Qt使用QCustomPlot开发
Posted 朱小勇
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Qt使用QCustomPlot开发相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、入门
1、下载源文件http://www.qcustomplot.com/;
2、把.cpp和.h放在工程目录下,并将cpp和h加入工程;
3、在.pro中:QT += printsupport;
4、在ui中添加一个Widget,右键提升为,输入:QCustomPlot,改变对象名称为customPlot;
5、加入代码:
void MainWindow::initUi()
{
QVector<double> x(101), y(101); // initialize with entries 0..100
for (int i=0; i<101; ++i)
{
x[i] = i/50.0 - 1; // x goes from -1 to 1
y[i] = x[i]*x[i]; // let\'s plot a quadratic function
}
ui->customPlot->addGraph();// 添加数据曲线(一个图像可以有多个数据曲线),graph(0);可以获取某个数据曲线(按添加先后排序);默认x1,y1轴
ui->customPlot->addGraph(ui->customPlot->xAxis,ui->customPlot->yAxis2);//添加的曲线以x1,y2为基准轴
ui->customPlot->graph(0)->setData(x, y);// setData();为数据曲线关联数据
ui->customPlot->xAxis->setLabel("x");// 为坐标轴添加标签
ui->customPlot->yAxis->setLabel("y");
ui->customPlot->xAxis->setRange(-1, 1);// 设置坐标轴的范围,以看到所有数据
ui->customPlot->yAxis->setRange(-1, 1);
ui->customPlot->replot();// 重画图像
//ui->customPlot->rescaleAxes();//自动设置最合适的显示范围
//ui->customPlot->setInteractions(QCP::iRangeDrag | QCP::iRangeZoom);//可移动可拖放
//ui->customPlot->graph(0)->addData(double,double);//追加点
}
效果:

6:、添加QCustomPlot的帮助文档
在下载的源码包里有个qch文件,放在:D:\\QT5.8\\Docs\\Qt-5.8里面,就可以使用帮助文档了
ps:
1、设置x坐标轴为时间
int showTime=60;//60秒 QDateTime dateTime = QDateTime::currentDateTime(); double now = dateTime.toTime_t(); QSharedPointer<QCPAxisTickerDateTime> xTicker(new QCPAxisTickerDateTime); xTicker->setTickCount(2); xTicker->setDateTimeFormat("yyyy.MM.dd-hh:mm");// ui->customPlot_4_1->xAxis->setTicker(xTicker); xTicker->setTickStepStrategy(QCPAxisTicker::tssMeetTickCount); ui->customPlot_4_1->xAxis->setRange(now-showTime,now+showTime);//显示多久的数据,前后60秒
最小单位是秒

2、设置位置
setPositionAlignment(Qt::AlignTop)
3、坐标轴刻度样式

使用QCPAxis::setTicker (QSharedPointer< QCPAxisTicker > )来定制刻度
4、设置刻度高度
setTickLength
5、设置坐标轴样式
setUpperEnding

6、设置两个线条之间填充
ui->customplot->graph(0)->setBrush(Qt::cyan);
ui->customplot->graph(0)->setChannelFillGraph(ui->customplot_2_1->graph(1));
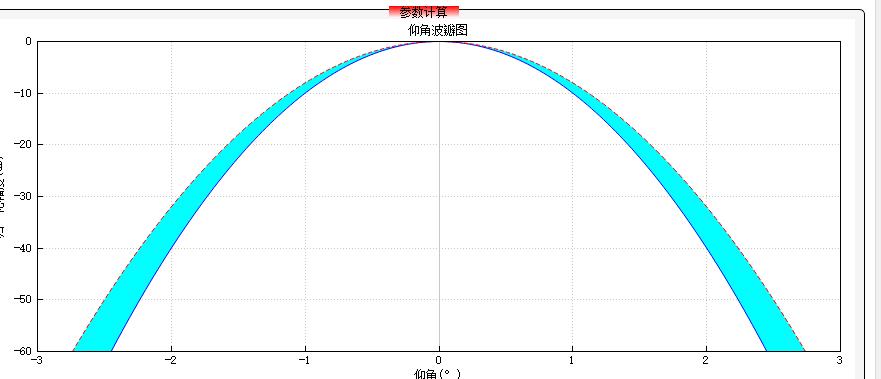
7、设置曲线形状
QCPGraph::setScatterStyle(QCPScatterStyle &style);
8、坐标轴相关参数命名
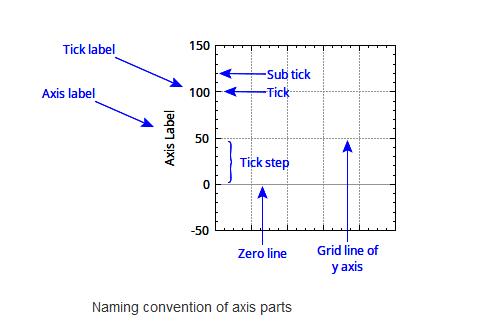
9、坐标区相关距离命名

