使用Kinect2.0控制VREP中的虚拟模型
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了使用Kinect2.0控制VREP中的虚拟模型相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
VREP中直接设置物体姿态的函数有3个:
- simSetObjectOrientation:通过欧拉角设置姿态
- simSetObjectQuaternion:通过四元数设置姿态
- simSetObjectMatrix:通过旋转矩阵设置姿态(同时也可以设置位置)
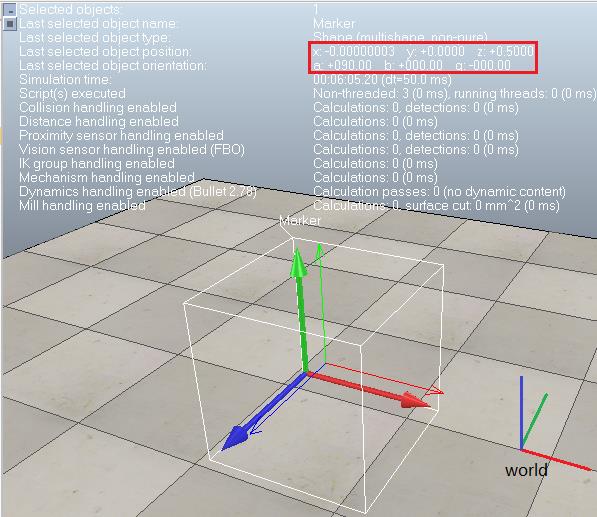
下面将一个坐标系绕X轴旋转90°,则可以分别使用欧拉角、四元数或变换矩阵实现:
handle=simGetObjectHandle(\'Marker\') local eulerAngles = {math.pi/2, 0, 0} -- X-Y-Z Euler angles local quaternion = {0.707, 0, 0, 0.707} -- {x,y,z,w} local matrix = {1,0,0,0, 0,0,-1,0, 0,1,0,0.5} simSetObjectOrientation(handle, -1, eulerAngles) --simSetObjectQuaternion(handle, -1, quaternion) --simSetObjectMatrix(handle, -1, matrix)
-
球关节
Spherical joints have three DoF and are used to describe rotational movements (with 3 DoF) between objects. Their configuration is defined by three values that represent the amount of rotation around their first reference frame\'s x-, y- and z-axis. The three values that define a spherical joint\'s configuration are specified as Euler angles. In some situations, a spherical joint can be thought of as 3 concurrent and orthogonal to each other joints, that are parented in a hierarchy-chain. Spherical joints are always passive joints, and cannot act as motors.
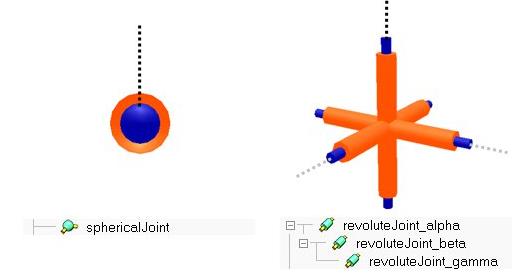
[Two equivalent mechanisms (in this configuration): spherical joint (left) and 3 revolute joints (right)]
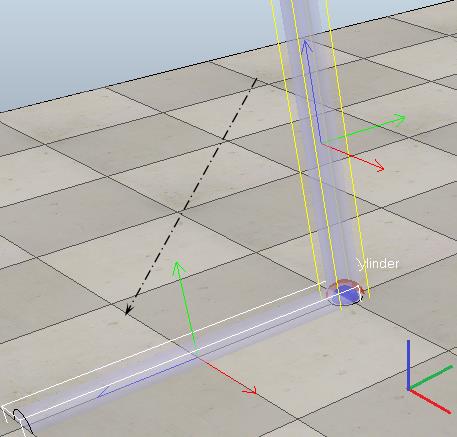
在场景中创建一个球关节和一个连杆(处于竖直状态),将连杆拖到球关节下面作为其子节点,球关节设置为Passive模式。下面的代码控制了球关节的姿态,使用simSetSphericalJointMatrix函数设置关节旋转矩阵,使得连杆绕X轴旋转90°
handle=simGetObjectHandle(\'Spherical_joint\') local matrix = {1,0,0,0, 0,0,-1,0, 0,1,0,0} -- the translational components will be ignored -- Sets the intrinsic orientation matrix of a spherical joint object. This function cannot be used with non-spherical joints simSetSphericalJointMatrix(handle, matrix)
- C++客户端程序与VREP通信
进行C++客户端程序与VREP服务端通信,需要对工程进行如下配置:
1. 在项目中包含下列文件(可以在V-REP安装路径的programming/remoteApi文件夹下找到这些文件)
- extApi.h
- extApi.c
- extApiPlatform.h (contains platform specific code)
- extApiPlatform.c (contains platform specific code)
2. 在项目属性-->C/C++-->预处理器-->预处理器定义中定义:NON_MATLAB_PARSING 和 MAX_EXT_API_CONNECTIONS=255

3. 在项目属性-->C/C++-->常规-->附加包含目录中包含:
C:\\Program Files\\V-REP3\\V-REP_PRO_EDU\\programming\\include
C:\\Program Files\\V-REP3\\V-REP_PRO_EDU\\programming\\remoteApi
