基于Qt的OpenGL可编程管线学习- obj模型绘制
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基于Qt的OpenGL可编程管线学习- obj模型绘制相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
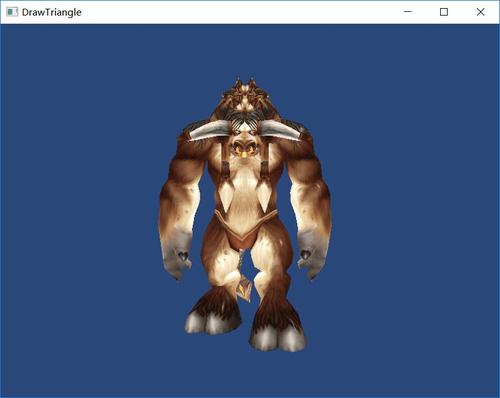
绘制一个Obj模型,效果如下图所示
这里给模型加载顶点和纹理的信息,加上环境光、漫反射和镜面反射,这里我用的是一个方向光。
并且让模型每一帧旋转一个角度达到动态旋转的效果。
1、Obj模型基本内容及加载
v 表示顶点数据
vt 表示纹理数据
vn 表示法线数据
f 表示一个面的顶点数据的Index
这里我是直接解析的模型,代码如下所示:
objmode.h
#ifndef OBJMODE_H
#define OBJMODE_H
#include <QObject>
#include <QString>
#include <QStringList>
#include <QVector>
#include <QFile>
#include <QTextStream>
struct VertexData
{
float postion[3];
float texcoord[2];
float normal[3];
};
struct VertexPos
{
float postion[3];
};
struct VertexTex
{
float coord[2];
};
struct VertexNor
{
float normal[3];
};
struct VertexIndex
{
int posIndex;
int coordIndex;
int normalIndex;
};
class ObjMode : QObject
{
public:
ObjMode();
~ObjMode();
bool loadObjModel(QString nFileStr, QVector&nVertextData, QVector&index);
private:
QVectorm_VertexInfo;
QVectorm_TextureInfo;
QVectorm_NormalInfo;
QVectorm_VertexIndex;
QVectorm_FaceIndex;
};
#endif // OBJMODE_H其中loadObjModel()函数就是加载模型的函数,输入为文件路径,会返回顶点的数据内容和每个面的三角形对应的顶点的索引。
函数实现如下所示:
bool ObjMode::loadObjModel(QString nFileStr, QVector<VertexData> &nVertextData, QVector<unsigned int> &index)
{
QFile nObjFile(nFileStr);
if (!nObjFile.exists())
return false;
if (!nObjFile.open(QFile::ReadOnly))
return false;
nVertextData.clear();
index.clear();
m_TextureInfo.clear();
m_NormalInfo.clear();
m_VertexInfo.clear();
m_VertexIndex.clear();
m_FaceIndex.clear();
QTextStream nTextStream(&nObjFile);
for (;!nTextStream.atEnd();)
{
QString nLineString = nTextStream.readLine();
QByteArray nData = nLineString.toLocal8Bit();
if (nData.length() <= 2)
continue;
if (nData.at(0) == ‘v‘)
{
QStringList nStrList = nLineString.split(" ");
if (nData[1] == ‘t‘)
{
if (nStrList.count() <= 0 || nStrList.at(0) != "vt")
continue;
VertexTex nTexture;
for (int i=1; i<nStrList.count(); ++i)
nTexture.coord[i - 1] = nStrList.at(i).toFloat();
m_TextureInfo << nTexture;
}
else if (nData[1] == ‘n‘)
{
if (nStrList.count() <= 0 || nStrList.at(0) != "vn")
continue;
VertexNor nNormal;
for (int i=1; i<nStrList.count(); ++i)
nNormal.normal[i - 1] = nStrList.at(i).toFloat();
m_NormalInfo << nNormal;
}
else
{
if (nStrList.count() <= 0 || nStrList.at(0) != "v")
continue;
VertexPos nPos;
for (int i=1; i<nStrList.count(); ++i)
nPos.postion[i - 1] = nStrList.at(i).toFloat();
m_VertexInfo << nPos;
}
}
else if (nData[0] == ‘f‘)
{
QStringList nStrList = nLineString.split(" ");
if (nStrList.count() <= 0 || nStrList.at(0) != "f")
continue;
for (int i=1; i<nStrList.count(); ++i)
{
VertexIndex nIndex;
QString nFaceIndexStr = nStrList.at(i);
QStringList nFaceList = nFaceIndexStr.split("/");
nIndex.posIndex = nFaceList.at(0).toUInt() - 1;
nIndex.coordIndex = nFaceList.at(1).toUInt() - 1;
nIndex.normalIndex = nFaceList.at(2).toUInt() - 1;
bool isFinded = false;
for (int j=0; j<m_VertexIndex.count(); ++j)
{
