Elk 进阶部署
Posted Eason_Footprint
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Elk 进阶部署相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
虚拟机两台:
192.168.1.42
192.168.1.46
系统环境保持一致:
cat /etc/redhat-release
uname -a

elk准备环境保持一致:
elasticsearch安装:
下载并安装GPG key
rpm --import https://packages.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
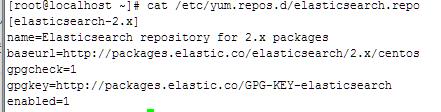
添加yum源:
安装elasticsearch
yum install -y elasticsearch
logstash安装
下载并安装GPG key
[root@linux-node2 ~]# rpm --import https://packages.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
添加yum仓库
[root@linux-node2 ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/logstash.repo[logstash-2.1]name=Logstash repository for 2.1.x packagesbaseurl=http://packages.elastic.co/logstash/2.1/centosgpgcheck=1gpgkey=http://packages.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearchenabled=1
安装logstash
[root@linux-node2 ~]# yum install -y logstash
安装kibana
[root@linux-node2 ~]#cd /usr/local/src[root@linux-node2 ~]#wget https://download.elastic.co/kibana/kibana/kibana-4.3.1-linux-x64.tar.gztar zxf kibana-4.3.1-linux-x64.tar.gz[root@linux-node1 src]# mv kibana-4.3.1-linux-x64 /usr/local/[root@linux-node2 src]# ln -s /usr/local/kibana-4.3.1-linux-x64/ /usr/local/kibana
安装Redis,nginx和java
yum install -y redis nginx java
管理配置elasticsearch
管理linux-node1的elasticsearch
修改elasticsearch配置文件,并授权
[root@linux-node1 src]# grep -n \'^[a-Z]\' /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml17:cluster.name: chuck-cluster 判别节点是否是统一集群23:node.name: linux-node1 节点的hostname33:path.data: /data/es-data 数据存放路径37:path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch/ 日志路径43:bootstrap.mlockall: true 锁住内存,使内存不会再swap中使用54:network.host: 0.0.0.0 允许访问的ip58:http.port: 9200 端口- transport.tcp.port: 9300
