跟着小程学微服务-自己动手扩展分布式调用链
Posted 小程故事多_80
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了跟着小程学微服务-自己动手扩展分布式调用链相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、说在前面
微服务是当下最火的词语,现在很多公司都在推广微服务,当服务越来越多的时候,我们是否会纠结以下几个问题:
- 面对一笔超时的订单,究竟是哪一步处理时间超长呢?
- 数据由于并发莫名篡改,到底都谁有重大嫌疑呢?
- 处理遗漏了一笔订单,曾经是哪个环节出错把它落下了?
- 系统莫名的报错,究竟是哪一个服务报的错误?
- 每个服务那么多实例服务器,如何快速定位到是哪一个实例服务器报错的呢?
现在很多系统都要求可用性达到99.9%以上,那么我们除了增加系统健壮性减少故障的同时,我们又如何在真正发生故障的时候,快速定位和解决问题,也将是我们的重中之重。
在做微服务框架选择的时候,Spring Cloud无疑是当下最火的,但是因为Spring Cloud是近二年的后起新秀,以及在使用方式上面的差别,目前在很多中小企业还是以dubbo为主,不过遗憾的是,dubbo从官方来讲已经不维护了,很多公司都是自己再去维护,那么今天我就来给大家介绍一下,我们是如何通过修改dubbo源码实现了分布式调用链的第一阶段:调用链日志的打印。
二、什么是分布式调用链
1、什么是调用链
基于Google Dapper论文,用户每次请求都会生成一个全局ID(traceId),通过它将不同系统的“孤立”的日志串在一起,重组成调用链。
2、调用链的调用过程
- 当用户发起一个请求时,首先到达前端A服务,然后分别对B服务和C服务进行RPC调用。
- B服务处理完给A做出响应,但是C服务还需要和后端的D服务和E服务交互之后再返还给A服务,最后由A服务来响应用户的请求。
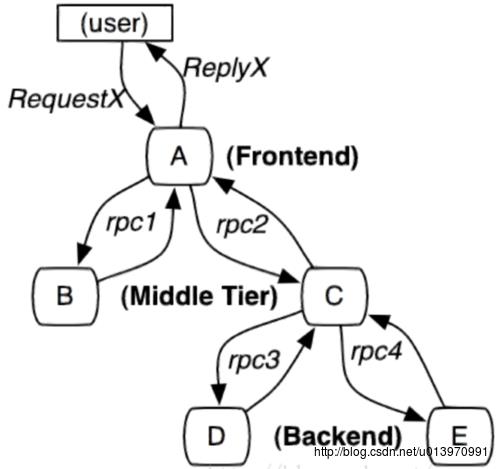
3、对整个调用过程的追踪
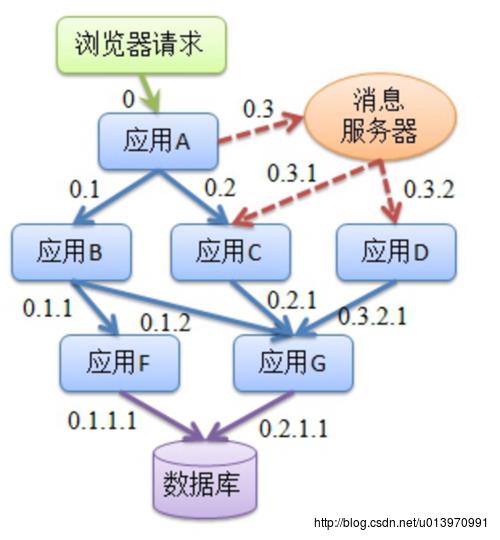
- 请求到来生成一个全局TraceID,通过TraceID可以串联起整个调用链,一个TraceID代表一次请求。
- 除了TraceID外,还需要SpanID用于记录调用父子关系。每个服务会记录下Parent id和Span id,通过他们可以组织一次完整调用链的父子关系。
- 一个没有Parent id的span成为root span,可以看成调用链入口。
