Unity3D 利用FSM设计相机跟随实现
Posted 海洋_
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Unity3D 利用FSM设计相机跟随实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
笔者介绍:姜雪伟,IT公司技术合伙人,IT高级讲师,CSDN社区专家,特邀编辑,畅销书作者,国家专利发明人;已出版书籍:《手把手教你架构3D游戏引擎》电子工业出版社和《Unity3D实战核心技术详解》电子工业出版社等。
CSDN视频网址:http://edu.csdn.net/lecturer/144
FSM有限状态机前面已经跟读者介绍过,使用Unity3D引擎实现了动作状态以及技能切换,FSM使用的条件是有限个状态切换,我们可以将FSM应用到相机中,很多人会问在相机中如何使用FSM,不论那种架构其主要目的是将模块之间的耦合性降低,传统的写法就是使用一个相机跟随类,所有的逻辑一股脑的写在一个类或者两个类中,这样一旦逻辑变动,修改起来非常麻烦,可能修改的就不是一个类两个类的事情,而如果我们采用FSM设计相机跟随,这样就容易多了。
接下来就实现FSM有限状态机,FSM作为一个通用类需要将其设置成模版的方式,具体代码如下所示:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace Core
{
public class FSM
{
public class Object<T, K>
where T : Object<T, K>
{
public delegate void Function(T self, float time);
#region Protected members
protected TimeSource timeSource = null;
protected Dictionary<K, State<T, K>> states = new Dictionary<K,State<T,K>>();
protected State<T, K> state = null;
protected State<T, K> prevState = null;
#endregion
#region Ctors
public Object()
{
timeSource = TimeManager.Instance.MasterSource;
}
public Object(TimeSource source)
{
timeSource = source;
}
#endregion
#region Public properties
public K PrevState
{
get
{
return prevState.key;
}
}
public K State
{
get
{
return state.key;
}
set
{
prevState = state;
if (prevState != null)
prevState.onExit(this as T, timeSource.TotalTime);
State<T, K> nextState;
if (states.TryGetValue(value, out nextState))
{
state = nextState;
state.onEnter(this as T, timeSource.TotalTime);
}
else
{
state = null;
}
}
}
public TimeSource TimeSource
{
get
{
return timeSource;
}
set
{
timeSource = value;
}
}
#endregion
#region Public methods
public void AddState(K key, Function onEnter, Function onExec, Function onExit)
{
State<T, K> newState = new State<T, K>();
newState.key = key;
newState.onEnter = onEnter;
newState.onExec = onExec;
newState.onExit = onExit;
states.Add(key, newState);
}
public void Update()
{
if (null == state) return;
state.onExec(this as T, timeSource.TotalTime);
}
#endregion
}
public class State<T, K>
where T : Object<T, K>
{
public K key;
public Object<T, K>.Function onEnter;
public Object<T, K>.Function onExec;
public Object<T, K>.Function onExit;
}
}
}
public class State<T, K>
where T : Object<T, K>
{
public K key;
public Object<T, K>.Function onEnter;
public Object<T, K>.Function onExec;
public Object<T, K>.Function onExit;
} public void AddState(K key, Function onEnter, Function onExec, Function onExit)
{
State<T, K> newState = new State<T, K>();
newState.key = key;
newState.onEnter = onEnter;
newState.onExec = onExec;
newState.onExit = onExit;
states.Add(key, newState);
} public void Update()
{
if (null == state) return;
state.onExec(this as T, timeSource.TotalTime);
}using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using Core;
public class FiniteStateMachine : MonoBehaviour
{
public enum UpdateFunction
{
Update = 0,
LateUpdate,
FixedUpdate
}
#region Public classes
public class FSMObject : FSM.Object<FSMObject, int>
{
public GameObject go;
public FSMObject(GameObject _go)
{
go = _go;
}
}
[Serializable]
public class StateType
{
public int id;
public string onEnterMessage;
public string onExecMessage;
public string onExitMessage;
public void onEnter(FSMObject fsmObject, float time)
{
fsmObject.go.SendMessage(onEnterMessage, time, SendMessageOptions.RequireReceiver);
}
public void onExec(FSMObject fsmObject, float time)
{
fsmObject.go.SendMessage(onExecMessage, time, SendMessageOptions.RequireReceiver);
}
public void onExit(FSMObject fsmObject, float time)