下面创建一个简单的场景使用Kinect来控制NAO机器人头部的运动。具体步骤是获得Neck关节的姿态四元数后将其转换为欧拉角,经过适当转换后通过simxSetJointPosition函数直接设置转动关节的角度(关节要设置为Passive模式)。如果不通过关节来控制头部的运动也可以直接采用上面提到的SetObjectOrientation、SetObjectQuaternion或SetObjectMatrix方式来设置头部姿态。需要注意的是Kinect的Head关节为末端节点,不包含姿态信息,因此这里采用了Neck关节的姿态来控制头部,但效果不是很好。如果想直接获取头部姿态,可以参考Kinect for Windows SDK 2.0中的HD Face Basics例子,其中FaceFrameResult Class可以获取代表面部姿态的四元数:
hr = pFaceFrameResult -> get_FaceRotationQuaternion(&faceRotation);
下面是一些与之相关的代码。最容易出错的部分是在于Kinect坐标系和VREP坐标系的姿态不一样,因此获得的角度要经过适当转换:Kinect中头部左右摇摆是绕Y轴,而VREP中是绕Z轴;Kinect中头向上仰为绕X轴正方向,而VREP中头向上仰是绕Y轴负方向...

#define PI 3.1415926 int Sign(double x) { if (x < 0) return -1; else return 1; } float R2D(float angle){ return angle * 180.0 / PI; } enum RotSeq{ zyx, xyz }; // 欧拉角旋转次序 CameraSpacePoint CBodyBasics::QuaternionToEuler(Vector4 q, RotSeq rotSeq) { CameraSpacePoint euler = { 0 }; const double Epsilon = 0.0009765625f; const double Threshold = 0.5f - Epsilon; switch (rotSeq) { case zyx: // Z-Y-X Euler angles(RPY angles) { double TEST = q.w*q.y - q.x*q.z; if (TEST < -Threshold || TEST > Threshold) // 奇异姿态,俯仰角为±90° { int sign = Sign(TEST); euler.Z = -2 * sign * (double)atan2(q.x, q.w); // yaw euler.Y = sign * (PI / 2.0); // pitch euler.X = 0; // roll } else { euler.X = atan2(2 * (q.y*q.z + q.w*q.x), q.w*q.w - q.x*q.x - q.y*q.y + q.z*q.z); // roll euler.Y = asin(-2 * (q.x*q.z - q.w*q.y)); // pitch euler.Z = atan2(2 * (q.x*q.y + q.w*q.z), q.w*q.w + q.x*q.x - q.y*q.y - q.z*q.z); // yaw } } break; case xyz: // X-Y-Z Euler angles { double TEST = q.x*q.z + q.w*q.y; if (TEST < -Threshold || TEST > Threshold) // 奇异姿态,俯仰角为±90° { int sign = Sign(TEST); euler.X = 2 * sign * (double)atan2(q.x, q.w); euler.Y = sign * (PI / 2.0); euler.Z = 0; } else { euler.X = atan2(-2 * (q.y*q.z - q.w*q.x), q.w*q.w - q.x*q.x - q.y*q.y + q.z*q.z); euler.Y = asin(2 * (q.x*q.z + q.w*q.y)); euler.Z = atan2(-2 * (q.x*q.y - q.w*q.z), q.w*q.w + q.x*q.x - q.y*q.y - q.z*q.z); } } } return euler; } /// Handle new body data void CBodyBasics::ProcessBody(IBody* pBody) { HRESULT hr; BOOLEAN bTracked = false; hr = pBody->get_IsTracked(&bTracked); // Retrieves a boolean value that indicates if the body is tracked if (SUCCEEDED(hr) && bTracked) // 判断是否追踪到骨骼 { Joint joints[JointType_Count]; JointOrientation jointOrientations[JointType_Count]; HandState leftHandState = HandState_Unknown; HandState rightHandState = HandState_Unknown; DepthSpacePoint *depthSpacePosition = new DepthSpacePoint[_countof(joints)]; // 存储深度坐标系中的关节点位置 