- 所有这些ID可用全局唯一的64位整数表示;
- 整个调用过程中每个请求都要透传TraceID和SpanID。
- 每个服务将该次请求附带的TraceID和附带的SpanID作为Parent id记录下,并且将自己生成的SpanID也记录下。
- 要查看某次完整的调用则只要根据TraceID查出所有调用记录,然后通过Parent id和Span id组织起整个调用父子关系。
最终的TraceId和SpanId的调用关系图如下所示:
三、基于Dubbo的实现
1、Dubbo的调用过程
在我们分析源码的时候,有一行代码是:
Protocol refprotocol = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getAdaptiveExtension();这行代码实际上是利用SPI机制,动态加载指定的Protocol注入到ProtocolFilterWrapper中,再通过Wrapper访问到可执行的Invoker对象,Dubbo默认使用的是DubboProtocol最终通过netty的方式进行通信,具体调用过程请看下图:
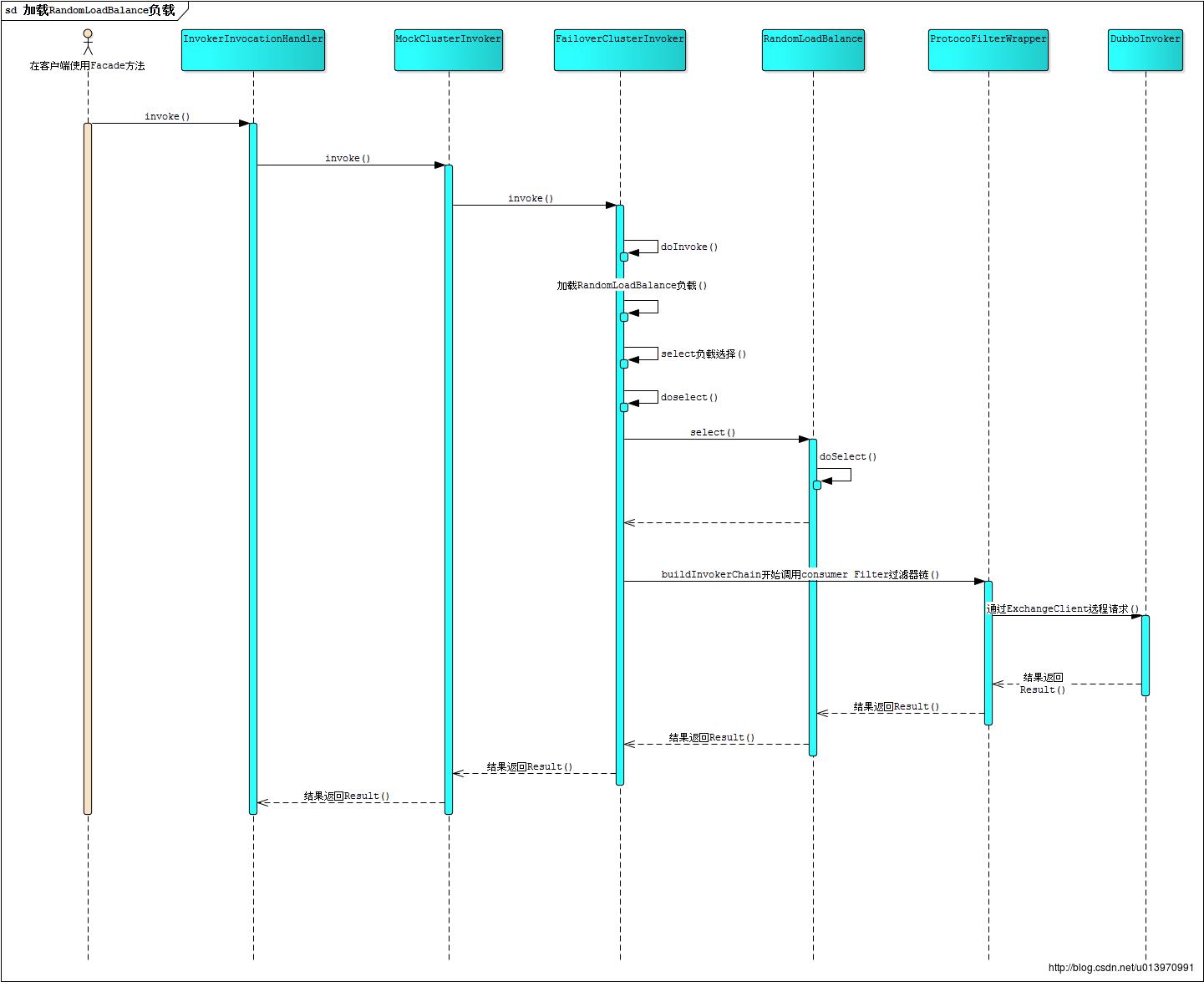
可以看到基本的流程是:
InvokerInvocationHandler ->ClusterInvoker ->LoadBalance -> ProtocolFilterWrapper -> Protocol -> DubboInvoker
而在调用链的实现过程中技术难点主要是有二个:
- 在哪里暂存调用链
- 调用链信息如何传递
2、Dubbo协议下的调用链传递过程
那么在默认的Dubbo协议下,实现调用链的过程很简单只需要在应用项目或者Dubbo源码中使用如下代码就可以实现调用链的传递。
RpcContext.getContext().setAttachment(CallChainContext.TRACEID, traceIdValue);
RpcInvocation rpcInvocation = (RpcInvocation) inv;
rpcInvocation.setAttachment(CallChainContext.TRACEID, traceIdValue);
rpcInvocation.setAttachment(CallChainContext.SPANID, spanIdValue);在DubboInvoker中最终通信的时候会将上述代码的RpcInvocation对象传递出去,那么我们只需要在接收端获取既可。