{
fsmObject.go.SendMessage(onExitMessage, time, SendMessageOptions.RequireReceiver);
}
}
#endregion
#region Public members
public bool manualUpdate = false;
public UpdateFunction updateFunction = UpdateFunction.Update;
public StateType[] states;
public int startState;
#endregion
#region Protected members
protected FSMObject fsmObject = null;
#endregion
#region Public properties
public int PrevState
{
get
{
return fsmObject.PrevState;
}
}
public int State
{
get
{
return fsmObject.State;
}
set
{
fsmObject.State = value;
}
}
public TimeSource TimeSource
{
get
{
return fsmObject.TimeSource;
}
set
{
fsmObject.TimeSource = value;
}
}
#endregion
#region Public methods
public void ForceUpdate()
{
fsmObject.Update();
}
#endregion
#region Unity callbacks
protected void Start()
{
fsmObject = new FSMObject(gameObject);
foreach (StateType state in states)
fsmObject.AddState(state.id, state.onEnter, state.onExec, state.onExit);
fsmObject.State = startState;
}
void Update()
{
//Debug.Log ("update");
if (manualUpdate)
return;
if (UpdateFunction.Update == updateFunction)
fsmObject.Update();
}
void LateUpdate()
{
if (manualUpdate)
return;
if (UpdateFunction.LateUpdate == updateFunction)
fsmObject.Update();
}
void FixedUpdate()
{
if (manualUpdate)
return;
if (UpdateFunction.FixedUpdate == updateFunction)
fsmObject.Update();
}
#endregion
}
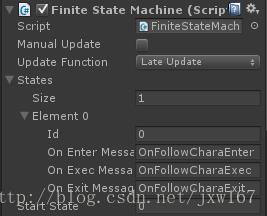
以上就是我们所封装的FSM有限状态机,接下来在项目中使用我们的FSM,先实现最基本的逻辑类如下所示:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class FollowCharacter : MonoBehaviour
{
public GameObject player;
public Vector3 sourceOffset = new Vector3(0.0f, 2.5f, -3.4f);
public Vector3 targetOffset = new Vector3(0.0f, 1.7f, 0.0f);
protected bool firstFrame;
protected float currHeightSmoothing;
protected float groundHeightTest;
protected bool slideshowActive = false;
protected float slideshowEnterTime = 0.0f;
protected float slideshowExitTime = 0.0f;
protected bool oldCameraActive = true;
protected float oldFov = 70.0f;
protected Vector3 oldCamSourceOffset = new Vector3(0.0f, 8.5f, -4.5f);
protected Vector3 oldCamTargetOffset = new Vector3(0.0f, 0.9f, 5.3f);
protected int cameraIndex = 3;
protected float[] cameraFovs = { 55.0f, 60.0f, 55.0f };
protected Vector3[] cameraSourceOffsets = {
new Vector3(0.0f, 5.8f, -3.8f),
new Vector3(0.0f, 6.04f, -4.0f),
new Vector3(0.0f, 8.5f, -6.7f)
};
protected Vector3[] cameraTargetOffsets = {
new Vector3(0.0f, 2.2f, 2.5f),
new Vector3(0.0f, 1.35f, 3.36f),
new Vector3(0.0f, 1.45f, 5.3f)
};
protected Vector3 newCamSourceOffset = new Vector3(0.0f, 6.04f, -4.0f);//Camera 2
protected Vector3 newCamTargetOffset = new Vector3(0.0f, 1.35f, 3.36f);//Camera 2
protected Vector3 testNewTurboSourceOffset = new Vector3(0.0f, 5.8f, -4.0f);
protected Vector3 testNewTurboTargetOffset = new Vector3(0.0f, 2.1f, 2.5f);
protected Vector3 testNewFinalSourceOffset = new Vector3(-6.5f, 5.0f, -5.5f);
protected Vector3 testNewFinalTargetOffset = new Vector3(-4.5f, 1.7f, 0.0f);
#region public Classes
public class ShakeData
{
public float duration;
public float noise;
public float smoothTime;
public ShakeData(float _duration, float _noise, float _smoothTime)
{
duration = _duration;
noise = _noise;
smoothTime = _smoothTime;
}
}
#endregion
public void OnFollowCharaEnter(float time)
{
prevPlayerPivot = player.transform.position;
firstFrame = true;
currHeightSmoothing = heightSmoothing;
deadTime = -1.0f;
actionTaken = false;
}
public void OnFollowCharaExec(float time)
{
if (player == null)
return;
float dt = Time.fixedDeltaTime;