- node.master: true
- node.data: true
- discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.1.46:9300", "192.168.1.42:9301"]
- discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 1
[root@linux-node1 ~]# mkdir -p /data/es-data[root@linux-node1 src]# chown elasticsearch.elasticsearch /data/es-data/
启动elasticsearch
[root@linux-node1 src]# systemctl start elasticsearch[root@linux-node1 src]# systemctl enable elasticsearchln -s \'/usr/lib/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service\' \'/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/elasticsearch.service\'[root@linux-node1 src]# systemctl status elasticsearchelasticsearch.service - ElasticsearchLoaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service; enabled)Active: active (running) since Thu 2016-01-14 09:30:25 CST; 14s agoDocs: http://www.elastic.coMain PID: 37954 (java)CGroup: /system.slice/elasticsearch.service└─37954 /bin/java -Xms256m -Xmx1g -Djava.awt.headless=true -XX:+UseParNewGC -XX:+UseConc...Jan 14 09:30:25 linux-node1 systemd[1]: Starting Elasticsearch...Jan 14 09:30:25 linux-node1 systemd[1]: Started Elasticsearch.[root@linux-node1 src]# netstat -lntup|grep 9200tcp6 0 0 :::9200 :::* LISTEN 37954/java
访问9200端口,会把信息显示出来
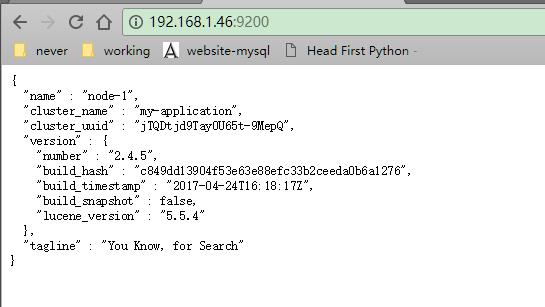
elasticsearch进行交互
交互的两种方法
- Java API :
node client
Transport client - RESTful API
javascript
.NET
php
Perl
Python
Ruby
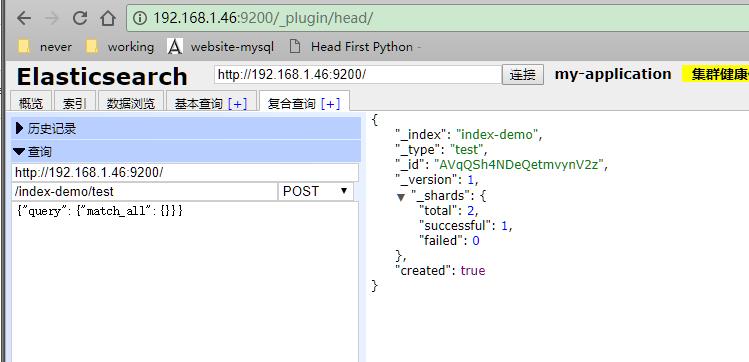
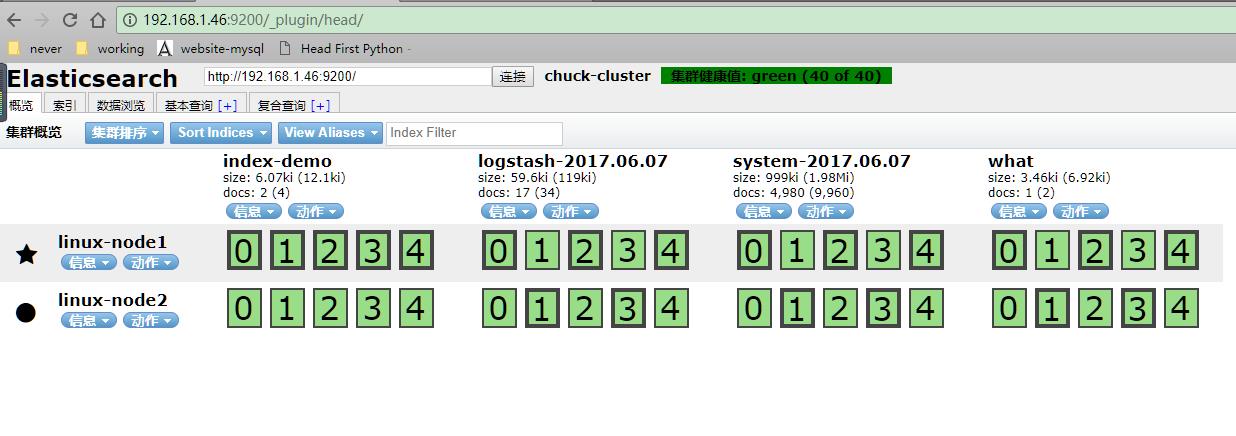
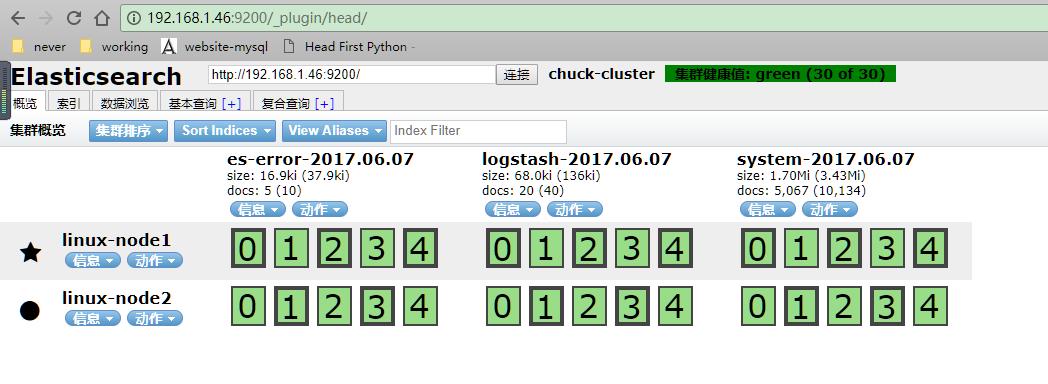
使用head插件显示索引和分片情况
/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/plugin install mobz/elasticsearch-head
在插件中添加一个index-demo/test的索引,提交请求
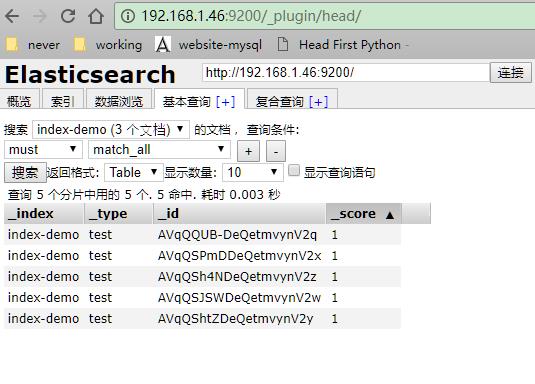
使用kopf插件监控elasticsearch
/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/plugin install lmenezes/elasticsearch-kopf
