Matlab绘图高级部分
Posted hellowOOOrld
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Matlab绘图高级部分相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/jeromeblog/p/3396494.html
图形是呈现数据的一种直观方式,在用Matlab进行数据处理和计算后,我们一般都会以图形的形式将结果呈现出来。尤其在论文的撰写中,优雅的图形无疑会为文章加分。本篇文章非完全原创,我的工作就是把见到的Matlab绘图代码收集起来重新跑一遍,修改局部错误,然后将所有的图贴上来供大家参考。大家可以先看图,有看中的可以直接把代码Copy过去改成自己想要的。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
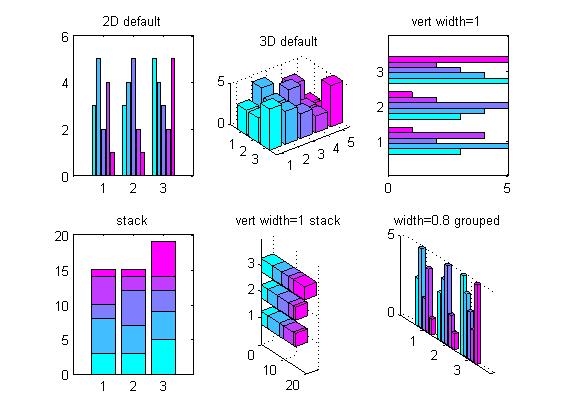
<br>%% 直方图图的绘制%直方图有两种图型:垂直直方图和水平直方图。而每种图型又有两种表现模式:累计式:分组式。figure;z=[3,5,2,4,1;3,4,5,2,1;5,4,3,2,5]; % 各因素的相对贡献份额colormap(cool);% 控制图的用色subplot(2,3,1);bar(z);%二维分组式直方图,默认的为\'group\'title(\'2D default\');subplot(2,3,2);bar3(z);%三维的分组式直方图title(\'3D default\');subplot(2,3,3);barh(z,1);%分组式水平直方图,宽度设置为1title(\'vert width=1\');subplot(2,3,4);bar(z,\'stack\');%累计式直方图,例如:1,1+2,1+2+3构成了第一个bartitle(\'stack\')subplot(2,3,5);bar3h(z,0.5,\'stacked\');%三维累计式水平直方图title(\'vert width=1 stack\');subplot(2,3,6);bar3(z,0.8,\'grouped\');%对相关数据的颜色进行分组,默认的位\'group\'title(\'width=0.8 grouped\'); |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
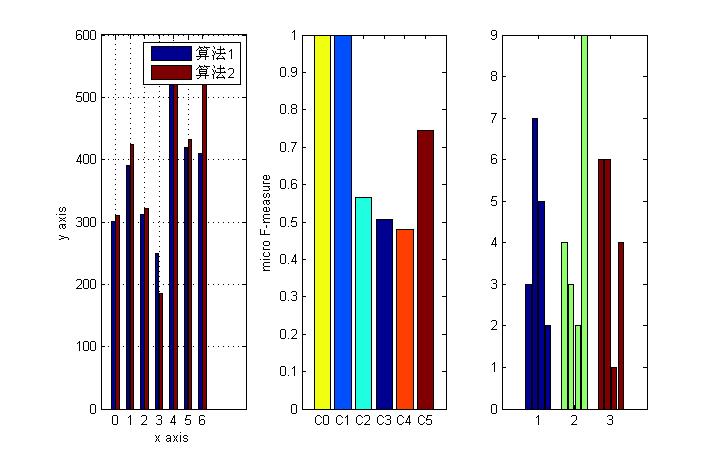
%% =========柱状图的进阶==========figure;y=[300 311;390 425; 312 321; 250 185; 550 535; 420 432; 410 520;];subplot(1,3,1);b=bar(y);grid on;set(gca,\'XTickLabel\',{\'0\',\'1\',\'2\',\'3\',\'4\',\'5\',\'6\'})legend(\'算法1\',\'算法2\');xlabel(\'x axis\');ylabel(\'y axis\');%使仅有的一组柱状图呈现不同颜色,默认的位相同颜色data = [1.0, 1.0, 0.565, 0.508, 0.481, 0.745];subplot(1,3,2);b = bar(data);ch = get(b,\'children\');set(ch,\'FaceVertexCData\',[4;2;3;1;5;6]);%使用Indexed形式指定每组bar的颜色set(gca,\'XTickLabel\',{\'C0\',\'C1\',\'C2\',\'C3\',\'C4\',\'C5\'})axis([0 7 0.0 1.0]);ylabel(\'micro F-measure\');%使每个bar颜色不同,默认的是每个元素在不同组的颜色相同data = [3, 7, 5, 2;4, 3, 2, 9;6, 6, 1, 4];subplot(1,3,3);b = bar(data);ch = get(b,\'children\');set(ch{1},\'FaceVertexCData\',[1;2;3]);%设置第一个元素在不同组的颜色set(ch{2},\'FaceVertexCData\',[1;2;3]);%设置第二个元素在不同组的颜色set(ch{3},\'FaceVertexCData\',[1;2;3]);set(ch{4},\'FaceVertexCData\',[1;2;3]); |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
