JAVA都有哪些适合进行数值计算,数据分析/机器学习的库
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JAVA都有哪些适合进行数值计算,数据分析/机器学习的库相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
直接搜关键词:numerical computations in java1、https //en wikipedia org/wiki/Java_programming_language
Apache Commons, is an open-source for creating reusable Java components. It has numerical packages for linear algebra and non-linear optimization.
ND4J is an open-source library that supports n-dimensional (ND) arrays, similar to NumPy. It runs on distributed GPUs or CPUs cross-platform. It supports thedeep learning library Deeplearning4j.
Colt provides a set of Open Source Libraries for High Performance Scientific and Technical Computing.
Efficient Java Matrix Library (EJML) is an open-source linear algebra library for manipulating dense matrices.
JAMA, a numerical linear algebra toolkit for the Java programming language. No active development has taken place since 2005, but it still one of the more popular linear algebra packages in Java.
Jblas: Linear Algebra for Java, a linear algebra library which is an easy to use wrapper around BLAS and LAPACK.
Parallel Colt is an open source library for scientific computing. A parallel extension of Colt.
DataMelt, an open-source Java libraries for numerical calculations, data I/O and visualization of scientific results. Used together with Jython.
JMSL Numerical Libraries, is a comprehensive set of mathematical, statistical, data mining, financial and 2D/3D charting classes.
Matrix Toolkit Java is a linear algebra library based on BLAS and LAPACK.
OjAlgo is an open source Java library for mathematics, linear algebra and optimisation.
exp4j is a small Java library for evaluation of mathematical expressions.
la4j is a tiny Java library and it provides linear algebra primitives and algorithms.
Universal Java Matrix Package UJM is a Java library which provides implementations for sparse and dense matrices, as well as linear algebra calculations such as matrix decomposition, inverse, multiply, mean, correlation, standard deviation, etc.
Java Matrix Library A thoughtfully designed Java library for dealing with Matrices ( Matrix Theory ). Simple, Intuitive and Flexible. The library revolves around a Matrix interface. Operations are thoughtfully distributed. Not guilty of exposing all-in-one Matrix class.
JDistLib Java Statistical Distribution Library is a Java package that provides routines for various statistical distributions. A manual translation of distributions provided by R statistical package.
SuanShu by Numerical Method Inc. is a large collection of numerical algorithms including linear algebra, (advanced) optimization, interpolation, Markov model, principal component analysis, time series analysis, hypothesis testing, regressions, statistics, ordinary and partial differential equation solvers.
2、Java Numerics: Main
Apfloat is a arbitrary precision floating-point arithmetic package.
ArciMath BigDecimal is an extension of java.math.BigDecimal based on IBM's Java Specification Request.
Colt is a free Java toolkit containing data structures and utilities intended for high performance computing.
Commons-Math The Jakarta Mathematics Library is is a library of lightweight, self-contained mathematics and statistics components addressing the most common problems not available in the Java programming language.
Drej, an open-source Java library for linear and non-linear least-squares regression and regularized least-squares classification.
A translation of the ELEFUNT Elementary Functions Testing Package has been ported to Java. The collection also contains extensions to java.lang.Math and new classes for numeric output formatting.
IBM's AlphaWorks contains several tools of interest, including
library of correctly rounded elementary functions intended for use with Java.
Ninja, a set of classes for numerically intensive Java, including complex, multidimensional arrays, and the BLAS. (RETIRED)
Java Numerical Toolkit (JNT)
Special functions including Bessel functions, Chebyshev series.
Zero root finder
Random Number generators for uniform and normal sequences of floating point numbers and long integers.
Java Ultimate Math Package, a framework for arbitrary precision computations.
The Java3D effort produced a matrix package for use in graphics.
JMSL, a collection of mathematical, statistical and charting classes, written in 100% Java, marketed by Visual Numeric, Inc. Includes linear algebra, zero finding, splines, ordinary differential equations, linear programming, nonlinear optimization, FFTs, special functions, regression, ANOVA, ARMA, Kalman filters.
JLargeArrays, a pure Java library of one-dimensional numeric arrays that can store up to 2^63 elements.
JSci, a set of Java packages for linear algebra, statistics, wavelets. Includes chart/graph components and a partial MathML DOM implementation.
jScience contains packages for numerical linear algebra, for computing with units (e.g., kg., sec.), and other utility operations.