9.1、设置整个cp坐标轴距离左侧的距离
ui.customPlot->yAxis->setPadding(40);//距离左边的距离
10、设置刻度label旋转
ui.customPlot->xAxis->setTickLabelRotation(60);

11、设置坐标轴方向
ui.customPlot->xAxis->setRangeReversed(false);//x轴反向
12、获取当前x、y轴range的左右值
realLeft = ui.customPlot->xAxis->range().lower;
realRight = ui.customPlot->xAxis->range().upper;
13、设置当前显示范围有多少个刻度
ticker->setTickCount(n);
ui->customplot_2_3->xAxis->ticker()->setTickCount(5);
14、设置长刻度步长
QCPAxisTickerFixed ticker->setTickStep(0.1);
15、时间轴定制
QDateTime dateTime = QDateTime::currentDateTime(); double now = dateTime.toTime_t(); QSharedPointer<QCPAxisTickerDateTime> yTicker(new QCPAxisTickerDateTime); yTicker->setTickCount(2); yTicker->setDateTimeFormat("yyyy.MM.dd-hh:mm");// ui->customPlot->xAxis->setTicker(yTicker); yTicker->setTickStepStrategy(QCPAxisTicker::tssMeetTickCount); ui->customPlot->xAxis->setRange(now-3600,now+3600);//显示3个小时的数据
默认tickStep为1s,所以没有setTickStep函数进行设置
一般坐标轴定制需要两个参数:坐标轴显示范围【range】;此坐标轴有多少个刻度【setTickCount】
16、QCPAbstractItem

17、绘制一个点后跳过2个点
customPlot->graph(0)->setScatterSkip(2);
18、设置位置
①、
itemText_2_2->position->setType(QCPItemPosition::ptPlotCoords);//以坐标点为参考
itemText_2_2->position->setCoords(100,200);//x=100,y=200
②、
itemText_2_2->position->setType(QCPItemPosition::ptAxisRectRatio);//用0~1比例代表整个plot
itemText_2_2->position->setCoords(1,1);//右下角
18、legend设置透明
ui->customplot_5_1->legend->setBrush(QColor(255,255,255,0));
19、清空某个线条已经绘制了的数据【线不回收】
pPlot->graph(0)->data().data()->clear();
注意有两个data
20、设置背景透明
ui->customplot_deduce_radar->setBackground(Qt::transparent); ui->customplot_deduce_radar->setStyleSheet("background: transparent;");
参考:https://www.pianshen.com/article/60931360320/
二、高级
1、单级柱状图【只有一种颜色】
①、Bar声明
QCPBars *cpBar;
②、定义
cpBar = new QCPBars(ui.customPlot->xAxis, ui.customPlot->yAxis);
③、设置值
QVector<double> ticks;//定制值
ticks << 1 << 2 << 3 << 4;
QVector<double> yCount;
yCount<<2<<3<<3<<1;
cpBar->setData(ticks, yCount);
ui.customPlot->replot();
④、效果