%% 彩色柱状图%用到的数据n = 8;Z = rand(n,1);figure;%默认图片subplot(1,3,1);bar(Z);%简单的作图% 这个图根据数据列中值的大小着色。每列中的值越大,颜色越突出subplot(1,3,2);h=bar(Z);colormap(summer(n));ch = get(h,\'Children\');fvd = get(ch,\'Faces\');%针对矩阵时,只能用fvd=get(ch{col},\'Faces\'),下同fvcd = get(ch,\'FaceVertexCData\');[~, izs] = sortrows(Z,1);for i = 1:n row = izs(i); fvcd(fvd(row,:)) = i;endset(ch,\'FaceVertexCData\',fvcd)%图片会以渐变的方式着色,效果非常不错subplot(1,3,3);h=bar(Z);ch = get(h,\'Children\');fvd = get(ch,\'Faces\');fvcd = get(ch,\'FaceVertexCData\');[zs, izs] = sortrows(Z,1);k = 128; % 准备生成128 *3 行的colormapcolormap(summer(k)); % 这样会产生一个128 * 3的矩阵,分别代表[R G B]的值% 检视数据whos ch fvd fvcd zs izs% Name Size Bytes Class Attributes%% ch 1x1 8 double% fvcd 66x1 528 double% fvd 13x4 416 double% izs 13x1 104 double% zs 13x1 104 double%shading interp % Needed to graduate colorsfor i = 1:n color = floor(k*i/n); % 这里用取整函数获得color在colormap中行 row = izs(i); % Look up actual row # in data fvcd(fvd(row,1)) = 1; % Color base vertices 1st index fvcd(fvd(row,4)) = 1; fvcd(fvd(row,2)) = color; % Assign top vertices color fvcd(fvd(row,3)) = color;endset(ch,\'FaceVertexCData\', fvcd); % Apply the vertex coloringset(ch,\'EdgeColor\',\'k\'); |

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
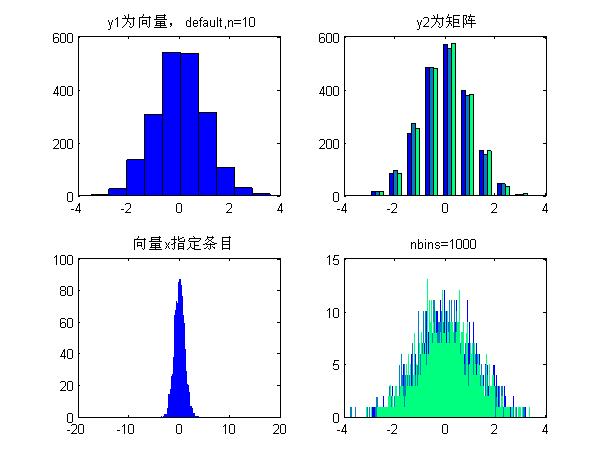
