以守护进程(socket)的方式传输数据(重点)
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了以守护进程(socket)的方式传输数据(重点)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
以守护进程(socket)的方式传输数据(重点)
部署环境:
分别用uname命令查看各系统相关信息
[[email protected]~]# uname -r 6.18-308.el5 [[email protected]~]# uname -s Linux [[email protected]~]# uname -o GNU/Linux [[email protected]~]# uname -i x86_64 [[email protected]~]# uname -n A-Server58
操作系统
主机名 | 网卡eth0 | 默认网关 | 用途 |
192.168.1.111 | 192.168.1.1 | Rsync服务端 | |
192.168.1.121 | 192.168.1.1 | Rsync 节点 | |
192.168.1.119 | 192.168.1.1 | Rsync 节点 |
子网掩码均为255.255.255.0
具体需求:
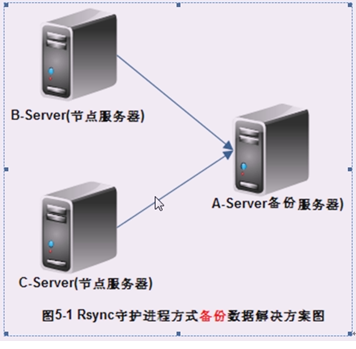
要求在A-Server上以rsync守护进程的方式部署rsync服务,使得所有rsync节点客户端主机,可以把本地数据通过rsync的方式备份到数据备份服务器A-Server上,本例的客户端仅以B-Server、C-Server为例
备份拓扑
1.部署rsync服务
1)rsync服务端配置过程
配置rsyncd.conf
首先确认软件是否安装
[[email protected] ~]# rpm -aq rsync rsync-3.0.6-4.el5_7.1 [[email protected] ~]# vi /etc/rsyncd.conf #增加如下配置, #Rsync server #created by oldboy 15:01 2009-6-5 ##rsyncd.conf start## uid = root gid = root use chroot = no max connections = 2000 timeout = 600 pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid lock file = /var/run/rsync.lock log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log ignore errors read only = false list = false hosts allow = 192.168.1.1/24 hosts deny = 0.0.0.0/32 auth users = rsync_backup secrets file = /etc/rsync.password [dingjian] comment = www by old0boy 14:18 2012-1-13 path = /dingjian/
[[email protected] ~]# dos2unix /etc/rsyncd.conf dos2unix: converting file /etc/rsyncd.confto UNIX format ...
[[email protected] /]# mkdir dingjian [[email protected] /]# ls -ld dingjian drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Apr 23 01:05dingjian
创建同步的本地目录/dingjian 并根据需要授权
目录和/etc/rsync.password为配置文件中path = /dingjian/参数的配置
配置用于rsync同步的账号、密码及账号文件以限
[[email protected] ~]# echo"rsync_backup:95862909">/etc/rsync.password
#其中rsync_backup:95862909中的rsync_backup为同步传输用到的虚拟账号,这个账号仅为rsync的账号,不需要是系统账号,后面的95862909为密码,不超过8位
[[email protected] ~]# chmod 600/etc/rsync.password #权限必须为600 [[email protected] ~]# cat/etc/rsync.password rsync_backup:95862909 [[email protected] ~]# ll /etc/rsync.password -rw------- 1 root root 22 Apr 22 19:47/etc/rsync.password [[email protected] ~]#
启动rsync服务
以守护进程方式来启动rsync服务
[[email protected] ~]# rsync --daemon
拓展:rsync的进程参数选项
--daemon #表示以守护进程的方式启动rsync服务
--address #绑定指定ip地址
--config=FILE #更改配置文件路径,而不是默认的/etc/rsyncd.conf
--port=PORT #更改其它端口提供服务,而不是缺省的873端口
提示:以上几个选项为了解内容,生产场景使用的不多
通过端口查服务
[[email protected] ~]# lsof -i tcp:873 COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME rsync 27185 root 3u IPv4 44404 0t0 TCP *:rsync (LISTEN) [[email protected] ~]# netstat -lntup|grep873 tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:873 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 27185/rsync
设置rsync服务开机自启动
[[email protected] ~]# echo"/usr/bin/rsync --daemon">>/etc/rc.local [[email protected]58 ~]# cat /etc/rc.local #!/bin/sh # # This script will be executed *after* allthe other init scripts. # You can put your own initialization stuffin here if you don‘t # want to do the full Sys V style initstuff. touch /var/lock/subsys/local /usr/bin/rsync –daemon
注意当然还可以用chkconfig rsync on命令,但是必须要编写适合chkconfig操作脚本才行
重起rsync的组合命令
[[email protected] ~]# pkill rsync #关闭rsync服务 [[email protected] ~]# rsync --daemon #启动rsync服务
检查启动的进程
[[email protected] ~]# ps -ef |grep rsync
几个进程管理命令
杀进程:pkill rsync
killall rsync 可能一次杀不死,要连按连杀
killall -9 rsync 强制杀死进程 -9
kill -9 4084 利用端口号加-9 强制进程,
2)rsync客户端配置过程
请注意与服务端的配置区别
服务端192.168.1.119 192.168.1.121分别做如下操作
[[email protected] ~]# echo"95862909">/etc/rsync.password #这里仅配置密码,不需要账号,这是与服务端的区别
[[email protected] ~]# chmod 600/etc/rsync.password #必须为600权限 [[email protected] ~]# cat/etc/rsync.password 95862909 [[email protected] ~]# ll /etc/rsync.password -rw-------. 1 root root 9 Apr 22 20:01/etc/rsync.password
此时rsync服务配置大功告成!
