Flume概述
Posted Super_Orco
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Flume概述相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Flume概述
常见的开源数据收集系统有:
非结构数据(日志)收集
Flume
结构化数据收集(传统数据库与 Hadoop 同步)
Sqoop:全量导入
Canal(alibaba):增量导入
Databus(linkedin):增量导入
Flume是什么:
由Cloudera公司开源
分布式、可靠、高可用的海量日志采集系统
数据源可定制,可扩展
数据存储系统可定制,可扩展
中间件:屏蔽了数据源和数据存储系统的异构性
Flume的两个版本
Flume OG 与 Flume NG
OG版本因为有一个巨大的BUG,所以进行升级改造,产出NG版本,NG 版本精简了代码,简化了架构
Flume NG的基本架构
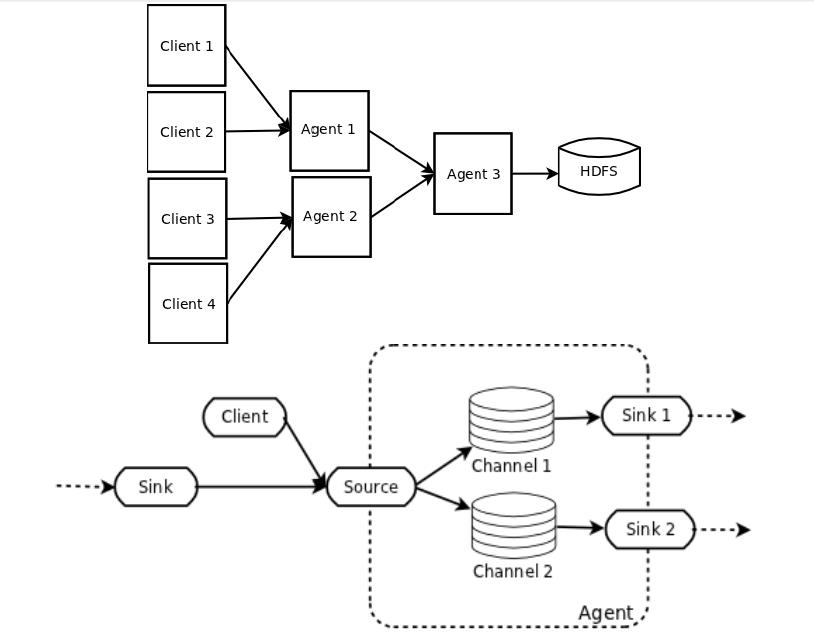
一个Agent就代表一个Flume
Flume 有三个组件,Sourc、Channel、Sink,分别对应了Producer、Buffer、Customer
Flume NG的核心概念
Event
Event是Flume数据传输的基本单元,Event由可选的header和载有数据的一个byte array构成,载有的数据对flume是不透明的,Flume 不关心数据是什么样子的,Header是容纳了key-value字符串对的无序集合,key在集合内是唯一的
Client
Client 一般不需要配置在 Flume 中,只需要配置 Agent 即可,Client是一个将原始log包装成events并且发送它们到一个或多个agent的实体,目的是从数据源系统中解耦Flume,在flume的拓扑结构中不是必须的。
Client的实例可以是 Flume log4j 的 Appender,或者可以使用Client SDK (org.apache.flume.api)定制特定的Client
Agent
一个Agent包含Source, Channel, Sink和其他组件,它利用这些组件将events从一个节点传输到另一个节点或最终目的,agent是flume流的基础部分
Source、Channel、Sink 这些的配置具体可以去官网看,比如 kafka 的 sink 怎么配置等,不过我还是列举了一些,图个印象
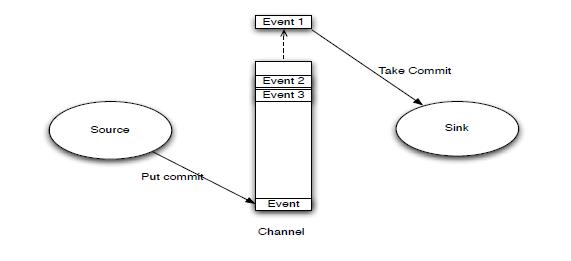
Source 将数据写入到 Channel 的尾部,然后 Sink 从 Channel 中获取头部 Event
Agent.Source
Source 负责接收日志数据,并将数据包装成Event,并将events批量的放到一个或多个Channel
不同类型的Source:
1、与系统集成的Source: Syslog, Netcat
2、自动生成事件的Source: Exec
可执行任意Unix命令,无容错性,比如将 tail -f 的标准输出作为输入源,但是有问题,因为再次运行 tail -f 不一定会接着上次的
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sources.r1.type = exec
a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /var/log/secure
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
3、监听文件夹下文件变化:
3.1、Spooling Directory Source(是暴露出来的,能直接使用的)
监听一个文件夹下新产生的文件,并读取内容,发至 channel
已经产生的文件不能进行任意修改,不然会停止处理
建议将文件(唯一文件名)写到一个临时目录下,之后move到监听目录下
spooling能监听新文件的产生,能监听文件的变化吗:
不可以,我可以将文件生成在一个文件夹,等文件写完了,将文件复制到一个文件夹,然后再去读取,总之,flum的spooling这种方式,监听的文件内容不能有修改,也不能有新增