2、多级柱状图
先看效果【官网】
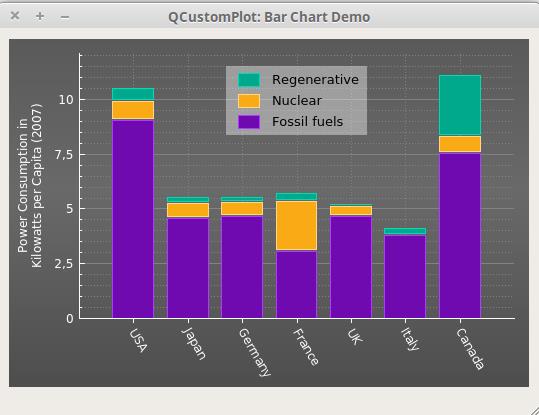
①、声明
QCPBars *max;
QCPBars *min;
QCPBars *sdDev;
QCPBars *varice;
②、定义
max = new QCPBars(ui.customPlot->xAxis, ui.customPlot->yAxis);
min = new QCPBars(ui.customPlot->xAxis, ui.customPlot->yAxis);
sdDev = new QCPBars(ui.customPlot->xAxis, ui.customPlot->yAxis);
varice = new QCPBars(ui.customPlot->xAxis, ui.customPlot->yAxis);
③、相关设置
max->setStackingGap(0);//设置上下bar之间的距离
min->setStackingGap(0);
sdDev->setStackingGap(0);
varice->setStackingGap(0);
max->setAntialiased(false); //提供更清晰、像素对齐的条形边框
min->setAntialiased(false);
sdDev->setAntialiased(false);
varice->setAntialiased(false);
sdDev->moveAbove(varice);//必须要写和这个,不然不会重叠
min->moveAbove(sdDev);//设置位置
max->moveAbove(min);
④、设置值
QVector<double> ticks;//定制值
ticks << 1 << 2 << 3 << 4;
QVector<double> yCount;
yCount<<2<<3<<3<<1;
max->setData(ticks, yCount);
min->setData(ticks, yCount);
varice->setData(ticks, yCount);
sdDev->setData(ticks, yCount);
ui.customPlot->replot();
3、更好看的网格线
①、默认

②、定制
ui.customPlot->xAxis->grid()->setVisible(true);
ui.customPlot->xAxis->grid()->setPen(QPen(QColor(130, 130, 130), 0, Qt::DotLine));
ui.customPlot->yAxis->grid()->setSubGridVisible(true);
ui.customPlot->yAxis->grid()->setPen(QPen(QColor(130, 130, 130), 0, Qt::SolidLine));
ui.customPlot->yAxis->grid()->setSubGridPen(QPen(QColor(130, 130, 130), 0, Qt::DotLine));