Jspline+ is a spline approximation library for Java developed at the Institute of Computational Mathematics and Mathematical Geophysics (RAS) in Novosibirsk. It contains classes for univariate and multivariate spline approximation on scattered meshes, as well as core matrix and linear system solution classes.
JTransforms, The first open source, multithreaded FFT library in pure Java.
Koalog Constraint Solver is a commercial Java library for solving combinatorial optimization problems using Constraint Programming or Local Search.
Least Squares Software markets the jCrunch[tm] class libraries for numerical computing.
mpjava is a Java implementation of David Bailey's Fortran-based multiprecision package. The package performs multi precision floating point arithmetic with arbitrary precision level. It takes advantage of Java's inheritance facility to provide smooth transition from primitive arithmetic types.
netlib has a small collection of Java numerical classes.
A Numerical Library in Java for Scientists and Engineers, a book published by CRC Press, contains a CD-ROM with translation into Java of the library NUMAL (NUMerical procedures in Algol 60). 参考技术A 关于产品经理书籍的话有很多:启示录、结网、设计心理学、简约之上、从0到1。。。视频嘛墙裂推荐刘文智老师的《产品经理深入浅出》系列,或者手把手教你做产品等等。
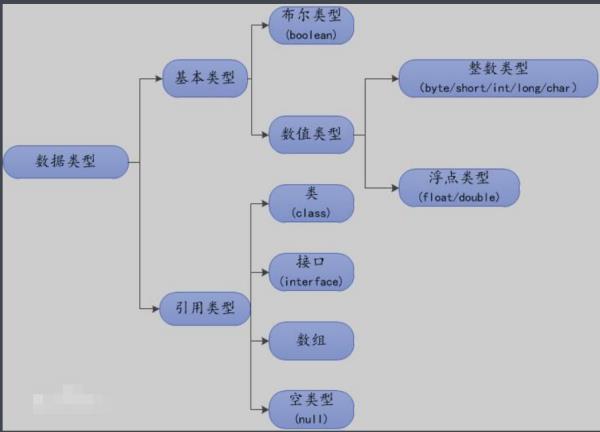
java的基本数据类型都有哪些
四种八类:
基本数据类型
整数类型:
byte:字节占用 1字节 8位,用来表达最小的数据单位,储存数据长度为 正负 127;
short:字节占用 2字节 16位,储存数值长度为 -32768-32767
int:字节占用 4字节 32位,最为常用的整数类型,储存长度为,-2^31-1~2^31 (21 亿)
long:字节占用 8字节 64位,当到达int数值极限时使用,储存长度为 看图片:

浮点数类型:
float:单精度浮点型 32位 取值范围 3.4e-38~3.4e-38
double:双精度浮点型 64位 ,java中默认的浮点类型 取值范围 1.7e-308~1.7e-308
字符类型:
char:16位 ,java字符使用Unicode编码;
布尔类型
boolean : true 真 和 false 假
引用数据类型:
类 class
接口 interface
数组
参考技术A JAVA数据类型分基本数据类型和引用数据类型。基本数据类型
Java里面包含8个基本数据类型,分别是:
boolean、byte、char、short、int、float、douboe、long
byte 字节
byte是JAVA中最小的数据类型,它在内存中占8位(8个bit),取值范围从-128到127
赋值:byte I = 127
short 短整型
short类型在内存中占2个字节,取值范围从 -32768到32767
赋值:short i = 32767;
char 字符型
char类型在内存中占2个字节。表示一个字符,也可以使用ASCII码范围内的值来给char型的变量赋值。由于字符在内存中的取值不存在负数范围,所有取值范围从 0 到 65535
赋值:char i = ‘a’; 或者 char i = 97;
int 整型
int型在内存中占4个字节。取值范围从 -2147483648 到 2147483647
赋值:int i = 10;
float 单精度浮点型
float型在内存中占4个字节。取值范围从 -3.4E38 到 3.4E38
赋值:float i = 1.0f;
long 长整型
long型在内存中占8个字节。取值范围从 -9223372036854775808 到 9223372036854775807
double 双精度浮点型
double 型在内存中占8个字节。取值范围从 -1.7E308 到 1.7E308
boolean 布尔型