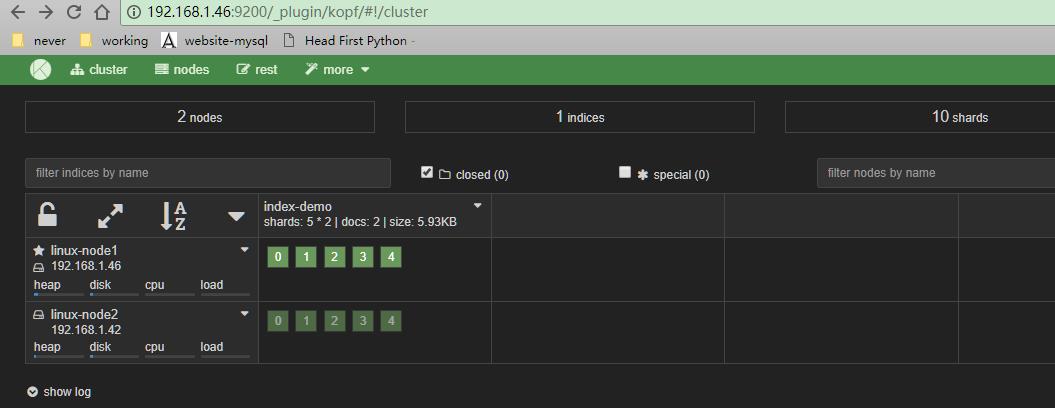
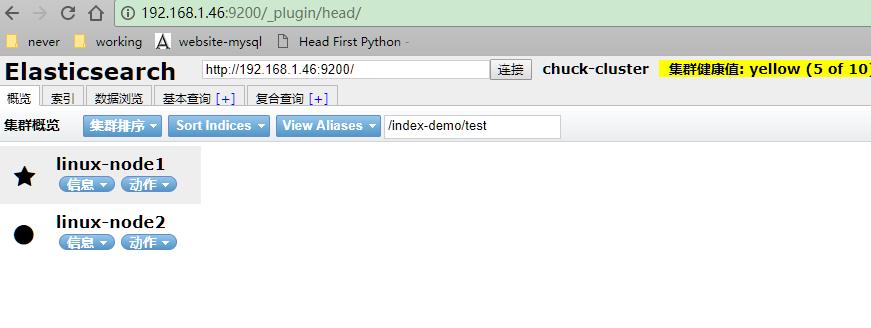
管理linux-node2的elasticsearch
将linux-node1的配置文件拷贝到linux-node2中,并修改配置文件并授权
配置文件中cluster.name的名字一定要一致,当集群内节点启动的时候,默认使用组播(多播),寻找集群中的节点
[root@linux-node1 src]# scp /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml 192.168.56.12:/etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml[root@linux-node2 elasticsearch]# sed -i \'23s#node.name: linux-node1#node.name: linux-node2#g\' elasticsearch.yml[root@linux-node2 elasticsearch]# mkdir -p /data/es-data[root@linux-node2 elasticsearch]# chown elasticsearch.elasticsearch /data/es-data/
注意修改:
vim elasticsearch.yml
transport.tcp.port: 9301
node.master: false
node.data: true
启动elasticsearch
[root@linux-node2 elasticsearch]# systemctl enable elasticsearch.serviceln -s \'/usr/lib/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service\' \'/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/elasticsearch.service\'[root@linux-node2 elasticsearch]# systemctl start elasticsearch.service[root@linux-node2 elasticsearch]# systemctl status elasticsearch.serviceelasticsearch.service - ElasticsearchLoaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service; enabled)Active: active (running) since Thu 2016-01-14 02:56:35 CST; 4s agoDocs: http://www.elastic.coProcess: 38519 ExecStartPre=/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-systemd-pre-exec (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)Main PID: 38520 (java)CGroup: /system.slice/elasticsearch.service└─38520 /bin/java -Xms256m -Xmx1g -Djava.awt.headless=true -XX:+UseParNewGC -XX:+UseConc...Jan 14 02:56:35 linux-node2 systemd[1]: Starting Elasticsearch...Jan 14 02:56:35 linux-node2 systemd[1]: Started Elasticsearch.
