网络配置文件
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了网络配置文件相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在网络配置工具中所有看到的配置信息,都是存放在Linux系统的网络配置文件中。所有用户可以通过直接更改配置文件的方法来对网络信息进行配置。
2.1、网络设备配置文件
网络配置工具的设备列表框中的每一个设备,在/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/目录下都有一个以‘<ifcfg-<设备名>‘命名的文件与之对应。使用ifconfig命令可以查看所有活动接口的相关信息。在更改配置文件信息时需要重启网络服务方可生效。
设备配置/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-INTERFACE_NAME
在/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-INTERFACE_NAME配置文件中常见的配置选项有:
DEVICE: 此配置文件应用到的设备; HWADDR: 对应的设备的MAC地址; BOOTPROTO: 激活此设备时使用的地址配置协议,常用的dhcp, static, none, bootp; NM_CONTROLLED:此网卡是否接受networkManager脚本控制;建议为“no”; ONBOOT: 在系统引导时是否激活此设备; TYPE: 接口类型;常见有的Ethernet, Bridge; UUID: 设备的惟一标识; IPADDR: 指明IP地址; NETMASK: 子网掩码; GATEWAY: 默认网关; DNS1: 第一个DNS服务器指向; DNS2: 第二个DNS服务器指向; USERCTL: 普通用户是否可控制此设备; PEERDNS:dhcp时是否允许dhcp server分配的dns服务器指向信息直接覆盖至/etc/resolv.conf文件中 |
[[email protected] ~]# ifconfig -a eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:0C:29:B7:AB:D0 #网络接口设备eth0 inet addr:192.168.191.128 Bcast:192.168.191.255 Mask:255.255.255.0 inet6 addr: fe80::20c:29ff:feb7:abd0/64 Scope:Link UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1 RX packets:161 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:130 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:15918 (15.5 KiB) TX bytes:14985 (14.6 KiB) lo Link encap:Local Loopback #回环接口信息 inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0 inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1 RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:0 RX bytes:0 (0.0 b) TX bytes:0 (0.0 b) [[email protected] ~]# cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ [[email protected] ~]# cat ifcfg-eth0 #网络设备eth0的配置信息 DEVICE=eth0 #设备名 HWADDR=00:0C:29:B7:AB:D0 #MAC地址 TYPE=Ethernet #类型为以太网 UUID=cd26724e-aee9-44da-af16-28b152152b1f #设备唯一标识吗 ONBOOT=yes #系统启动时是否激活此设备 NM_CONTROLLED=yes #此网卡是否接受networkManager脚本控制 BOOTPROTO=dhcp #激活此设备时使用的地址配置协议,dhcp, static, none, bootp等
DNS配置/etc/resolv.conf
[[email protected] network-scripts]# cat /etc/resolv.conf ; generated by /sbin/dhclient-script #启动通过/sbin/dhclient-script脚本控制 search localdomain nameserver 192.168.191.2 #DNS服务器
network主机名配置/etc/sysconfig/network
[[email protected] network-scripts]# cat /etc/sysconfig/network NETWORKING=yes #是否启动 HOSTNAME=localhost.localdomain #主机名
hosts文件配置主机名和IP地址映射/etc/hosts
在hosts文件中可以添加主机名和IP地址的映射关系,对于已经添加进该文件的主机名,无序经过DNS服务器即可解析到对应的IP地址。文件中每一行记录定义了一对映射关系,各字段以空格或Tab键为分割,如果有多个主机对应同一个IP地址,可以写在同一行,记录格式为:
IP地址 主机名1 [主机名2]...
[[email protected] network-scripts]# cat /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
2.2、常用网络命令
ifconfig管理网络接口
ifcconfig命令用于查看和更改网络接口的地址和相关参数,包括IP地址、网络掩码、广播地址,该命令只能由root执行,命令格式为:
ifconfig <interface> ifconfig interface [aftype] option | address ...