%% 绘制统计直方图%hist(y):如果y是向量,则把其中元素放入10个条目中,且返回每条中的元素的个数;如果y为矩阵,则分别对每列进行处理,显示多组条形。%[n,xout]=hist(y,x):非递减向量x的指定bin的中心。向量xout包含频率计数与条目的位置。x=-10:.1:10;y1=randn(2008,1);y2=randn(2008,3);figure;colormap(winter);subplot(2,2,1);hist(y1);%把其中元素放入10个条目中title(\'y1为向量,default,n=10\');subplot(2,2,2);hist(y2);%分别对每列进行处理,显示多组条形title(\'y2为矩阵\');subplot(2,2,3);hist(y1,x);%用户也可以使用[n,xout]=hist(y1,x);bar(xout,n)绘制条形直方图title(\'向量x指定条目\');subplot(2,2,4);hist(y2,1000);%第二个参数为标量时指定bin的数目title(\'nbins=1000\'); |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
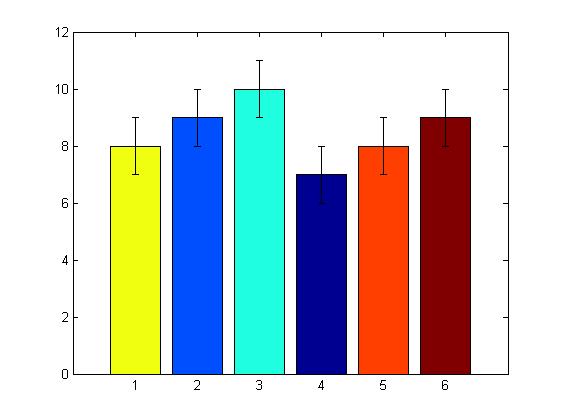
%% ========均值方差直方图========a=[8 9 10 7 8 9];%meanb=[1 1 1 1 1 1];%stdfigure();h=bar(a);ch=get(h,\'children\');set(ch,\'FaceVertexCData\',[4;2;3;1;5;6]);%使用Indexed形式指定每组bar的颜色hold on;errorbar(a,b,\'k\',\'LineStyle\',\'none\'); |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
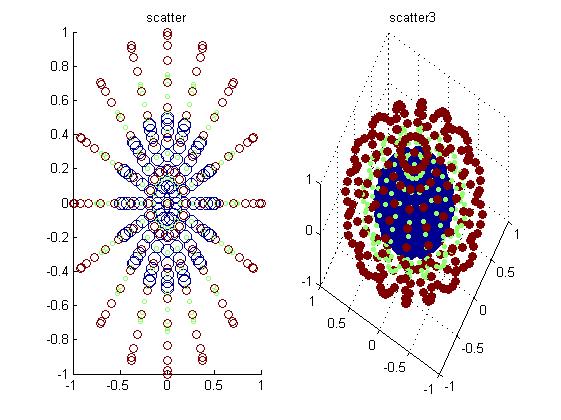
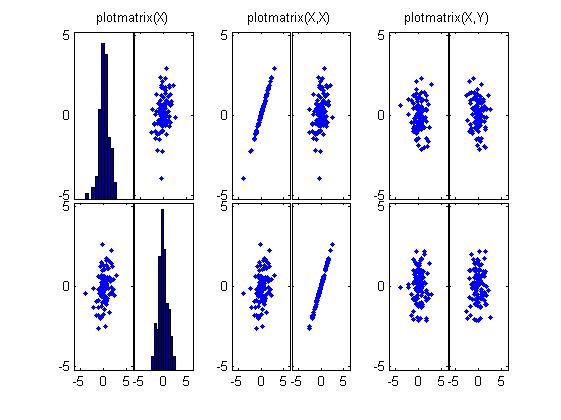
%% =======散点图scatter , scatter3 , plotmatrix======%scatter3(X,Y,Z,S,C):在由向量X、Y和Z指定的位置显示大小和颜色分别由S和C决定的离散点figure;[x,y,z] = sphere(16);X = [x(:)*.5 x(:)*.75 x(:)];Y = [y(:)*.5 y(:)*.75 y(:)];Z = [z(:)*.5 z(:)*.75 z(:)];S = repmat([10 2 5]*10,numel(x),1);C = repmat([1 2 3],numel(x),1);subplot(1,2,1);scatter(X(:),Y(:),S(:),C(:));title(\'scatter\');subplot(1,2,2);scatter3(X(:),Y(:),Z(:),S(:),C(:),\'filled\'), view(-60,60);title(\'scatter3\');%plotmatrix(X,Y)绘出X(p*M)与Y(p*N)的列组成的散度图(N,M)figure;X=randn(100,2);Y=randn(100,2); subplot(1,3,1),plotmatrix(X);%等价于plotmatrix(X,X),除了对角上的图为X每一列的直方图hist(X(:,col))title(\'plotmatrix(X)\');subplot(1,3,2),plotmatrix(X,X);title(\'plotmatrix(X,X)\');subplot(1,3,3),plotmatrix(X,Y);title(\'plotmatrix(X,Y)\'); |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
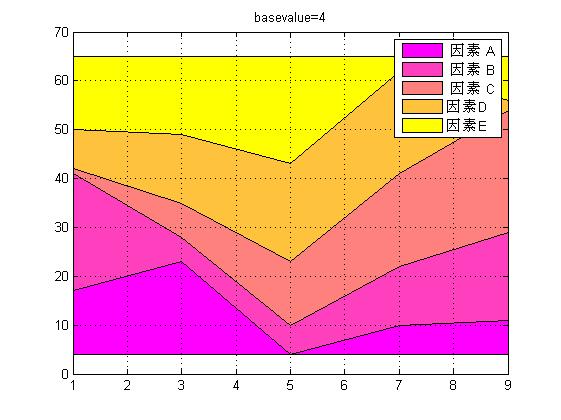
%% =========绘制区域图===========%区域图特点是:在图上绘制多条曲线时,每条曲线(除第一条外)都是把“前”条曲线作基线,再取值绘制而成。因此,该指令所画的图形,能醒目地反映各因素对最终结果的贡献份额。figure;x=1:2:9;% 注意:自变量要单调变化y=magic(5);% 各因素的相对贡献份额,每一列相当于一个因素colormap(spring);% 控制图的用色area(x,y,4);%area(y)则以列下标作为自变量,第三个参数为基准线(默认为0)set(gca,\'layer\',\'top\');%图层设置为top层,显示网格title(\'basevalue=4\');legend(\' 因素 A\',\' 因素 B\',\' 因素 C\',\'因素D\',\'因素E\');grid on; |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