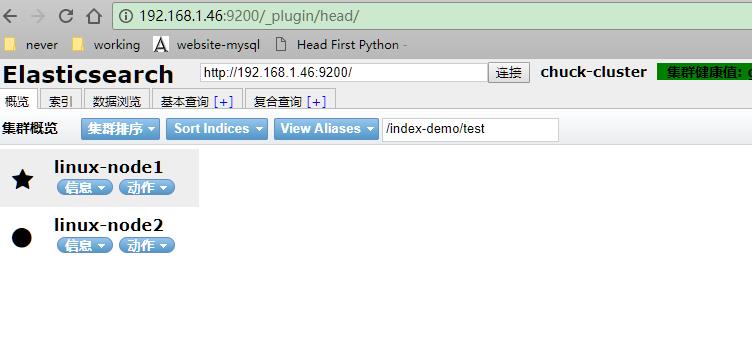
输入master的ip访问,出现了两个节点的信息:
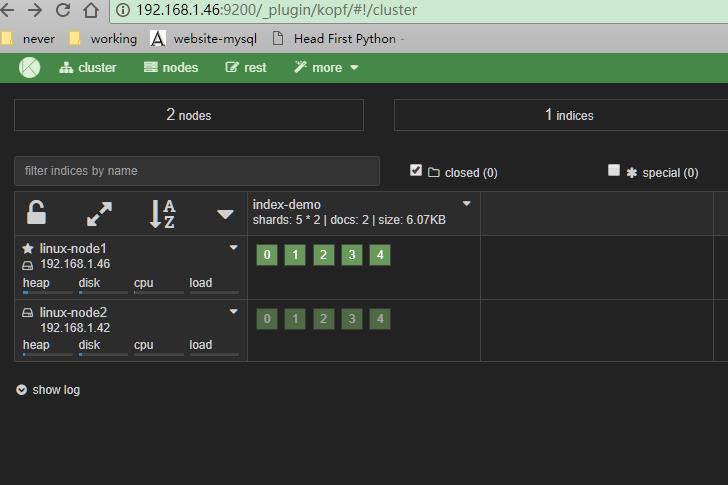
配置logstash
使用rubudebug显示详细输出,codec为一种编解码器
[root@linux-node1 bin]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -e \'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{ codec => rubydebug} }\'Settings: Default filter workers: 1Logstash startup completedchuck ==>输入{"message" => "chuck","@version" => "1","@timestamp" => "2016-01-14T06:07:50.117Z","host" => "linux-node1"} ==>使用rubydebug输出
使用logstash将信息写入到elasticsearch
[root@linux-node1 bin]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -e \'input { stdin{} } output { elasticsearch { hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"] } }\'Settings: Default filter workers: 1Logstash startup completedmaliangchuckchuck-blog.comwww.chuck-bllog.com
使用logstash启动一个配置文件,会在elasticsearch中写一份
[root@linux-node1 ~]# cat normal.conf