if (nIndex.posIndex == m_VertexIndex.at(j).posIndex && nIndex.coordIndex == m_VertexIndex.at(j).coordIndex && nIndex.normalIndex == m_VertexIndex.at(j).normalIndex)
{
isFinded = true;
m_FaceIndex << j;
break;
}
}
if (!isFinded)
{
m_VertexIndex << nIndex;
m_FaceIndex << m_VertexIndex.count() - 1;
}
}
}
}
nObjFile.close();
for (int i=0; i<m_VertexIndex.count(); ++i)
{
VertexData nPerVertextData;
int posIndex = m_VertexIndex.at(i).posIndex;
int textureIndex = m_VertexIndex.at(i).coordIndex;
int normalIndex = m_VertexIndex.at(i).normalIndex;
memcpy(nPerVertextData.postion, m_VertexInfo.at(posIndex).postion, sizeof(VertexPos));
memcpy(nPerVertextData.texcoord, m_TextureInfo.at(textureIndex).coord, sizeof(VertexTex));
memcpy(nPerVertextData.normal, m_NormalInfo.at(normalIndex).normal, sizeof(VertexNor));
nVertextData.push_back(nPerVertextData);
}
for (int i=0; i<m_FaceIndex.count(); ++i)
{
index.push_back(m_FaceIndex.at(i));
}
return true;
}2、创建纹理
GLuint OpenGLOperate::createTexture(QString nFile)
{
GLuint textureId = 0;
QFile file(nFile);
if (!file.exists())
return 0;
QImage image(nFile);
QImage textureImage;
int width = image.width();
int height = image.height();
textureImage = image.convertToFormat(QImage::Format_RGBA8888);
textureImage = textureImage.mirrored();
m_OpenGLCore->glGenTextures(1, &textureId);
m_OpenGLCore->glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureId);
m_OpenGLCore->glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
m_OpenGLCore->glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
m_OpenGLCore->glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
m_OpenGLCore->glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
m_OpenGLCore->glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGB, width, height, 0, GL_RGBA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, textureImage.bits());
m_OpenGLCore->glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0);
return textureId;
}为Shader的纹理赋值,默认使用0号纹理单元
m_Texture = m_OpenGLOperate->createTexture(":/niutou.bmp");
OpenGLCore->glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, m_Texture);
OpenGLCore->glUniform1i(m_TextureLocation, 0);3、关于环境光、漫反射及高光
环境光:在无光源下的环境的亮度;这里将环境光直接写到fragment shader中(也可以在用uniform在CPU上设置)
设置环境光的亮度及材质
// Ambient vec4 M_AmbientLightColor = vec4(0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 1.0); vec4 M_AmbientMaterial = vec4(0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 1.0); vec4 ambientColor = M_AmbientLightColor * M_AmbientMaterial;
漫反射:在光的照射下物体反射的颜色,也就是物体反射的颜色
光照强度的计算:物体表面的点指向光源的向量 点乘 法线,就是发光强度。
分析:指向光源的向量与法线的夹角为0度时,反射的光线越多,发光强度越大。夹角为90度时,发光强度就为0,如果大于90度则为背光面。
// Diffuse vec3 M_LightPos = vec3(10.0, 10.0, 0.0); vec3 LightNormal = normalize(M_LightPos); // 指向光源的单位向量,方向光 vec3 NormalNormal = normalize(M_normal); // 法线的单位向量 // 点乘获取光照强度 vec4 M_DiffuseLightColor = vec4(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0); vec4 M_DiffuseMaterial = vec4(0.9, 0.9, 0.9, 1.0); vec4 diffuseColor = M_DiffuseLightColor * M_DiffuseMaterial * max(0.0, dot(NormalNormal, LightNormal));