a1.channels = ch-1
a1.sources = src-1
a1.sources.src-1.type = spooldir
a1.sources.src-1.channels = ch-1
a1.sources.src-1.spoolDir = /var/log/apache/flumeSpool
a1.sources.src-1.fileHeader = true
3.2、Taildir Source(没有暴露出来,不可以直接使用,某公司内部貌似修改源码,内部可以使用了,说实话,既然不暴露出来给我用,设计出来的用意是什么)
监听文件内容,一旦新写入一行新数据,则读取之
支持断点续读,定期将最新读取数据的偏移量写入json 文件
根据文件修改时间决定读取优先级,最新的文件优先读取
读取完的文件不会做任何处理(比如删除,重命名等)
目前仅支持文本文件
 a1.sources = r1
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sources.r1.type = TAILDIR
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sources.r1.positionFile = /var/log/flume/taildir_position.json
a1.sources.r1.filegroups = f1 f2
a1.sources.r1.filegroups.f1 = /var/log/test1/example.log
a1.sources.r1.headers.f1.headerKey1 = value1
a1.sources.r1.filegroups.f2 = /var/log/test2/.*log.*
a1.sources.r1.headers.f2.headerKey1 = value2
a1.sources.r1.headers.f2.headerKey2 = value2-2
a1.sources.r1.fileHeader = true
4、用于Agent和Agent之间通信的 IPC Source: Avro、Thrift(比json、fastjson、xml更好的数据传输结构),下面以Avro 为例

a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sources.r1.type = avro
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sources.r1.bind = 0.0.0.0
a1.sources.r1.port = 4141
5、Source必须至少和一个channel关联
Agent.Channel
Channel位于Source和Sink之间,用于缓存event
当Sink成功将event发送到下一跳的channel或最终目的,event从Channel移除
不同的Channel提供的持久化水平也是不一样的
1、Memory Channel: volatile,基于内存的这种方式优点肯定是快,缺点是可能会丢失
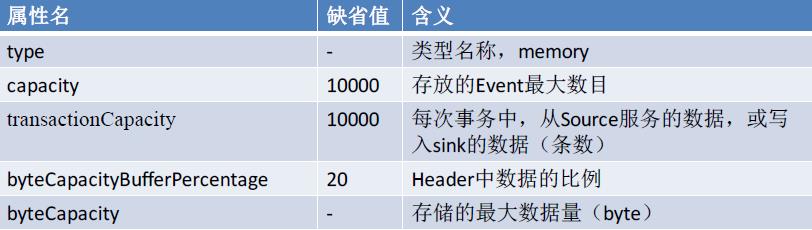 a1.channels = c1
a1.channels = c1
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 10000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 10000
a1.channels.c1.byteCapacityBufferPercentage = 20
a1.channels.c1.byteCapacity = 800000
2、File Channel: 基于WAL(预写式日志Write-Ahead Logging)实现,缺点就是慢,优点是不会丢失,和memory权衡使用吧
 a1.channels = c1
a1.channels = c1
a1.channels.c1.type = file
a1.channels.c1.checkpointDir = /mnt/flume/checkpoint
a1.channels.c1.dataDirs = /mnt/flume/data
3、JDBC Channel: 基于嵌入Database实现
Channel支持事务,提供较弱的顺序保证
可以和任何数量的Source和Sink工作
Agent.Sink
Sink负责将event传输到下一跳或最终目的,成功完成后将event从channel移除
必须作用于一个确切的channel
不同类型的Sink:
1、存储event到最终目的的终端Sink. 比如:
1.1、HDFS

a1.channels = c1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = /flume/events/%y-%m-%d/%H%M/%S
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = eventsa1.
sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 10
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = minute
#a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.codeC=gzip, bzip2, lzo, lzop, snappy
#a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType=SequenceFile, DataStream,CompressedStream
1.2、HBase

a1.sinks = k1
a1.sinks.k1.type = hbase
a1.sinks.k1.table = foo_table
a1.sinks.k1.columnFamily = bar_cf
a1.sinks.k1.serializer = org.apache.flume.sink.hbase.RegexHbaseEventSerializer
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
1.3、hive