3、Hessian协议下的调用链传递过程
大家都知道,Dubbo在实现通信的协议上使用的有Netty、Hessian、Rest等方式,由于我们项目的特殊性,目前采用的是Dubbo的Hessian协议。
先看如下代码:
protected <T> T doRefer(Class<T> serviceType, URL url) throws RpcException {
HessianProxyFactory hessianProxyFactory = new HessianProxyFactory();
String client = url.getParameter(Constants.CLIENT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_HTTP_CLIENT);
if ("httpclient".equals(client)) {
hessianProxyFactory.setConnectionFactory(new HttpClientConnectionFactory());
} else if (client != null && client.length() > 0 && ! Constants.DEFAULT_HTTP_CLIENT.equals(client)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unsupported http protocol client=\\"" + client + "\\"!");
}
int timeout = url.getParameter(Constants.TIMEOUT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
hessianProxyFactory.setConnectTimeout(timeout);
hessianProxyFactory.setReadTimeout(timeout);
return (T) hessianProxyFactory.create(serviceType, url.setProtocol("http").toJavaURL(), Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader());
}通过代码可以看到,实际上在使用Hessian通信的时候并没有将RpcInvocation里面设定的TraceId和SpanId传递出去,调用在这一块中止了。
那我们如何自己来实现呢?