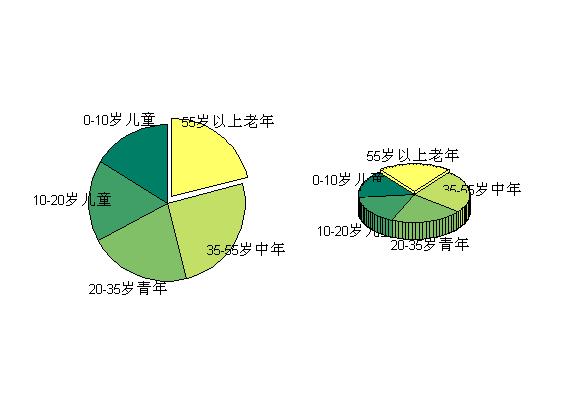
%% =========绘制饼状图=========%饼图指令pie和pie3用来表示各元素占总和的百分数。该指令第二个参数为与第一参数等长的 0-1%向量,1使对应扇块突出。第三个参数指定个扇区的labelfigure;colormap(summer);% 控制图的用色x=[16 17 21 25 21];subplot(1,2,1);pie(x,[0 0 0 0 1],{\'0-10岁儿童\',\'10-20岁儿童\',\'20-35岁青年\',\'35-55岁中年\',\'55岁以上老年\'});subplot(1,2,2);pie3(x,[0 0 0 0 1],{\'0-10岁儿童\',\'10-20岁儿童\',\'20-35岁青年\',\'35-55岁中年\',\'55岁以上老年\'}); |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
%% 绘制填色多边形。若每列的首尾元素不重合,则将默认把最后一点与第一点相连,强行使多边形封闭。%fill和fill3用于绘制填色多边形%fill(X1,Y1,C1,X2,Y2,C2,...)%fill3(X1,Y1,Z1,C1,X2,Y2,Z2,C2,...)%参数1和2为等长向量时,多边形的节点数由项链长度决定;而当其为矩阵时,每一列对应一个多边形%参数3为颜色(用颜色字符r/g/b/c或[r g b]表示)figure;colormap(autumn);% 控制图的用色n=10; % 多边形的边数dt=2*pi/n;t=0:dt:2*pi;t=[t,t(1)]; %fill 指令要求数据向量的首位重合,使图形封闭。x=sin(t);y=cos(t);subplot(1,2,1);fill(x,y,[1 1 0]);axis off % 画填色多边形,隐去坐标轴。X=[0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5;0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5;0 1 1 0]; Y=[0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5;0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5;0 0 1 1];Z=[1 1 1 1;0 0 0 0;0 0 0 0];C=[1 0 0 1;0 1 0 1;0 0 1 0];subplot(1,2,2);fill3(X,Y,Z,C);view([-10 55]);xlabel(\'x\'),ylabel(\'y\');box on;grid on; |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
%% =======绘制离散数据杆状图===========%stem和stem3函数用于绘制二维或三维的离散数据杆状图%stem(Y)可以理解成绘制离散点的plot(y)函数%stem(X,Y)可以理解成绘制离散点的plot(x,y)函数%stem(...,\'filled\')改变数据点显示的空、实状态。%stem(...,\'LINESPEC\')Linespec代表直线属性设置参量。x=1:.1:10;y=exp(x.*sin(x));figure;subplot(1,3,1);plot(x,y,\'.-r\');title(\'plot(x,y)\');subplot(1,3以上是关于Matlab绘图高级部分的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
|