检查部置的rsync服务
默认情况,以下均为rsync客户端执行操作,下面以ip192.168.1.121B-Server为例说明:
推送(即从客户端同步文件或目录到服务器端)
从客户端推送/etc 目录到服务端rsync指定的目录(本文档为/dingjian)下
rsync -avzP /[email protected]::dingjian/ --password-file=/etc/rsync.password
从服务端指定的/dingjian目录把数据拉取到客户端本地/tmp目录下
rsync [email protected]::dingjian/ --password-file=/etc/rsync.password /tmp
2.
排除打包
方法一:
在客户端操作:
[[email protected]]# rsync -avz --exclude=etc --exclude=tmp [email protected]::dingjian --password-file=/etc/rsync.password
使用--exclude=进行排除
方法二:
在服务端配置rsyncd.conf参数实现
加入排除参数 exclude=etc tmp
[[email protected] dingjian]# cat/etc/rsyncd.conf sync server #created by oldboy 15:01 2009-6-5 ##rsyncd.conf start## uid = root gid = root use chroot = no max connections = 2000 timeout = 600 pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid lock file = /var/run/rsync.lock log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log ignore errors read only = false list = false hosts allow = 192.168.1.1/24 hosts deny = 0.0.0.0/32 auth users = rsync_backup secrets file = /etc/rsync.password exclude=tmp etc [dingjian] comment = www by old0boy 14:18 2012-1-13 path = /dingjian/
重启rsync服务杀进程,重启服务
[[email protected] dingjian]# pkill rsync [[email protected] dingjian]# ps -ef|greprsync root 27624 27033 0 22:45 pts/0 00:00:00 grep rsync [[email protected] dingjian]# rsync --daemon [[email protected] dingjian]# ps -ef|greprsync root 27626 1 0 22:45 ? 00:00:00 rsync --daemon root 27632 27033 0 22:45 pts/0 00:00:00 grep rsync
测试推送备份
[[email protected] tmp]# rsync -avz [email protected]::dingjian --password-file=/etc/rsync.password
3.
无差异同步
要实现这种同步方法就要使用--delete参数了
本地测试
[[email protected] tmp]# rsync -avzP --delete/null/ /tmp/
拉取方法
[[email protected] tmp]# rsync -avzrtopg--delete --progress [email protected]::dingjian/ /tmp/ --password-file=/etc/rsync.password
推送方法
[[email protected] tmp]# rsync -avzrtopg--delete --progress . [email protected]::dingjian/--password-file=/etc/rsync.password
执行--delete参数从rsync服务端往rsync客户端拉取数据时,一定要小心,最好不用,它比从rsync客户端带--delete参数往rsync服务端推送危险得多,客户端带--delete参数往服务端推送仅删除服务端模块下的数据,而前者有能力删除rsync客户端本地的所有数据,包括根下的所有目录
生场场景没有特殊要求,应避免使用,一般是有需要两台服务器之间,必须要求数据一致且时时性又不是很高的情况,如两台负载均衡下面的web服务器之间的同步,或者高可用双机配置之间的同步等。
4.
多目录模块同步
配置/etc/rsyncd.conf配置文件
#Rsync server #created by oldboy 15:01 2009-6-5 ##rsyncd.conf start## uid = root gid = root use chroot = no max connections = 2000 timeout = 600 pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid lock file = /var/run/rsync.lock log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log ignore errors read only = false list = false hosts allow = 10.0.0.0/24 hosts deny = 0.0.0.0/32 auth users = rsync_backup secrets file = /etc/rsync.password ######################################## [dingjian] comment = www by old0boy 14:18 2012-1-13 path = /dingjian/ ##################################### [www] comment = www by old0boy 14:18 2012-1-13 path = /data0/www/www/ ##################################### [bbs] comment = bbs by old0boy 14:18 2012-1-13 path = /data0/www/bbs/ ##################################### [blog] comment = blog by old0boy 14:18 2012-1-13 path = /data0/www/blog/
重启rsync服务
pkill rsync
ps -ef|grep rsync
rsync --daemon
ps -ef|grep rsync
本文出自 “Mr.Xiong`s 运维日志” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://mrxiong2017.blog.51cto.com/12559394/1933720
以上是关于以守护进程(socket)的方式传输数据(重点)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章