4、鼠标事件
头文件中:
void myMousePressEvent(QMouseEvent *event);
void myMouseReleaseEvent(QMouseEvent *event);
绑定:
connect(ui.customPlot, SIGNAL(mousePress(QMouseEvent*)), this, SLOT(myMousePressEvent(QMouseEvent*)));
connect(ui.customPlot, SIGNAL(mouseRelease(QMouseEvent*)), this, SLOT(myMouseReleaseEvent(QMouseEvent*)));
实现:
void RoadAllData::myMousePressEvent(QMouseEvent *event)
{
if (event->button() != Qt::LeftButton)return;//如果不是鼠标左键按下则返回
int x_pos = event->pos().x();
int y_pos = event->pos().y();
// 把鼠标坐标点 转换为 QCustomPlot 内部坐标值 (pixelToCoord 函数)
// coordToPixel 函数与之相反 是把内部坐标值 转换为外部坐标点
double x_val = ui.customPlot->xAxis->pixelToCoord(x_pos);
double y_val = ui.customPlot->yAxis->pixelToCoord(y_pos);
}
void RoadAllData::myMouseReleaseEvent(QMouseEvent *event)
{
if (event->button() != Qt::LeftButton)return;
}
5、textitem的使用
①、声明
QCPItemText* itemText = NULL;
②、定义
QCPItemText* itemText = new QCPItemText(ui->customplot_1_1); itemText->setPositionAlignment(Qt::AlignHCenter | Qt::AlignBottom);//以哪个位置为标准 itemText->position->setType(QCPItemPosition::ptAxisRectRatio);//以屏幕可见范围为参考 itemText->position->setCoords(0.5, 0.95); //位置,从坐标矩形左上开始为(0,0),右下角为(1,1),x是向右,y是向下 itemText->setFont(QFont(font().family(), 12)); //字体库,大小 itemText->setTextAlignment(Qt::AlignLeft); #if CLOSE_IF itemText->setPen(QPen(Qt::black)); //边框 #endif itemText->setText("增益下降0.225dB\\n指向偏离0°\\n波束展宽4.9954%\\n副瓣抬高7.353dB");// itemText->setBrush(QBrush(QColor("#C4DDC3")));//背景色 itemText->setPadding(QMargins(3, 3, 3, 3));
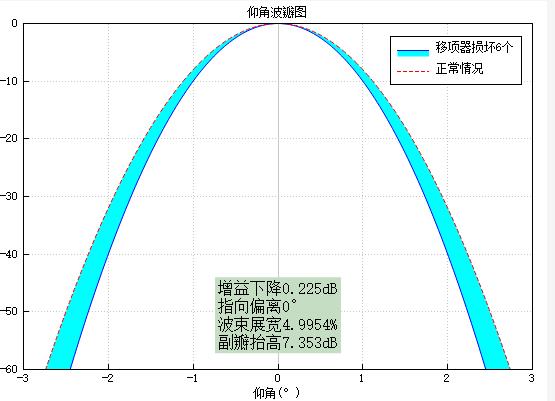
相关设置可参考:https://blog.csdn.net/umke888/article/details/54572647
③、设置值
itemText->setText("......");
6、QSlider与显示range对应
①、使用QSlider,按下、释放、获取值
QObject::connect(ui.horizontalSlider, SIGNAL(valueChanged(int)), this, SLOT(sliderMovedSlot(int))); QObject::connect(ui.horizontalSlider, SIGNAL(sliderPressed()), this, SLOT(sliderPressSlot())); QObject::connect(ui.horizontalSlider, SIGNAL(sliderReleased()), this, SLOT(sliderReleaseSlot()));
②、通过设置range来显示Customplot当前位置
ui.customPlot->xAxis->setRange(realMax, realMax );
7、例子,在线用户数统计
ui->customplot_online->setBackground(QColor(34,38,72)); ui->customplot_online->xAxis->setBasePen(QPen(QColor(34,38,72))); ui->customplot_online->yAxis->setBasePen(QPen(Qt::white)); ui->customplot_online->xAxis2->setBasePen(QPen(QColor(34,38,72))); ui->customplot_online->yAxis2->setBasePen(QPen(QColor(34,38,72))); ui->customplot_online->xAxis->setTickLabelColor(Qt::white); ui->customplot_online->yAxis->setTickLabelColor(Qt::white); ui->customplot_online->xAxis->setRange(0,8); ui->customplot_online->yAxis->setRange(0,10); ui->customplot_online->xAxis->setSubTicks(false);
ui->customplot_online->xAxis->setTickLabels(false);
ui->customplot_online->legend->setBrush(QColor(255,255,255,50));//铭牌样式;透明
ui->customplot_online->legend->setVisible(true);
ui->customplot_online->legend->setTextColor(QColor(255,255,255));
ui->customplot_online->legend->setBorderPen(QColor(255,0,0));
ui->customplot_online->axisRect()->insetLayout()->setInsetAlignment(0, Qt::AlignLeft|Qt::AlignTop);//设置铭牌位置
ui->customplot_online->addGraph()->setName("运控用户");
ui->customplot_online->addGraph()->setName("监控用户");
ui->customplot_online->addGraph()->setName("运维用户");
QPen pen; pen.setWidth(2);//线宽 pen.setStyle(Qt::PenStyle::DashLine);//虚线
pen.setColor(Qt::yellow); ui->customplot_online->graph(0)->setPen(pen);
pen.setColor(Qt::white); ui->customplot_online->graph(1)->setPen(pen);
pen.setColor(Qt::green); ui->customplot_online->graph(2)->setPen(pen);
ui->customplot_online->graph(0)->setLineStyle(QCPGraph::lsLine);
ui->customplot_online->graph(0)->setScatterStyle(QCPScatterStyle(QCPScatterStyle::ScatterShape::ssDisc,5));
ui->customplot_online->graph(1)->setLineStyle(QCPGraph::lsLine);
ui->customplot_online->graph(1)->setScatterStyle(QCPScatterStyle(QCPScatterStyle::ScatterShape::ssDisc,5));
ui->customplot_online->graph(2)->setLineStyle(QCPGraph::lsLine);
ui->customplot_online->graph(2)->setScatterStyle(QCPScatterStyle(QCPScatterStyle::ScatterShape::ssDisc,5));
QVector<double> x,y1,y2,y3; // initialize with entries 0..100
x << 0 << 1 << 2 << 3 << 4 << 5;
y1 << 3 << 4 << 6 << 7 << 9 << 8;
y2 << 1 << 2 << 3 << 5 << 6 << 9;
y3 << 3 << 5 << 6 << 4 << 3 << 5;
ui->customplot_online->graph(0)->setData(x,y1);
ui->customplot_online->graph(1)->setData(x,y2);
ui->customplot_online->graph(2)->setData(x,y3);
ui->customplot_online->replot();