常用的选项为:
-a: 默认只显示激活的网络接口信息,使用该选项或显示全部网路接口信息 address: 设置指定接口设备的IP地址 broadcast 地址:设置接口的广播地址 down: 关闭指定的网络接口 interface: 指定的网络接口名,如eth0和eth1 netmask 掩码: 设置接口的子网掩码 -s: 只显示网络接口的摘要信息 up: 激活指定的网络接口 |
查看激活网络接口的信息
[[email protected] network-scripts]# ifconfig eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:0C:29:B7:AB:D0 inet addr:192.168.191.128 Bcast:192.168.191.255 Mask:255.255.255.0 inet6 addr: fe80::20c:29ff:feb7:abd0/64 Scope:Link UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1 RX packets:552 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:381 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:51005 (49.8 KiB) TX bytes:49219 (48.0 KiB) lo Link encap:Local Loopback inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0 inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1 RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:0 RX bytes:0 (0.0 b) TX bytes:0 (0.0 b)
显示所有网络接口信息
[[email protected] network-scripts]# ifconfig -a eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:0C:29:B7:AB:D0 inet addr:192.168.191.128 Bcast:192.168.191.255 Mask:255.255.255.0 inet6 addr: fe80::20c:29ff:feb7:abd0/64 Scope:Link UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1 RX packets:566 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:390 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:52259 (51.0 KiB) TX bytes:51101 (49.9 KiB) lo Link encap:Local Loopback inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0 inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1 RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:0 RX bytes:0 (0.0 b) TX bytes:0 (0.0 b)
激活或关闭网络接口
ifconfig eth0 down或者 ifdown eth0 #关闭网络接口eth0 ifconfig eth0 up或者 ifup eth0 #激活网络接口eth1
更改网路接口配置信息
[[email protected] network-scripts]# ifconfig eth0 192.168.191.100 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.191.255 #更改网络接口eth0的IP192.168.191.100 #子网掩码255.255.255.0 #广播地址192.168.191.255
使用hostname查看主机名
hostname命令用于查看和更改系统的主机名,使用hostname更改后的主机名仅对当前的启动有效,系统重启后所做更改将会消失。命令格式为
hostname [主机名]
[[email protected] network-scripts]# hostname #查看当前主机名 localhost.localdomain [[email protected] network-scripts]# hostname mylinux #更改主机名为mylinux [[email protected] network-scripts]# hostname mylinux
使用route命令管理路由
Linux系统支持系统自定义路由,用户可以使用route命令管理系统的路由表,包括查看路由表信息、添加和删除路由表记录等。路由的作用,实现主机、网络的通信的信息转发。网关的作用,控制通信转发是否允许,默认时就是路由。路由的route命令格式为:
route [-CFvnee] route [-v] [-A family] add [-net|-host] target [netmask Nm] [gw Gw] [metric N] [mss M] [window W] [irtt I] [reject] [mod] [dyn] [reinstate] [[dev] If] route [-v] [-A family] del [-net|-host] target [gw Gw] [netmask Nm] [metric N] [[dev] If] route [-V] [--version] [-h] [--help]
命令常用选项为:
-add: 添加路由记录 -delete: 删除路由记录 dev: 指定的网络接口名,如eth0 gw: 指定路由的网关 -host: 路由到达的是一台主机 -net: 路由到达的是一个网络 -netmask 子网掩码: 指定路由目标的子网掩码 |
查看路由表
[[email protected] network-scripts]# route Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface 192.168.191.0 * 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0 link-local * 255.255.0.0 U 1002 0 0 eth0 default 192.168.191.2 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
