white, 1 is pure black.
tva = [ (255-x)*1.0/255.0 for x in tv]
#print(tva)
return tva
"""
This function returns the predicted integer.
The imput is the pixel values from the imageprepare() function.
"""
# Define the model (same as when creating the model file)
result=imageprepare()
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784])
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10])
def weight_variable(shape):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape,stddev = 0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.1,shape = shape)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def conv2d(x,W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides = [1,1,1,1], padding = 'SAME')
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1,2,2,1], strides=[1,2,2,1], padding='SAME')
W_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32])
b_conv1 = bias_variable([32])
x_image = tf.reshape(x,[-1,28,28,1])
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image,W_conv1) + b_conv1)
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1)
W_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64])
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64])
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)
W_fc1 = weight_variable([7 * 7 * 64, 1024])
b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024])
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7*7*64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1)
keep_prob = tf.placeholder("float")
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob)
W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024, 10])
b_fc2 = bias_variable([10])
y_conv=tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2)
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y_conv))
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv,1), tf.argmax(y_,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
saver.restore(sess, "./WModel/model.ckpt")#这里使用了之前保存的模型参数
print ("Model restored.")
prediction=tf.argmax(y_conv,1)
predint=prediction.eval(feed_dict=x: [result],keep_prob: 1.0, session=sess)
print(h_conv2)
print('识别结果:')
print(predint[0])
识别结果如图所示:
以上是关于手写数字集介绍的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章