a1.channels = c1
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.sinks = k1
a1.sinks.k1.type = hive
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k1.hive.metastore = thrift://127.0.0.1:9083
a1.sinks.k1.hive.database = logsdb
a1.sinks.k1.hive.table = weblogs
a1.sinks.k1.hive.partition = asia,%{country},%y-%m-%d-%H-%M
a1.sinks.k1.useLocalTimeStamp = false
a1.sinks.k1.round = true
a1.sinks.k1.roundValue = 10
a1.sinks.k1.roundUnit = minute
a1.sinks.k1.serializer = DELIMITED
a1.sinks.k1.serializer.delimiter = "\\t"
a1.sinks.k1.serializer.serdeSeparator = \'\\t\'
a1.sinks.k1.serializer.fieldnames =id,,msg
2、自动消耗的Sink. 比如: Null Sink,生产环境中很少用,主要用于测试环境
3、用于Agent间通信的 IPC sink: Avro
还有一些其他重要组件
Interceptor
作用于Source,按照预设的顺序在必要地方装饰和过滤events
Channel Selector
允许Source基于预设的标准,从所有Channel中,选择一个或多个Channel
Sink Processor
多个Sink可以构成一个Sink Group。Sink Processor可以通过组中所有Sink实现负载均衡;也可以在一个Sink失败时转移到另一个
两个常用的拓扑示例



a1.channels = c1 a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 k2 a1.sinkgroups = g1 a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = LOAD_BALANCE a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.selector = ROUND_ROBIN a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.backoff = true a1.channels.c1.type = FILE a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sources.r1.type = AVRO a1.sources.r1.bind = 0.0.0.0 a1.sources.r1.port = 41414 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 a1.sinks.k1.type = AVRO a1.sinks.k1.hostname = a21.example.org a1.sinks.k1.port = 41414 a1.sinks.k2.channel = c1 a1.sinks.k2.type = AVRO a1.sinks.k2.hostname = a22.example.org a1.sinks.k2.port = 41414

a2.channels = c1 a2.sources = r1 a2.sinks = k1 a2.channels.c1.type = FILE a2.sources.r1.channels = c1 a2.sources.r1.type = AVRO a2.sources.r1.bind = 0.0.0.0 a2.sources.r1.port = 41414 a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1 a2.sinks.k1.type = HDFS a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://namenode.example.org a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
LogAgent.sources = mysource LogAgent.channels = mychannel LogAgent.sinks = mysink LogAgent.sources.mysource.type = spooldir LogAgent.sources.mysource.channels = mychannel LogAgent.sources.mysource.spoolDir =/tmp/logs LogAgent.sinks.mysink.channel = mychannel LogAgent.sinks.mysink.type = hdfs LogAgent.sinks.mysink.hdfs.path = hdfs://node1:9000/data/logs/%Y/%m/%d/%H/ LogAgent.sinks.mysink.hdfs.batchSize = 1000 LogAgent.sinks.mysink.hdfs.rollSize= 0 LogAgent.sinks.mysink.hdfs.rollCount = 10000 LogAgent.sinks.mysink.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true LogAgent.channels.mychannel.type = memory LogAgent.channels.mychannel.capacity = 10000 LogAgent.channels.mychannel.transactionCapacity = 100
启动方式:
$ bin/flume-ng agent -n LogAgent -c conf -f conf/logagent.properties -Dflume.root.logger=DEBUG,console

flume当提示报错,进入safe mod,可能是删掉hdfs的什么文件了, 以下是老师的方法: [orco@node1 resources]$ hadoop fs -rm -r -skipTrash / rm: Cannot delete /. Name node is in safe mode. [orco@node1 resources]$ hadoop dfsadmin -safemode leave DEPRECATED: Use of this script to execute hdfs command is deprecated. Instead use the hdfs command for it. Safe mode is OFF [orco@node1 resources]$ hadoop fs -rm -r -skipTrash / rm: `/\': Input/output error [orco@node1 resources]$ hadoop fs -rm -r -skipTrash /* rm: `/bin\': No such file or directory rm: `/boot\': No such file or directory rm: `/dev\': No such file or directory rm: `/etc\': No such file or directory rm: `/home\': No such file or directory rm: `/lib\': No such file or directory rm: `/lib64\': No such file or directory rm: `/lost+found\': No such file or directory rm: `/media\': No such file or directory rm: `/mnt\': No such file or directory rm: `/opt\': No such file or directory rm: `/proc\': No such file or directory rm: `/root\': No such file or directory rm: `/sbin\': No such file or directory rm: `/selinux\': No such file or directory rm: `/srv\': No such file or directory rm: `/sys\': No such file or directory Deleted /tmp rm: `/usr\': No such file or directory rm: `/var\': No such file or directory [orco@node1 resources]$ hadoop fs -rm -r -skipTrash /hdfs Deleted /hdfs [orco@node1 resources]$ hadoop fs -rm -r -skipTrash /user Deleted /user [orco@node1 resources]$
以上是关于Flume概述的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