各字段说明: Destination 目标网段或者主机 Gateway 网关地址,”*” 表示目标是本主机所属的网络,不需要路由 Genmask 网络掩码 Flags 标记。一些可能的标记如下: U — 路由是活动的 H — 目标是一个主机 G — 路由指向网关 R — 恢复动态路由产生的表项 D — 由路由的后台程序动态地安装 M — 由路由的后台程序修改 ! — 拒绝路由 Metric 路由距离,到达指定网络所需的中转数(linux 内核中没有使用) Ref 路由项引用次数(linux 内核中没有使用) Use 此路由项被路由软件查找的次数 Iface 该路由表项对应的输出接口 |
添加到主机的路由记录
[[email protected] network-scripts]# route add -host 192.168.191.100 gw 192.168.191.1 dev eth0 #添加到主机192.168.191.100 ,网关192.168.191.1,网络接口eth0 [[email protected] network-scripts]# route Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface 192.168.191.100 192.168.191.1 255.255.255.255 UGH 0 0 0 eth0 192.168.191.0 * 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0 link-local * 255.255.0.0 U 1002 0 0 eth0 default 192.168.191.2 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
添加到网络的路由记录
[[email protected] network-scripts]# route add -net 192.168.12.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 192.168.191.1 dev eth0 [[email protected] network-scripts]# route Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface 192.168.191.100 192.168.191.1 255.255.255.255 UGH 0 0 0 eth0 192.168.12.0 192.168.191.1 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0 192.168.191.0 * 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0 link-local * 255.255.0.0 U 1002 0 0 eth0 default 192.168.191.2 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
删除路由记录
[[email protected] network-scripts]# route del -host 192.168.191.100 [[email protected] network-scripts]# route Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface 192.168.1.0 192.168.191.1 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0 192.168.12.0 192.168.191.1 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0 192.168.191.0 * 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0 link-local * 255.255.0.0 U 1002 0 0 eth0 default 192.168.191.2 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
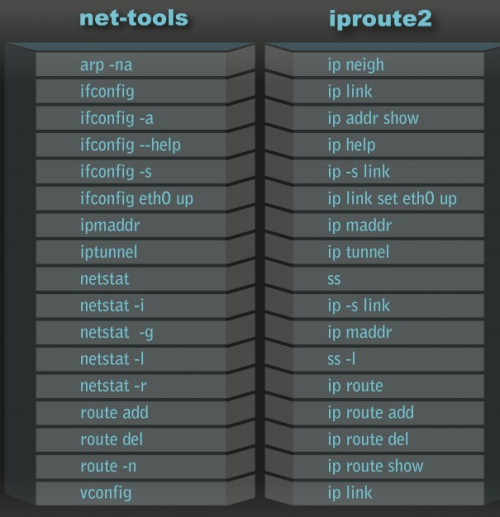
ip类命令显示或管理路由、网络设备
Linux的ip命令和ifconfig类似,但前者功能更强大,并旨在取代后者。使用ip命令,只需一个命令,你就能很轻松地执行一些网络管理任务。ifconfig是net-tools中已被废弃使用的一个命令,许多年前就已经没有维护了。iproute2套件里提供了许多增强功能的命令,ip命令即是其中之一。
命令使用格式:
ip [ OPTIONS ] OBJECT { COMMAND | help }
OBJECT := { link | addr | route }ip link OBJECT:启动/关闭网络设备接口
setdev IFACE [up | down]
show[dev IFACE][up]
ip address - 协议地址管理
ip addr { add | del } IFADDR dev STRING 一个接口上配置多个地址而不使用别名
[label LABEL]: 添加地址时指明网卡别名
[scope {global|link|host}]:指明作用域
global: 全局可用;
link: 仅链接可用;
host: 本机可用;
[broadcast ADDRESS]:指明广播地址
ip addr show - 查看地址
[dev DEVICE][label PATTERN][primary and secondary]
ip addr flush Interface [to Net_Address] 刷新
ip route - 路由管理
添加路由:ip route add TARGET via GW [dev IFACE src SOURCE_IP]
TARGET:
主机路由:IP
网络路由:NETWORK/MASK
删除路由:ip route del TARGET
显示路由: ip route show刷新:ip route flush
添加网关:ip route add defalt via GW [dev IFACE]
网络管理或监测命令ping/netstat/ss
使用ping检测主机是否激活
ping命令是Linux系统使用最多的网络命令,该命令基于ICMP协议,通常被用来检测网络是否联通,以及远端主机的响应速度,命令格式为:
ping [ -LRUbdfnqrvVaAB] [ -c count] [ -i interval] [ -l preload] [ -p pattern] [ -s packetsize] [ -t ttl] [ -w deadline] [ -F flowlabel] [ -I interface] [ -M hint] [ -Q tos] [ -S sndbuf] [ -T timestamp option] [ -W timeout] [ hop ...]