pBody->get_HandLeftState(&leftHandState); // 获取左右手状态 pBody->get_HandRightState(&rightHandState); hr = pBody->GetJointOrientations(_countof(joints), jointOrientations); // 获取joint orientation if (SUCCEEDED(hr)) { CameraSpacePoint euler = QuaternionToEuler(jointOrientations[JointType_Neck].Orientation, xyz); // 四元数转换为X-Y-Z欧拉角 simxSetJointPosition(clientID, Handle_Yaw, euler.Y, simx_opmode_oneshot); // 控制头部左右摆动 simxSetJointPosition(clientID, Handle_Pitch, PI-euler.X, simx_opmode_oneshot); // 控制头部俯仰 extApi_sleepMs(5); } hr = pBody->GetJoints(_countof(joints), joints); // 获得25个关节点 if (SUCCEEDED(hr)) { // Filtered Joint filter.Update(joints); const DirectX::XMVECTOR* vec = filter.GetFilteredJoints(); // Retrive Filtered Joints for (int type = 0; type < JointType_Count; type++) { if (joints[type].TrackingState != TrackingState::TrackingState_NotTracked) { float x = 0.0f, y = 0.0f, z = 0.0f; // Retrieve the x/y/z component of an XMVECTOR Data and storing that component\'s value in an instance of float referred to by a pointer DirectX::XMVectorGetXPtr(&x, vec[type]); DirectX::XMVectorGetYPtr(&y, vec[type]); DirectX::XMVectorGetZPtr(&z, vec[type]); CameraSpacePoint cameraSpacePoint = { x, y, z }; m_pCoordinateMapper->MapCameraPointToDepthSpace(cameraSpacePoint, &depthSpacePosition[type]); } } DrawBody(joints, depthSpacePosition); DrawHandState(depthSpacePosition[JointType_HandLeft], leftHandState); DrawHandState(depthSpacePosition[JointType_HandRight], rightHandState); } delete[] depthSpacePosition; } cv::imshow("skeletonImg", skeletonImg); cv::waitKey(5); // 延时5ms /// Constructor CBodyBasics::CBodyBasics() : m_pKinectSensor(NULL), m_pCoordinateMapper(NULL), m_pBodyFrameReader(NULL) { clientID = simxStart((simxChar*)"127.0.0.1", 19999, true, true, 2000, 5); // 连接VREP服务端 if (clientID != -1) { std::cout << "Connected to remote API server" << std::endl; // Send some data to V-REP in a non-blocking fashion: simxAddStatusbarMessage(clientID, "Connected to V-REP!", simx_opmode_oneshot); Handle_Yaw = 0; Handle_Pitch = 0; simxGetObjectHandle(clientID, "HeadYaw", &Handle_Yaw, simx_opmode_oneshot_wait); // 获取VREP中Yaw关节的句柄 simxGetObjectHandle(clientID, "HeadPitch", &Handle_Pitch, simx_opmode_oneshot_wait); // 获取VREP中Pitch关节句柄 } } /// Destructor CBodyBasics::~CBodyBasics() { SafeRelease(m_pBodyFrameReader); SafeRelease(m_pCoordinateMapper); if (m_pKinectSensor) { m_pKinectSensor->Close(); } SafeRelease(m_pKinectSensor); // Close the connection to V-REP: simxFinish(clientID); }