- 第一步、我们在Dubbo源码中自己实现了一个Filter(不是Dubbo的Filter),用来产生TraceId和SpanId,以及最后的清理工作,请看代码如下:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// 将请求转换成HttpServletRequest请求
HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = (HttpServletRequest) request;
try {
archieveId(request);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.log(Level.SEVERE, "traceId或spanId解析出错!", e);
}
try {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
} catch (IOException e) {
//还原线程名称
throw e;
} catch (ServletException e) {
//还原线程名称
throw e;
} finally {
CallChainContext.getContext().clearContext();
}
}在Filter中产生TraceId和SpanId以后,会将二个值放到我们封装好的CallChainContext中进行暂存。
- 第二步、我们将HessianProxyFactory进行继承改造
public class HessianProxyWrapper extends HessianProxy {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 353338409377437466L;
private static final Logger log = Logger.getLogger(HessianProxyWrapper.class
.getName());
public HessianProxyWrapper(URL url, HessianProxyFactory factory, Class<?> type) {
super(url, factory, type);
}
protected void addRequestHeaders(HessianConnection conn) {
super.addRequestHeaders(conn);
conn.addHeader("traceId", CallChainContext.getContext().getTraceId());
conn.addHeader("spanId", CallChainContext.getContext().getSpanId());
}
}我们将CallChainContext中暂存的TraceId和SpanId放入到Hessian的header中。
继承Dubbo的HessianProxyFactory这个类,新类名是HessianProxyFactoryWrapper,在create方法中将HessianProxy替换为新封装的HessianProxyWrapper,代码如下:
public Object create(Class<?> api, URL url, ClassLoader loader) {
if (api == null)
throw new NullPointerException(
"api must not be null for HessianProxyFactory.create()");
InvocationHandler handler = null;
//将HessianProxy修改为HessianProxyWrapper
handler = new HessianProxyWrapper(url, this, api);
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, new Class[] { api,
HessianRemoteObject.class }, handler);
}修改后的HessianProtocol的代码如下:
protected <T> T doRefer(Class<T> serviceType, URL url) throws RpcException {
//新继承的
HessianProxyFactoryWrapper hessianProxyFactory = new HessianProxyFactoryWrapper();
String client = url.getParameter(Constants.CLIENT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_HTTP_CLIENT);
if ("httpclient".equals(client)) {
hessianProxyFactory.setConnectionFactory(new HttpClientConnectionFactory());