常见选项:
-c #:测试次数,ping命令默认会一直发送包,直到用户强行终止 -w deadline: 测试执行时长 -i 间隔:指定收发包的间隔秒数 -n:只输出数值 -q:只显示开头和结尾的摘要信息,而不显示指令执行过程的信息 -r:忽略普通的路由表,直接将数据包送到远端主机 -R:记录路由过程 -s 包大小:设置数据包的大小,单位为字节 -t 存活数值:设置存活数值TTL的大小 |
[[email protected] home]# ping 192.168.191.1 PING 192.168.191.1 (192.168.191.1) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.191.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.408 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.191.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.310 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.191.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.304 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.191.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.367 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.191.1: icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=0.335 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.191.1: icmp_seq=6 ttl=64 time=0.196 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.191.1: icmp_seq=7 ttl=64 time=0.214 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.191.1: icmp_seq=8 ttl=64 time=0.273 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.191.1: icmp_seq=9 ttl=64 time=0.236 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.191.1: icmp_seq=10 ttl=64 time=0.371 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.191.1: icmp_seq=11 ttl=64 time=0.369 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.191.1: icmp_seq=12 ttl=64 time=0.364 ms ^C --- 192.168.191.1 ping statistics --- 12 packets transmitted, 12 received, 0% packet loss, time 11717ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.196/0.312/0.408/0.067 ms
限制检测次数
[[email protected] home]# ping -c 3 192.168.191.1 PING 192.168.191.1 (192.168.191.1) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.191.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.354 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.191.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.271 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.191.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.328 ms --- 192.168.191.1 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2000ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.271/0.317/0.354/0.040 ms
指定检测包的大小
[[email protected] home]# ping -s 2048 -c 3 192.168.191.1 PING 192.168.191.1 (192.168.191.1) 2048(2076) bytes of data. 2056 bytes from 192.168.191.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.253 ms 2056 bytes from 192.168.191.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.517 ms 2056 bytes from 192.168.191.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.348 ms --- 192.168.191.1 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2002ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.253/0.372/0.517/0.111 ms
使用netstat命令产看网络信息
netstat命令是一个综合的网络状态的查看工具,除了Linux查看自身的网络状况,它还可以显示路由表、网络接口状态、统计信息等。
netstat [address_family_options] [--tcp|-t] [--udp|-u] [--raw|-w] [--listening|-l]
[--all|-a] [--numeric|-n] [--numeric-hosts][--numeric-ports][--numeric-ports]
[--symbolic|-N] [--extend|-e[--extend|-e]] [--timers|-o] [--program|-p]
[--verbose|-v] [--continuous|-c] [delay]
netstat {--route|-r} [address_family_options] [--extend|-e[--extend|-e]]
[--verbose|-v] [--numeric|-n] [--numeric-hosts][--numeric-ports]
[--numeric-ports] [--continuous|-c] [delay]
netstat {--interfaces|-I|-i} [iface] [--all|-a] [--extend|-e] [--verbose|-v]
[--program|-p] [--numeric|-n] [--numeric-hosts][--numeric-ports]
[--numeric-ports] [--continuous|-c] [delay]
netstat {--groups|-g} [--numeric|-n] [--numeric-hosts][--numeric-ports]
[--numericports] [--continuous|-c] [delay]
netstat {--masquerade|-M} [--extend|-e] [--numeric|-n] [--numeric-hosts]
[--numericports][--numeric-ports] [--continuous|-c] [delay]
netstat {--statistics|-s} [--tcp|-t] [--udp|-u] [--raw|-w] [delay]
netstat {--version|-V}
netstat {--help|-h}常用命令选项:
显示网络连接: -t: tcp协议相关 -u: udp协议相关 -w: raw socket相关 -l: 处于监听状态 -a: 所有状态 -n: 以数字显示IP和端口; -e:扩展格式 -p: 显示相关进程及PID 显示路由表: -r: 显示内核路由表 -n: 数字格式 |
[[email protected] home]# netstat -apn Active Internet connections (servers and established) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1083/sshd tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1159/master tcp 0 52 192.168.191.128:22 192.168.191.1:55556 ESTABLISHED 1198/sshd tcp 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 1083/sshd tcp 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 1159/master udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:68 0.0.0.0:* 977/dhclient