另外还有一个问题就是原始数据的抖动比较大,头部旋转的时候不够平滑,有很多种滤波方式可以解决这一问题。最简单的移动平均滤波参考代码如下:

#include <iostream> #include <stddef.h> #include <assert.h> using std::cout; using std::endl; // Simple_moving_average class SMA { public: SMA(unsigned int period) :period(period), window(new double[period]), head(NULL), tail(NULL), total(0) { assert(period >= 1); } ~SMA() { delete[] window; } // Adds a value to the average, pushing one out if nescessary void add(double val) { // Special case: Initialization if (head == NULL) { head = window; *head = val; tail = head; inc(tail); total = val; return; } // Were we already full? if (head == tail) { // Fix total-cache total -= *head; // Make room inc(head); } // Write the value in the next spot. *tail = val; inc(tail); // Update our total-cache total += val; } // Returns the average of the last P elements added to this SMA. // If no elements have been added yet, returns 0.0 double avg() const { ptrdiff_t size = this->size(); if (size == 0) return 0; // No entries => 0 average return total / (double)size; // Cast to double for floating point arithmetic } private: unsigned int period; double * window; // Holds the values to calculate the average of. // Logically, head is before tail double * head; // Points at the oldest element we\'ve stored. double * tail; // Points at the newest element we\'ve stored. double total; // Cache the total so we don\'t sum everything each time. // Bumps the given pointer up by one. // Wraps to the start of the array if needed. void inc(double * & p) { if (++p >= window + period) { p = window; } } // Returns how many numbers we have stored. ptrdiff_t size() const { if (head == NULL) return 0; if (head == tail) return period; return (period + tail - head) % period; } }; int main(int argc, char * * argv) { SMA foo(3); SMA bar(5); int data[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 }; for (int * itr = data; itr < data + 10; itr++) { foo.add(*itr); cout << "Added " << *itr << " avg: " << foo.avg() << endl; } cout << endl; for (int * itr = data; itr < data + 10; itr++) { bar.add(*itr); cout << "Added " << *itr << " avg: " << bar.avg() << endl; } return 0; }
下面是NAO随着我的头部先进行俯仰,然后左右摇摆的动态图: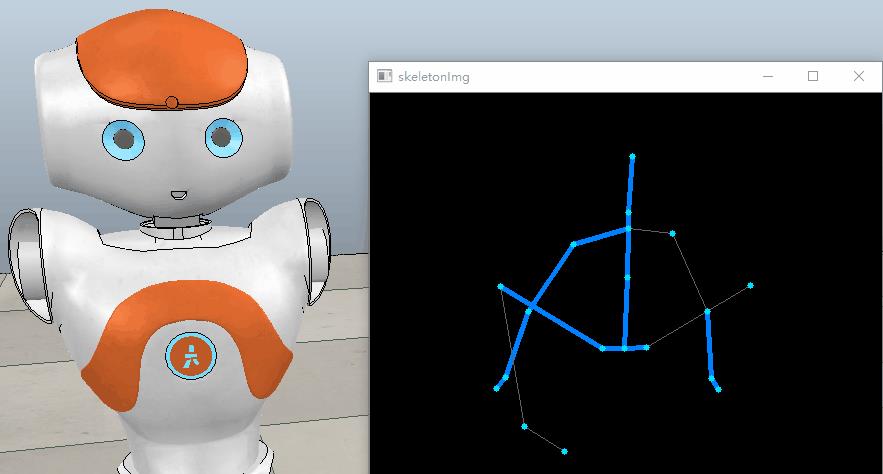
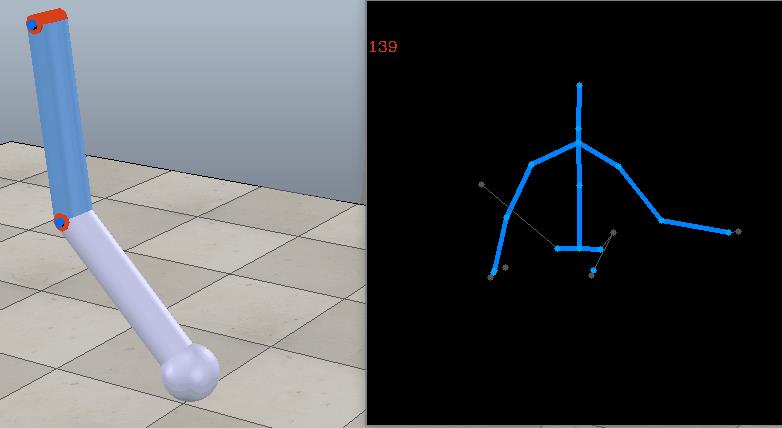
另外也可以使用获取到的三维坐标点计算出关节夹角,以此来控制虚拟模型。下面计算出肘关节和肩关节角度,来控制VREP场景中的一个2自由度手臂:
参考:
以上是关于使用Kinect2.0控制VREP中的虚拟模型的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