} else if (client != null && client.length() > 0 && ! Constants.DEFAULT_HTTP_CLIENT.equals(client)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unsupported http protocol client=\\"" + client + "\\"!");
}
int timeout = url.getParameter(Constants.TIMEOUT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
hessianProxyFactory.setConnectTimeout(timeout);
hessianProxyFactory.setReadTimeout(timeout);
return (T) hessianProxyFactory.create(serviceType, url.setProtocol("http").toJavaURL(), Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader());
}通过以上方式可以将我们产生的TraceId和SpanId通过Hessian的方式传递出去,我们在接收请求的时候,只需要使用如下代码的方式就可以获取到二个值。
String traceIdValue = request.getHeader("traceId");
String spanIdValue = request.getHeader("spanId"); - 第三步、如何打印调用链信息
我们在项目中使用的是Logback的方式打印日志,首先想到的是继承一个ClassicConverter对象,实现Logback的自定义格式转换器,参考代码如下:
public class CallChainConverter extends ClassicConverter {
@Override
public String convert(ILoggingEvent event) {
Map<String,String> globalMap = CallChainContext.getContext().get();
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
if(null == globalMap) {
globalMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
CallChainContext.getContext().add(globalMap);
} else {
String traceId = globalMap.get("traceId");
String spainId = globalMap.get("spanId");
if(traceId == null) {
traceId = String.valueOf(Thread.currentThread().getId());
}
if(spainId == null) {
spainId = "1";
}
builder.append("GUID[");
builder.append(traceId);
builder.append("] - LEVEL[");
builder.append(spainId);
builder.append("] ");
}
return builder.toString();
}
}在Logback配置文件中进行如下修改:
<conversionRule conversionWord="callContext" converterClass="com.ulpay.dubbox.core.util.CallChainConverter" />
<layout class="com.ulpay.dubbox.core.util.CallChainPatternLayout">
<pattern>%d %-5p %c [%t] %callContext - %m%n</pattern>
</layout>
最终打印的日志格式如下样式:
[RMI TCP Connection(127.0.0.1:2181)] GUID[760a1fedd7ab4ff8a309cebaa01cc61d] - LEVEL[15.27.1] - [执行时间] - [xxx项目] - [xxx服务.xxx方法] - 耗时[7]毫秒4、采集日志信息实现分布式调用链界面展示
一个最简单的demo示意图如下:
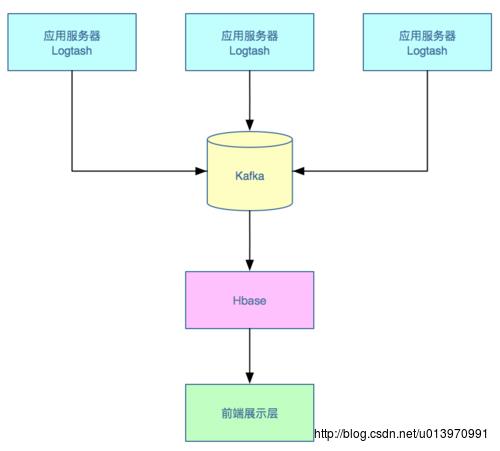
- 通过logstash采集日志到kafka
- kafka负责提供数据给Hbase
- 通过Hbase进行数据分析
最终效果展示图如下:
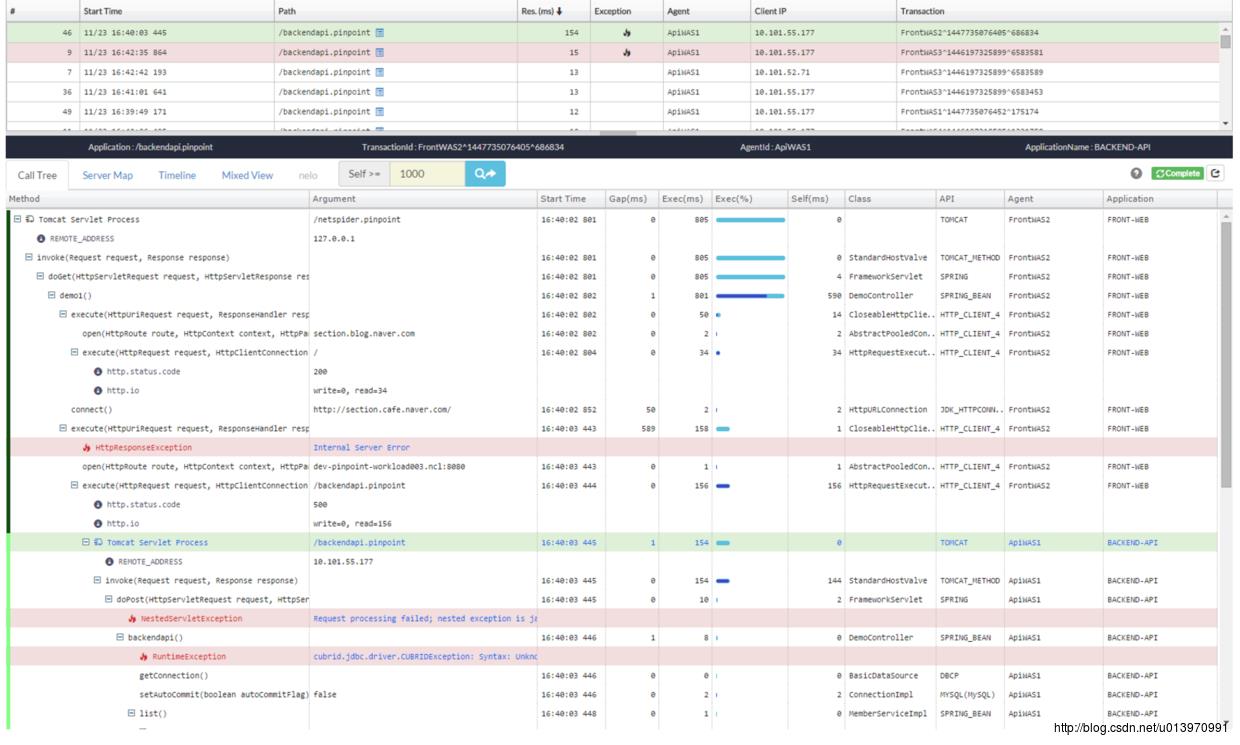
四、总结
对于分布式调用链来说,目前市面上有很多开源的工具,比如:pinpoint,Cat以及sky-walking等等,将这些工具与我们扩展的调用链日志结合起来将起到更好的效果。
出于公司的考虑,以上的代码采用的是伪代码,但也具有一定参考价值,我写这篇文章的目的也是希望能够给大家提供一些思路,希望大家能够多提建议,我会持续改进。
以上是关于跟着小程学微服务-自己动手扩展分布式调用链的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章