8、tick和subtick的区别

9、例子
QFont font; font.setFamily("Microsoft YaHei"); font.setPixelSize(12); ui->customplot->setBackground(QColor(1,23,68)); ui->customplot->xAxis->setBasePen(QPen(QColor(202,241,255))); ui->customplot->yAxis->setBasePen(QPen(QColor(202,241,255))); ui->customplot->xAxis->setTickLabelColor(QColor(202,241,255)); ui->customplot->yAxis->setTickLabelColor(QColor(202,241,255)); ui->customplot->xAxis->setRange(0,16); ui->customplot->yAxis->setRange(0,219); ui->customplot->yAxis->ticker()->setTickCount(10); ui->customplot->xAxis->setSubTicks(false); ui->customplot->yAxis->setSubTicks(false); ui->customplot->xAxis->grid()->setVisible(false); ui->customplot->yAxis->grid()->setPen(QPen(QColor(22,44,85), 0, Qt::SolidLine)); ui->customplot->xAxis->setTickPen(QPen(QColor(202,241,255))); ui->customplot->xAxis->setTickLength(0); ui->customplot->yAxis->setTickPen(QPen(QColor(202,241,255))); ui->customplot->yAxis->setTickLength(0); ui->customplot->xAxis->setTickLabelFont(font); ui->customplot->yAxis->setTickLabelFont(font); missionBarTotal = new CustomBars(ui->customplot->xAxis,ui->customplot->yAxis); missionBarZS = new CustomBars(ui->customplot->xAxis,ui->customplot->yAxis); missionBarZC = new CustomBars(ui->customplot->xAxis,ui->customplot->yAxis); missionBarTotal->setFont(font);missionBarTotal->setSpacing(0); missionBarZS->setFont(font);missionBarZS->setSpacing(0); missionBarZC->setFont(font);missionBarZC->setSpacing(0); missionBarTotal->setAntialiased(false); missionBarZS->setAntialiased(false); missionBarZC->setAntialiased(false); missionBarTotal->setPen(QPen(QColor(36,201,217))); missionBarTotal->setBrush(QColor(36,201,217)); missionBarZS->setPen(QPen(QColor(59,172,131))); missionBarZS->setBrush(QColor(59,172,131)); missionBarZC->setPen(QPen(QColor(189,143,43))); missionBarZC->setBrush(QColor(189,143,43)); QVector<double> ticks; ticks << 3 << 8 << 13; QVector<QString> labels;//坐标轴定制 labels << "总任务数" << "ZS任务数" << "ZC任务数"; QSharedPointer<QCPAxisTickerText> textTicker(new QCPAxisTickerText); textTicker->addTicks(ticks,labels); ui->customplot->xAxis->setTicker(textTicker);