float now = TimeManager.Instance.MasterSource.TotalTime;
Vector3 playerPivot = player.transform.position;
playerPivot.x = 0.0f;
playerPivot.y = 0.0f;
float targetHeight = playerPivot.y;
if (firstFrame)
{
lastPivotHeight = targetHeight;
prevPlayerPivot = playerPivot;
heightVelocity = 0.0f;
firstFrame = false;
}
else
{
float targetSmoothTime = 0.1f;
smoothTime = Mathf.MoveTowards(smoothTime, targetSmoothTime, 2.5f * dt);
lastPivotHeight = Mathf.SmoothDamp(lastPivotHeight, targetHeight, ref heightVelocity, smoothTime, 50.0f, dt);
prevPlayerPivot = playerPivot;
}
Vector3 camPivot = new Vector3(prevPlayerPivot.x * 0.8f, lastPivotHeight, prevPlayerPivot.z);
lastSourceOffset = this.EaseTo(lastSourceOffset, goalSourceOffset, sourceOffset);
lastTargetOffset = this.EaseTo(lastTargetOffset, goalTargetOffset, targetOffset);
transform.position = camPivot + lastSourceOffset + offset * 0.1f + noise * noiseStrength; // +noise * noiseStrength + noiseTremor * 0.00069f * kinematics.PlayerRigidbody.velocity.z; //PIETRO
transform.LookAt(camPivot + lastTargetOffset + offset * 0.1f, Vector3.up);
if (!TimeManager.Instance.MasterSource.IsPaused)
{
//Camera Shake
if (shakeCameraActive)
ShakeCamera(dt);
//tremor (always active
this.UpdateTremor(dt);
}
//check if is dead
if (now - deadTime > 3.6f && !actionTaken && deadTime > 0.0f)
{
actionTaken = true;
//Debug.Log("GO TO REWARD");
LevelRoot.Instance.BroadcastMessage("GoToOffgame"); //GoToReward");
}
}
public void OnFollowCharaExit(float time)
{
}
void OnReset()
{
//Debug.Log("RESET CAM");
interpolating = false;
shakeCameraActive = false;
sourceOffset = defaultSourceOffset;
targetOffset = defaultTargetOffset;
}
void ShakeCamera(float deltaTime)
{
if (TimeManager.Instance.MasterSource.TotalTime - shakeStartTime <= currentShakeData.duration)
{
if (currentShakeData.smoothTime > 0.0f)
noiseStrength = Mathf.SmoothDamp(noiseStrength, currentShakeData.noise, ref noiseStrengthVel, currentShakeData.smoothTime, 300.0f, deltaTime);
else
noiseStrength = currentShakeData.noise; // go directly
if (noiseStrength > 0.0f)
{
Vector3 v = UnityEngine.Random.onUnitSphere;
noise += (v - noise) * deltaTime * 8.0f;
}
else
noise = SRVector3.zero;
}
if (TimeManager.Instance.MasterSource.TotalTime - shakeStartTime >= currentShakeData.duration)
StopShakeCamera();
}
void StopShakeCamera()
{
currentShakeData = new ShakeData(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
noiseStrength = 0.0f;
noise = SRVector3.zero;
shakeCameraActive = false;
}
public string ChangeCamera()
{
string buttonText = "";
buttonText = cameraIndex == 0 ? "Old camera on" : "camera " + cameraIndex + " on";
if (cameraIndex == 0)
{
gameObject.GetComponent<Camera>().fieldOfView = oldFov;
lastSourceOffset = defaultSourceOffset = sourceOffset = oldCamSourceOffset;
lastTargetOffset = defaultTargetOffset = targetOffset = oldCamTargetOffset;
goalSourceOffset = oldCamSourceOffset;
goalTargetOffset = oldCamTargetOffset;
}
else
{
gameObject.GetComponent<Camera>().fieldOfView = cameraFovs[cameraIndex - 1];
lastSourceOffset = defaultSourceOffset = sourceOffset = cameraSourceOffsets[cameraIndex - 1];
lastTargetOffset = defaultTargetOffset = targetOffset = cameraTargetOffsets[cameraIndex - 1];
goalSourceOffset = cameraSourceOffsets[cameraIndex - 1];
goalTargetOffset = cameraTargetOffsets[cameraIndex - 1];
}
return buttonText;
}
}
其中脚本中加粗的函数是有限状态机执行的具体逻辑。。。。。。。另外其他的变量声明和函数实现是根据策划需求添加的,读者只需要关注加粗的函数实现就可以了。
附图如下所示:
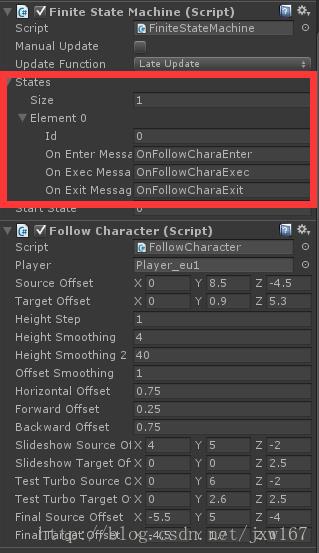
以上是关于Unity3D 利用FSM设计相机跟随实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章