input { stdin { } }
output {
elasticsearch { hosts => ["localhost:9200"] }
stdout { codec => rubydebug }
}
[root@linux-node1 ~]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f normal.conf
Settings: Default filter workers: 1
Logstash startup completed
123
{
"message" => "123",
"@version" => "1",
"@timestamp" => "2016-01-14T06:51:13.411Z",
"host" => "linux-node1
收集系统日志的conf
[root@linux-node1 ~]# cat system.conf
input {
file {
path => "/var/log/messages"
type => "system"
start_position => "beginning"
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"]
index => "system-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
[root@linux-node1 ~]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f system.conf
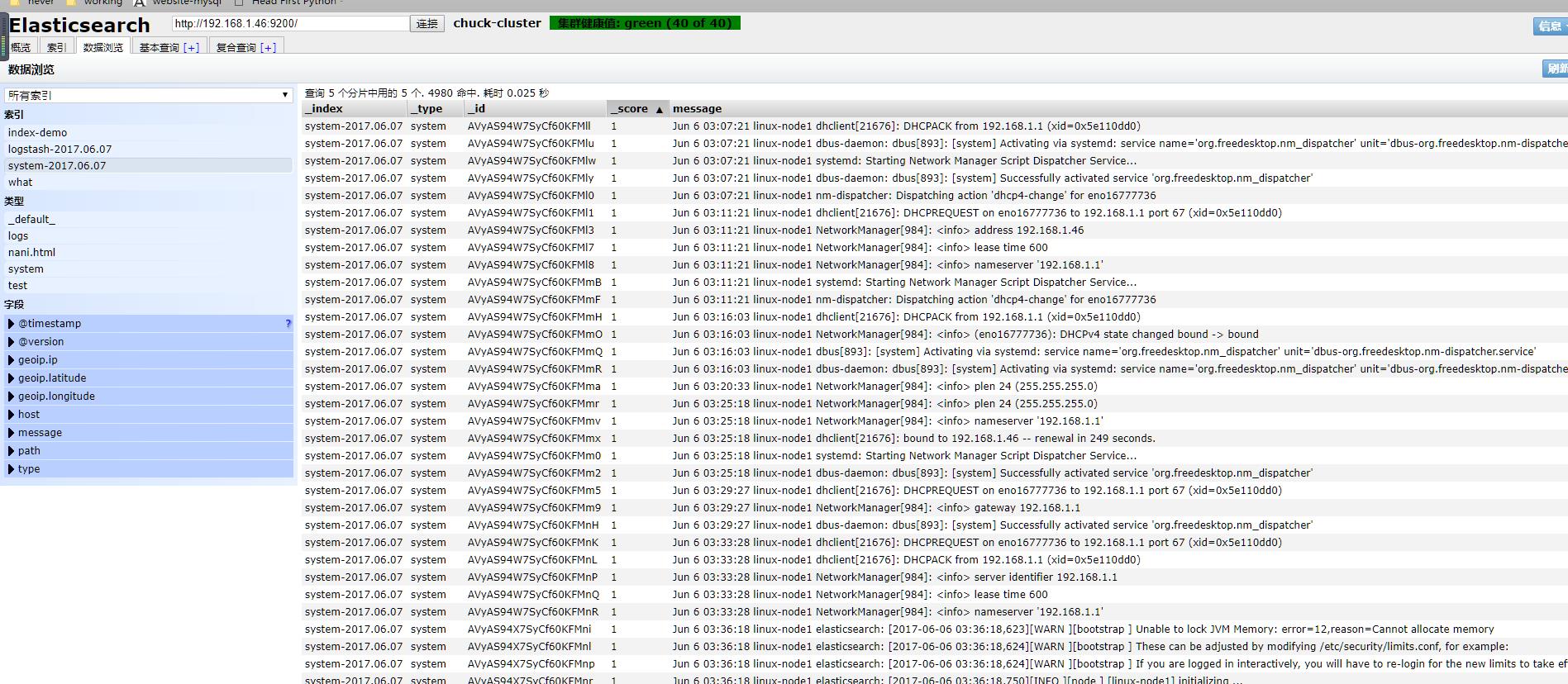
收集elasticsearch的error日志
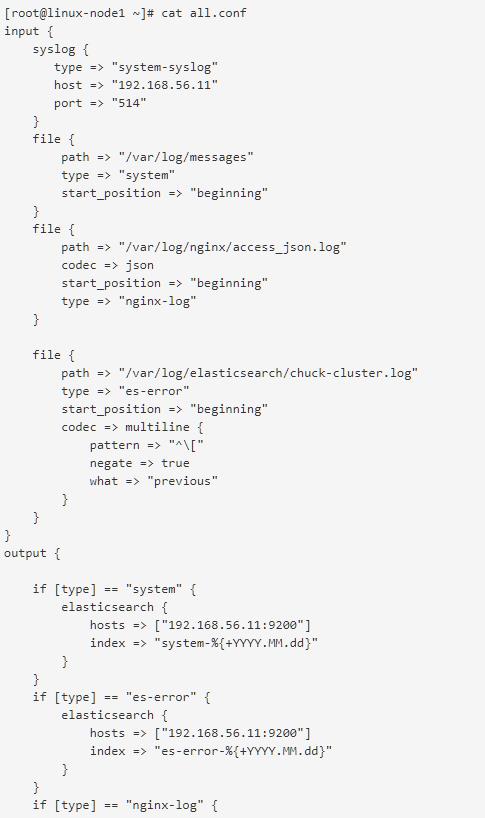
此处把上个system日志和这个error(java程序日志)日志,放在一起。使用if判断,两种日志分别写到不同索引中.此处的type(固定的就是type,不可更改)不可以和日志格式的任何一个域(可以理解为字段)的名称重复,也就是说日志的域不可以有type这个名称。