10、上面使用到的每个Bar,是继承QCpbar之后重写设置的,继承后的类名为:CustomBars
①、头文件
#ifndef CUSTOMBARS_H #define CUSTOMBARS_H #pragma once #include <QWidget> #include "qcustomplot.h" class CustomBars : public QCPBars { Q_OBJECT public: explicit CustomBars(QCPAxis *keyAxis, QCPAxis *valueAxis); Qt::Alignment textAligment() const { return mTextAlignment; } double spacing() const { return mSpacing; } QFont font() const { return mFont; } void setTextAlignment(Qt::Alignment alignment); void setSpacing(double spacing); void setFont(const QFont &font); void setTextValue(const QString& value){ mTextValue = value; } protected: Qt::Alignment mTextAlignment; // 文字对齐方式 double mSpacing = 10; // 文字与柱状图的间距,这里按像素大小 QFont mFont; // 文字使用的字体 QString mTextValue; virtual void draw(QCPPainter *painter) Q_DECL_OVERRIDE; }; #endif // CUSTOMBARS_H
②、cpp
#include "custombars.h" CustomBars::CustomBars(QCPAxis *keyAxis, QCPAxis *valueAxis) : QCPBars(keyAxis, valueAxis), mTextAlignment(Qt::AlignCenter), mSpacing(5), mFont(QFont(QLatin1String("sans serif"), 12)) { } void CustomBars::setTextAlignment(Qt::Alignment alignment) { mTextAlignment = alignment; } void CustomBars::setSpacing(double spacing) { mSpacing = spacing; } void CustomBars::setFont(const QFont &font) { mFont = font; } void CustomBars::draw(QCPPainter *painter) { if (!mKeyAxis || !mValueAxis) { qDebug() << Q_FUNC_INFO << "invalid key or value axis"; return; } if (mDataContainer->isEmpty()) return; QCPBarsDataContainer::const_iterator visibleBegin, visibleEnd; getVisibleDataBounds(visibleBegin, visibleEnd); // loop over and draw segments of unselected/selected data: QList<QCPDataRange> selectedSegments, unselectedSegments, allSegments; getDataSegments(selectedSegments, unselectedSegments); allSegments << unselectedSegments << selectedSegments; for (int i = 0; i < allSegments.size(); ++i) { bool isSelectedSegment = i >= unselectedSegments.size(); QCPBarsDataContainer::const_iterator begin = visibleBegin; QCPBarsDataContainer::const_iterator end = visibleEnd; mDataContainer->limitIteratorsToDataRange(begin, end, allSegments.at(i)); if (begin == end) continue; for (QCPBarsDataContainer::const_iterator it = begin; it != end; ++it) { // draw bar: if (isSelectedSegment && mSelectionDecorator) { mSelectionDecorator->applyBrush(painter); mSelectionDecorator->applyPen(painter); } else { painter->setBrush(mBrush); painter->setPen(mPen); } applyDefaultAntialiasingHint(painter); QRectF barRect = getBarRect(it->key, it->value); //自己加的 painter->drawPolygon(barRect); // 以上是拷贝的源码部分 painter->drawPolygon(barRect); // 我们仅需在 painter->drawPolygon(barRect); 这行下增加以下的内容即可 // 计算文字的位置 painter->setFont(mFont); // 设置字体 //QString text = QString::number(it->value); // 取得当前value轴的值,保留两位精度 QString text = mTextValue; QRectF textRect = painter->fontMetrics().boundingRect(0, 0, 0, 0, Qt::TextDontClip | mTextAlignment, text); // 计算文字所占用的大小 if (mKeyAxis.data()->orientation() == Qt::Horizontal) { // 当key轴为水平轴的时候 if (mKeyAxis.data()->axisType() == QCPAxis::atTop) // 上轴,移动文字到柱状图下面 textRect.moveTopLeft(barRect.bottomLeft() + QPointF(0, mSpacing)); else // 下轴,移动文字到柱状图上面 textRect.moveBottomLeft(barRect.topLeft() - QPointF(0, mSpacing)); textRect.setWidth(barRect.width()); painter->drawText(textRect, Qt::TextDontClip | mTextAlignment, text); } else { // 当key轴为竖直轴的时候 if (mKeyAxis.data()->axisType() == QCPAxis::atLeft) // 左轴,移动文字到柱状图右边 textRect.moveTopLeft(barRect.topRight() + QPointF(mSpacing, 0)); else // 右轴,移动文字到柱状图左边 textRect.moveTopRight(barRect.topLeft() - QPointF(mSpacing, 0)); textRect.setHeight(barRect.height()); painter->drawText(textRect, Qt::TextDontClip | mTextAlignment, text); } } } }
这里参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40501206/article/details/108065801?utm_medium=distribute.pc_aggpage_search_result.none-task-blog-2~all~first_rank_v2~rank_v28-18-108065801.nonecase&utm_term=qcustomplot%E6%B7%BB%E5%8A%A0%E6%96%87%E5%AD%97&spm=1000.2123.3001.4430
可参考:
1、线样式:https://blog.csdn.net/yxy244/article/details/100033549
2、设置线的颜色等,只能通过先构造pen,不能返回QPen再设置,可以理解为本身是没有QPen对象的,需要先设置,否则返回的是无意义的

以上是关于Qt使用QCustomPlot开发的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章