各字段的含义:
Proto 协议名称,TCP或UDP协议 Local Address 本地计算机的IP地址和正在使用的端口号 Foreign Address 连接该网络服务客户端的IP地址和端口号 State TCP的连接状态,其中LISTEN表示正在监听,ESTABLISHED表示已经建立连接 PID/Program name 使用Socket相关程序的进程ID和名称 |
查看UDP协议的统计信息查看路由表
[[email protected] home]# netstat -rn Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags MSS Window irtt Iface 192.168.1.0 192.168.191.1 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0 192.168.12.0 192.168.191.1 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0 192.168.191.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0 169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 eth0 0.0.0.0 192.168.191.2 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
使用traceroute命令跟踪路由
在网络中,数据的传输是通过网络中许多段的传输介质和设备(包括网关、交换机、路由器和服务器等),经过多个节点后才能从本机到达目标主机。使用traceroute命令,可以获得从当前主机到目标主机的路由信息。
[[email protected] ~]# traceroute www.douyu.com traceroute to www.douyu.com (14.119.124.100), 30 hops max, 60 byte packets 1 * * * 2 10.249.248.150 (10.249.248.150) 0.798 ms 0.824 ms 1.112 ms 3 10.200.135.37 (10.200.135.37) 1.236 ms 1.326 ms 1.407 ms 4 113.108.236.222 (113.108.236.222) 2.674 ms 113.108.236.218 (113.108.236.218) 2.676 ms 3.685 ms 5 121.14.60.129 (121.14.60.129) 3.248 ms 14.119.117.129 (14.119.117.129) 2.667 ms 121.14.60.117 (121.14.60.117) 2.724 ms 6 121.14.50.25 (121.14.50.25) 6.478 ms 121.14.50.9 (121.14.50.9) 6.480 ms 113.108.209.233 (113.108.209.233) 3.984 ms 7 * * * 8 * * * 9 * * * 10 113.103.43.194 (113.103.43.194) 17.160 ms 16.977 ms 16.755 ms 11 14.119.124.100 (14.119.124.100) 19.918 ms 19.322 ms 19.470 ms
使用tcpdump分析报文
tcpdump [options] [Protocol] [Direction] [Host(s)] [Value] [Logical Operations] [Other expression]
常用选项:
-i any :指定网络接口 -n : 不反解IP到主机名 -nn : 不反解IP到主机名和端口到主机名 -v, -vv, -vvv : 详细信息 -X : 报文内容转码十六进制和 ASCII. -XX : 同-X,还显示以太网首部 -c # : 指定显示报文数后就终止 -s : 定义捕获字节大小 -s0获取所有信息 -e : 获取以太网首部 -S : 显示序列号 -A :报文内容转码ASCII. -w /path/to/some_file : 捕获报文输出文件 -tttt:用可读的时间戳数据包捕获 -r /path/from/some_file : 从指定文件读取报文 |
Protocol(协议):ether, fddi, ip, arp, rarp, decnet, lat, sca, moprc, mopdl, tcp and udp.
(未指定协议时,所有协议都将探测)
Direction(流向):src, dst, src and dst, src or dst (默认是src or dst)
Host(s)(主机):net, port, host, portrange.如果此段没有指定关键字,默认host。
Logical Operations:
(1) AND (and or &&)
(2) OR (or or ||)
(3) EXCEPT (not or !)
Linux网络故障处理步骤
1、检查网卡是否安装
[[email protected] home]# dmesg | grep eth e1000 0000:02:01.0: eth0: (PCI:66MHz:32-bit) 00:0c:29:b7:ab:d0 e1000 0000:02:01.0: eth0: Intel(R) PRO/1000 Network Connection e1000: eth0 NIC Link is Up 1000 Mbps Full Duplex, Flow Control: None eth0: no IPv6 routers present
2、检查网卡是否启用
[[email protected] home]# ifconfig -a eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:0C:29:B7:AB:D0 inet addr:192.168.191.128 Bcast:192.168.191.255 Mask:255.255.255.0 inet6 addr: fe80::20c:29ff:feb7:abd0/64 Scope:Link UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1 RX packets:10479 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:6487 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:9873652 (9.4 MiB) TX bytes:689328 (673.1 KiB) lo Link encap:Local Loopback inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0 inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1 RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:0 RX bytes:0 (0.0 b) TX bytes:0 (0.0 b)
3、检查TCP/IP协议是否安装
[[email protected] home]# ping 127.0.0.1 PING 127.0.0.1 (127.0.0.1) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 127.0.0.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.079 ms 64 bytes from 127.0.0.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.039 ms 64 bytes from 127.0.0.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.031 ms ^C --- 127.0.0.1 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2956ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.031/0.049/0.079/0.022 ms
4、检查网卡的IP地址配置是否正确
检查网卡的IP地址、子网掩码、网关等配置信息是否正确
如果在主机上配置有多个IP地址,应检查IP地址是否冲突
检查网卡IP地址是否与同一级中其他主机的IP地址冲突
5、检查路由信息
检查是否有配置默认网关
执行ping命令检查主机与网关之间的连通性
执行netstat -rn 命令检查主机的路由表信息是否正确
6、检查DNS
本文出自 “随风而飘” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://yinsuifeng.blog.51cto.com/10173491/1926019
以上是关于网络配置文件的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章