Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, returnnull.
Posted 洞拐洞幺
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, returnnull. 相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, returnnull.
Follow up:
思路:
1)同linked-list-cycle-i一题,使用快慢指针方法,判定是否存在环,并记录两指针相遇位置(Z);
2)将两指针分别放在链表头(X)和相遇位置(Z),并改为相同速度推进,则两指针在环开始位置相遇(Y)。
证明如下:
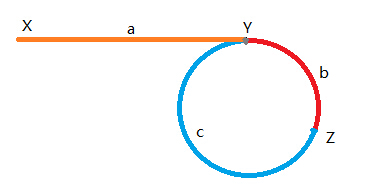
如下图所示,X,Y,Z分别为链表起始位置,环开始位置和两指针相遇位置,则根据快指针速度为慢指针速度的两倍,可以得出:
2*(a + b) = a + b + n * (b + c);即
a=(n - 1) * b + n * c = (n - 1)(b + c) +c;
注意到b+c恰好为环的长度,故可以推出,如将此时两指针分别放在起始位置和相遇位置,并以相同速度前进,当一个指针走完距离a时,另一个指针恰好走出
绕环n-1圈加上c的距离。
故两指针会在环开始位置相遇。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(head == NULL){
return 0;
}
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow == fast){
break;
}
}
if(fast == NULL || fast->next == NULL){
return NULL;
}
slow = head;
while(slow != fast){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
};
以上是关于Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, returnnull. 的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章