boolean类型只有两个值:true和false。
基本数据类型的相互转换
转型规则
JAVA中所有的数字变量都是有符号(正负)的。
JAVA不允许类型的随意转换。只有数字变量可以进行转换,但是不能随意。
带有小数点的数字变量默认都为double型。定义float型必须进行强制类型转换。
所占字节数小的数字型变量赋值给所占字节数比它大的类型时不用强制类型转换,此时是自动转型。
int型变量赋值给char型变量时,JVM会以int型变量值到ASCII码表中查找出所对应的字符,再赋值给char型变量。反之也是。但是遵循第4条规则。
初始化简单数据类型时要注意赋值的范围,超出则会产生编译错误。
基本数据类型默认初值
类型 初始值
boolean false
byte 0
char 0
short 0
int 0
float 0.0
double 0.0
long 0
基本数据类型默认初值表
引用数据类型
JAVA中,非简单数据类型的类型都是引用数据类型。 参考技术B
java的基本数据类型有:
1、布尔型(boolean)
取值范围:True 或 False
2、字节型(byte)
取值范围:0 - 255
3、短整型(short)
取值范围:-32,768 ~ 32767
4、整型(int)
取值范围:-2,147,483,648 ~ 2,147,483,647
5、长整型(long)
取值范围:-9223372036854775808~9223372036854775807
6、单精度浮点型(float)
负数范围:
-3.402823E38 ~ -1.401298E-45
正数范围:
1.401298E-45 ~ 3.402823E38
7、双精度浮点型(double)
负数范围:
-1.797,693,134,862,32E308 ~
-4.940,656,458,412,47E-324
正数范围:
4.940,656,458,412,47E-324 ~
1.797,693,134,862,32E308
8、字符型(char)
取值范围:'\\u0000'~'\\ufff'
扩展资料
任何数据类型的数组都需要 20 个字节的内存空间,加上每一数组维数占 4 个字节,再加上数据本身所占用的空间。数据所占用的内存空间可以用数据元数目乘上每个元素的大小加以计算。
例如,以 4 个 2 字节之 Integer 数据元所组成的一维数组中的数据,占 8 个字节。这 8 个字节加上额外的 24 个字节,使得这个数组所需总内存空间为 32 个字节。
参考资料:百度百科——数据类型
java四类八种基本数据类型
第一类:整型 byte short int long
第二类:浮点型 float double
第三类:逻辑型 boolean(它只有两个值可取true false)
第四类:字符型 char
在栈中可以直接分配内存的数据是基本数据类型。
引用数据类型:是数据的引用在栈中,但是他的对象在堆中。
要想学好Java必须知道各种数据的在内存中存储位置。 对内存有了很好的了解,可以有助你分析程序。
字节:
boolean 布尔型 1/8
byte 字节类型 1
char 字符型 2 一个字符能存储一个中文汉字
short 短整型 2
int 整数类型 4
float 浮点类型(单精度) 4
long 长整形 8
double 双精度类型(双精度) 8
java中默认的整数类型是int类型,如果要定义为float型,则要在数值后加上l或L;
默认的浮点型也是双精度浮点,如果要定义为float型,则要在数值后加上f或F。
一个字节等于8位,一个字节等于256个数,就是-128到127一共256。
kB就是kBytes Bytes就是“字节”的意思!
K就是千的意思,因为计算机是通过二进制来计算,10个1正好是1024
1111111111(二进制)=1024(十进制)
1Bytes(字节)=8bit(比特)
一个英文字母或一个阿拉伯数字就是一个字符,占用一个字节
一个汉字就是两个字符,占用两个字节。
一般讲大小是用Bytes,大写的“B”,讲网络速率是用bit,注意是小写的“b”。
例:一个文件有8MBytes
例:我下载文件的速率是256KB/s,即2Mbit,这通常就是我们宽带上网的速率。
基本数据类型自动转换
byte->short,char -> int -> long
float -> double
int -> float
long -> double
记住:小可转大,大转小会失去精度!!! 参考技术D
Java的基本数据类型分为:整数类型、浮点类型、字符类型、布尔类型这四个类型。
1、整数类型
整数类型变量用来表示整数的数据类型。整数类型又分为字节型(byte)、短整型(short)、整型(int)、长整型(long)这四种。

2、浮点类型
浮点类型用来表示小数的数据类型。浮点类型分为float(单精度型)和double(双精度类型)这两种。float(单精度型)一般在精度要求不高的时候使用。double(双精度类型)一般在数值精度高的时候使用。

3、字符类型
字符类型的关键字是“char”。

4、布尔类型
布尔类型是表示逻辑值的基本数据类型。boolean常量有“真”和“假”这两个状态。一般用true表示“真”、false表示“假”。它的定义方法是在变量名前加上类型关键字boolean。
以上是关于JAVA都有哪些适合进行数值计算,数据分析/机器学习的库的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章