镜面发射:高光,在金属等物体表面的光
标准phong模型 光照强度的计算:反射光线 点乘 直线眼睛的向量作为基底,然后取一个幂
分析:当反射光线与指向眼睛的向量夹角为0度时,则为最亮的部分
// 镜面反射 vec4 specularLightColor = vec4(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0); vec4 specularMaterial = vec4(0.4, 0.4, 0.4, 1.0); vec3 reflerDir = normalize(reflect(-LightNormal, NormalNormal)); vec3 eyeDir = normalize(vec3(0.0) - M_WordPos); vec4 specularColor = specularLightColor * specularMaterial * pow(max(0.0, dot(reflerDir, eyeDir)), 180);
4、法线矩阵(Normal Matrix)
当模型矩阵变换时,法线也会变,需要重新计算法线,公式为:
法线矩阵 = 模型矩阵的逆的转置
变换后的法线 = 法线矩阵 * 法线
QMatrix4x4 nMormalMat; // 法线矩阵 QMatrix4x4 nModeMat; // 模型矩阵 nModeMat.translate(0, -50, -200); if (m_Rote > 360) m_Rote = 0; else m_Rote += 1.0f; nModeMat.rotate(m_Rote, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f); QMatrix4x4 nNormalMatrix = nModeMat.inverted().transposed();
Vertex Shader:
attribute vec3 pos;
attribute vec2 coord;
attribute vec3 normal;
uniform mat4 M;
uniform mat4 V;
uniform mat4 P;
uniform mat4 NM;
varying vec2 M_coord;
varying vec3 M_normal;
varying vec3 M_WordPos;
void main()
{
M_coord = coord;
M_WordPos = vec3(M * vec4(pos, 1.0));
M_normal = mat3(NM) * normal;// 计算法线
gl_Position = P * V * M * vec4(pos, 1.0);
}Fragment Shader
uniform sampler2D U_MainTexture;
varying vec2 M_coord;
varying vec3 M_normal;
varying vec3 M_WordPos;
//uniform vec3 M_LightPos; // 平行光
//uniform vec4 M_AmbientLightColor;
//uniform vec4 M_AmbientMaterial;
//uniform vec4 M_DiffuseLightColor;
//uniform vec4 M_DiffuseMaterial;
void main()
{
// Ambient
vec4 M_AmbientLightColor = vec4(0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 1.0);
vec4 M_AmbientMaterial = vec4(0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 1.0);
vec4 ambientColor = M_AmbientLightColor * M_AmbientMaterial;
// Diffuse
vec3 M_LightPos = vec3(10.0, 10.0, 0.0);
vec3 LightNormal = normalize(M_LightPos); // 指向光源的单位向量
vec3 NormalNormal = normalize(M_normal); // 法线的单位向量
// 点乘获取光照强度
vec4 M_DiffuseLightColor = vec4(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
vec4 M_DiffuseMaterial = vec4(0.9, 0.9, 0.9, 1.0);
vec4 diffuseColor = M_DiffuseLightColor * M_DiffuseMaterial *
max(0.0, dot(NormalNormal, LightNormal));
// 镜面反射
vec4 specularLightColor = vec4(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
vec4 specularMaterial = vec4(0.4, 0.4, 0.4, 1.0);
vec3 reflerDir = normalize(reflect(-LightNormal, NormalNormal));
vec3 eyeDir = normalize(vec3(0.0) - M_WordPos);
vec4 specularColor = specularLightColor * specularMaterial *
pow(max(0.0, dot(reflerDir, eyeDir)), 180);
gl_FragColor = ambientColor + texture2D(U_MainTexture, M_coord) * 1
+ specularColor;
}为了使模型看的更清楚,我没用漫反射。如果使用漫反射可以将最后一句改成:
gl_FragColor = ambientColor + texture2D(U_MainTexture, M_coord) * diffuseColor + specularColor;
本文出自 “不会飞的纸飞机” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://douzhq.blog.51cto.com/12552184/1930978
以上是关于基于Qt的OpenGL可编程管线学习- obj模型绘制的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章