[root@linux-node1 ~]# cat all.conf
input {
file {
path => "/var/log/messages"
type => "system"
start_position => "beginning"
}
file {
path => "/var/log/elasticsearch/chuck-cluster.log"
type => "es-error"
start_position => "beginning"
}
}
output {
if [type] == "system" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"]
index => "system-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
if [type] == "es-error" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.56.11:9200"]
index => "es-error-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
}
[root@linux-node1 ~]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f all.conf
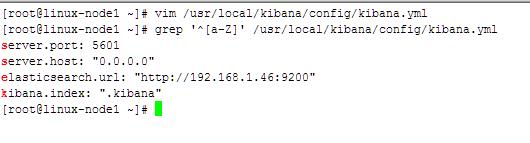
kibana配置
启动一个screen,并启动kibana
[root@linux-node1 ~]# screen[root@linux-node1 ~]# /usr/local/kibana/bin/kibana使用crtl +a+d退出screen
使用浏览器打开192.168.1.46:5601
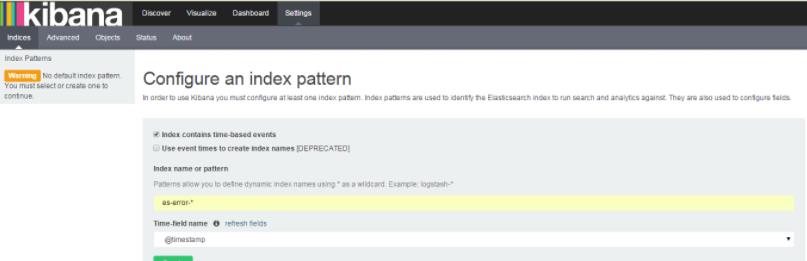
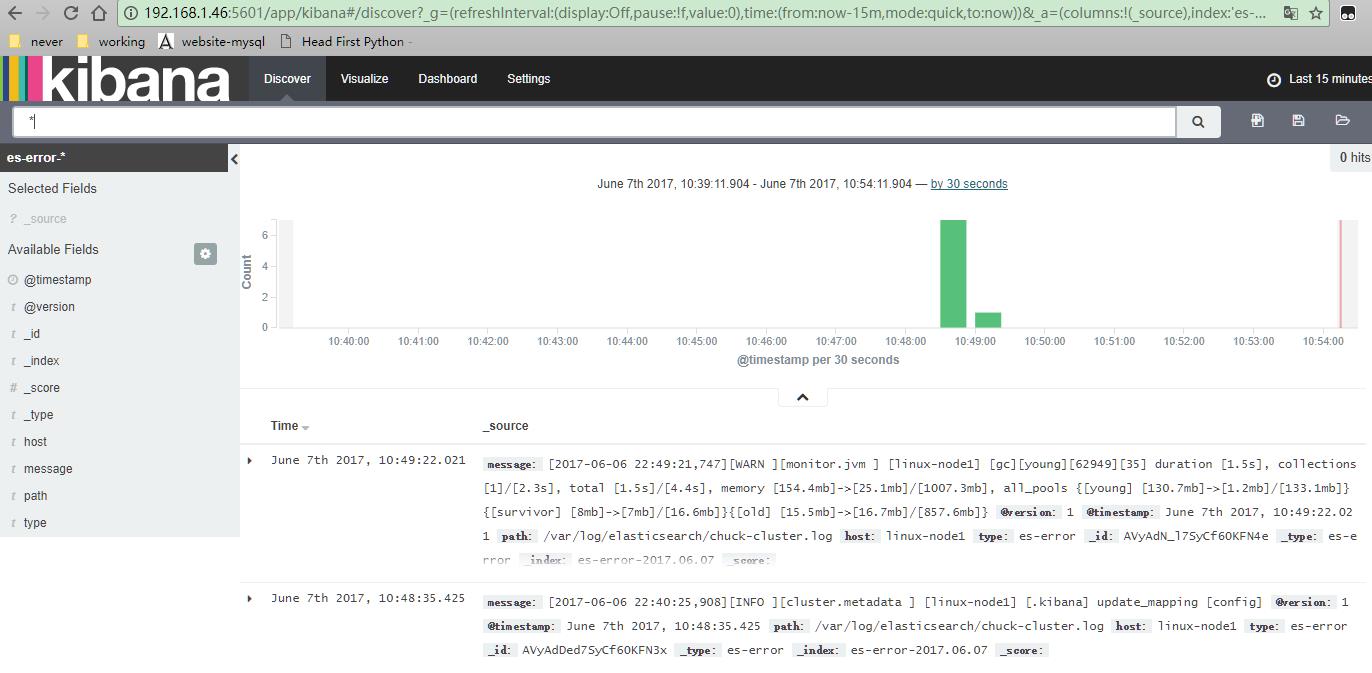
logstash手机nginx、syslog和tcp日志
收集nginx的访问日志
在这里使用codec的json插件将日志的域进行分段,使用key-value的方式,使日志格式更清晰,易于搜索,还可以降低cpu的负载
更改nginx的配置文件的日志格式,使用json
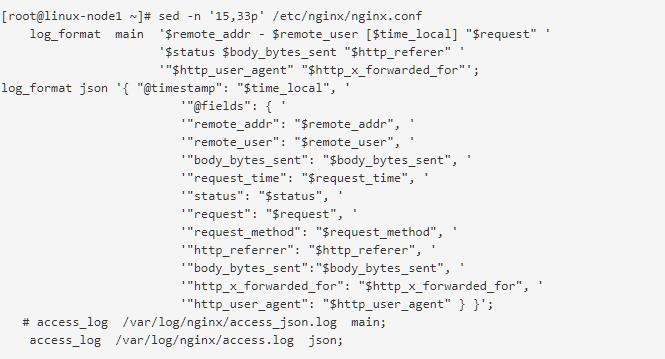
启动nginx
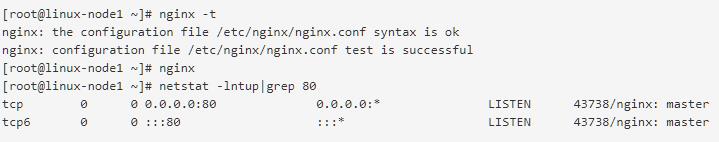
使用logstash将nginx访问日志收集起来,继续写到all.conf中
收集系统syslog日志
使用文件file的形式收集了系统日志/var/log/messages,但是实际生产环境是需要使用syslog插件直接收集
修改syslog的配置文件,把日志信息发送到514端口上
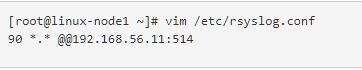
将system-syslog放到all.conf中,启动all.conf
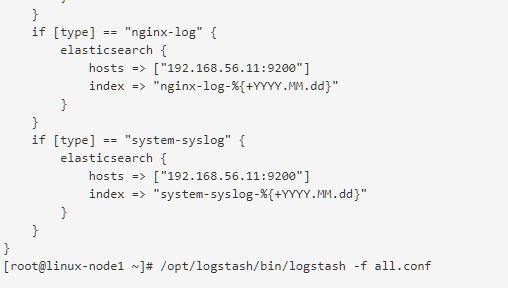
在elasticsearch插件中就可见到增加的system-syslog索引
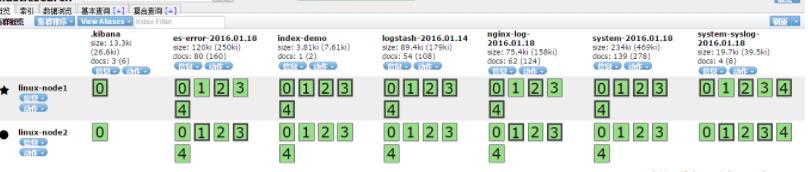
编写tcp.conf
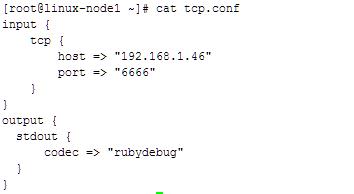
使用nc对6666端口写入数据
[root@linux-node1 ~]# nc 192.168.1.46 6666 </var/log/yum.log
将信息输入到tcp的伪设备中
echo "chuck" >/dev/tcp/192.168.1.46/6666
暂时到此结束....
以上是关于Elk 进阶部署的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章