JDK源码分析--HashMap
Posted willowWind
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JDK源码分析--HashMap相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
HashMap为大家常用的java数据结构工具类,下面对HashMap进行源码分析。
类图结构如下:
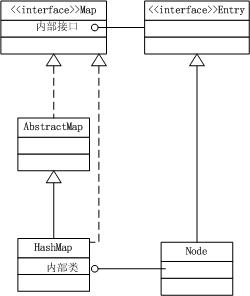
其中AbstractMap实现了
public V get(Object key) ,
public V remove(Object key),
public Set<K> keySet(),
public Collection<V> values()等常用Map操作方法。
下面先分析下HashMap中的常量定义:
/** * The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two. */ static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16 初始化容量为16 /** * The maximum capacity, used if a higher value is implicitly specified * by either of the constructors with arguments. * MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30. */ static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; //最大容量为230 /** * The load factor used when none specified in constructor. */ static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; //装载因子 /** * The bin count threshold for using a tree rather than list for a * bin. Bins are converted to trees when adding an element to a * bin with at least this many nodes. The value must be greater * than 2 and should be at least 8 to mesh with assumptions in * tree removal about conversion back to plain bins upon * shrinkage. */ static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; //由链表转换成树的阈值 /** * The bin count threshold for untreeifying a (split) bin during a * resize operation. Should be less than TREEIFY_THRESHOLD, and at * most 6 to mesh with shrinkage detection under removal. */ static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6; //由树转换成链表的阈值 /** * The smallest table capacity for which bins may be treeified. * (Otherwise the table is resized if too many nodes in a bin.) * Should be at least 4 * TREEIFY_THRESHOLD to avoid conflicts * between resizing and treeification thresholds. */ static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64; //当桶中的bin被树化时最小的hash表容量
正常情况下HashMap是使用链表数据来存储数据,定义了NODE数据结构:
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; V value; Node<K,V> next; Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { this.hash = hash; this.key = key; this.value = value; this.next = next; } public final K getKey() { return key; } public final V getValue() { return value; } public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; } ............. }
同时数据存储在Node数组中
/** * The table, initialized on first use, and resized as * necessary. When allocated, length is always a power of two. * (We also tolerate length zero in some operations to allow * bootstrapping mechanics that are currently not needed.) */ transient Node<K,V>[] table; //Node数组 /** * Holds cached entrySet(). Note that AbstractMap fields are used * for keySet() and values(). */ transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet; //entry集合
下面举例来说明其中的其他使用方法。
通常我们是这样使用HashMap的:
import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class HashTableMain { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<String,String>(); map.put("key1", "value1"); map.put("key2", "value2"); if(map.containsKey("key")){ System.out.println("Find the key"); } } }
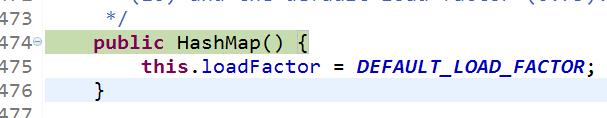
通过Debug代码,我们可以知道,首先HashMap走了默认构造函数,设置了默认装载因子0.75,即map里面元素容量超过设置容量的75%即扩展map容量
当执行put方法添加元素的时候,执行了putVal方法

下面对putVal方法进行详细分析:
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
//在这里初始化,记得1.7之前版本是在构造方法里面初始化 if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
//resize方法里面初始化容器大小为16,因子为0.75,阈值为16*0.75 n = (tab = resize()).length; if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
//插入数组tab数据 tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); else { Node<K,V> e; K k; if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) e = p; else if (p instanceof TreeNode) e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); else { for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { if ((e = p.next) == null) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st treeifyBin(tab, hash); break; } if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break; p = e; } } if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } ++modCount;
//如果大于阈值,重新分配数组大小 if (++size > threshold) resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null; }
待续。。。。
以上是关于JDK源码分析--HashMap的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Java中HashMap底层实现原理(JDK1.8)源码分析
Java中HashMap底层实现原理(JDK1.8)源码分析