数据结构--二项队列的思想与实现
Posted waitforyoull
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构--二项队列的思想与实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
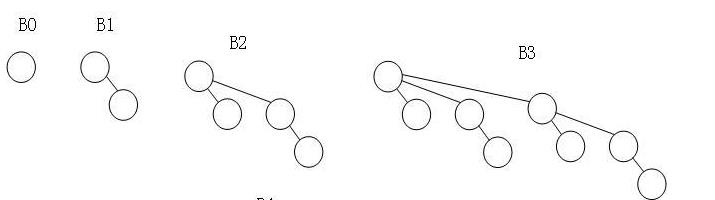
二项队列不是一颗堆序的树,而是堆序树的集合,称为森林,森林中每棵树都是有约束的形式,称为二项树,高度为k的第k个二项树Bk由一个根节点和B0, B1, .......B(k-1)构成,高度为k的二项树的结点个数为2^k,因此可以用二项树的结合表示任意大小的优先队列。例如,大小为13的优先队列就可以用B3,B2,B0来表示,2^0+2^2+2^3 = 13.因此二进制的表示为1101。
例如,二项树B0,B1,B2,B3表示如下:
把所有二项树的根节点按规律放在一个根节点组成的数组中,就组成二项队列,如下图所示:

二项队列也是优先队列的一种,其基本操作就是合并操作和删除最小元操作,本文给出的代码还包括插入,和查找操作,代码如下:
#include<iostream> using namespace std; typedef struct BinNode *Position; typedef struct BinNode *BinTree; typedef struct Collection *BinQueue; #define MaxTrees 30 #define Capacity ((1<<MaxTrees)-1) //为2^0+2^1+2^2+2^(MaxTrees-1) #define Infinity 65536 struct BinNode { int Element; Position LeftChild; Position NextSibling; }; struct Collection { int CurrentSize; //二项队列中节点的个数 BinTree TheTrees[MaxTrees]; }; BinQueue Initialize() { BinQueue H = (BinQueue)malloc(sizeof(struct Collection)); if (H == NULL) cout << "out of space" <<endl; for (int i = 0; i < MaxTrees; i++) H->TheTrees [i] = NULL; H->CurrentSize = 0; return H; } BinTree CombineTrees (BinTree T1,BinTree T2) //合并同样大小两颗二项树 { if(T1->Element > T2->Element ) return CombineTrees(T2,T1); T2->NextSibling = T1->LeftChild ; T1->LeftChild = T2; return T1; } BinQueue Merge(BinQueue H1,BinQueue H2) { BinTree T1, T2,Carry = NULL; //Carry记录上一次两个二项树合并的结果 int i,j; if(H1->CurrentSize + H2->CurrentSize > Capacity) cout << "Merge would exceed capacity" << endl; H1->CurrentSize += H2->CurrentSize ; for(i = 0, j = 1; j <= H1->CurrentSize; i++,j *= 2) //i用来遍历两个二项队列,j用来结束循环 { T1 = H1->TheTrees [i]; T2 = H2->TheTrees [i]; switch(!!T1 + 2 * !!T2 + 4 * !!Carry) //!!运算符表示把T的空或者非空转换为0或者1 { case 0: //没有树 case 1: //只有H1 break; case 2: //只有H2 H1->TheTrees [i] = T2; H2->TheTrees [i] = NULL; break; case 4: //只有Carry H1->TheTrees [i] = Carry; Carry = NULL; break; case 3: //有H1和H2 Carry = CombineTrees(T1,T2); H1->TheTrees [i] = H2->TheTrees [i] = NULL; break; case 5: //H1和Carry Carry = CombineTrees(T1,Carry); H1->TheTrees [i] = NULL; break; case 6: //H2和Carry Carry = CombineTrees(T2,Carry); H2->TheTrees [i] = NULL; break; case 7: //3个树都有 H1->TheTrees [i] = Carry; Carry = CombineTrees(T1,T2); H2->TheTrees [i] = NULL; break; } } return H1; } void Insert(int x, BinQueue H) //通过合并操作来完成,先对元素x建立一个二项队列,接着把这个队列和原来的队列合并 { BinQueue temp = Initialize(); temp->CurrentSize = 1; temp->TheTrees [0] = (BinTree)malloc(sizeof(struct BinNode)); if (temp->TheTrees[0] == NULL) cout << "Empty binomial queue" << endl; temp->TheTrees[0]->Element = x; temp->TheTrees[0]->LeftChild = NULL; temp->TheTrees[0]->NextSibling = NULL; Merge(H, temp); free(temp); } bool IsEmpty(BinQueue H) { if(H->CurrentSize == 0) return true; else return false; } int Find_Min (BinQueue H) { int MinItem = Infinity; for(int i = 0;i < MaxTrees; i++) { if(H->TheTrees [i] && H->TheTrees [i]->Element < MinItem) { MinItem = H->TheTrees [i]->Element; } } return MinItem; } int Delete (BinQueue H) //删除最小值并返回最小值 { int i, j; int MinTree; //最小的元素所在的二项树 BinQueue DeletedQueue; Position DeletedTree,OldRoot; int MinItem; //要返回的最小值 if(IsEmpty(H)) { cout << "Empty binomial queue" << endl; return -Infinity; } //寻找最小值,只可能在根处 MinItem = Infinity; for(i = 0;i < MaxTrees; i++) { if(H->TheTrees [i] && H->TheTrees [i]->Element < MinItem) { MinItem = H->TheTrees [i]->Element; MinTree = i; } } DeletedTree = H->TheTrees [MinTree]; OldRoot = DeletedTree; DeletedTree = DeletedTree->LeftChild; free(OldRoot); DeletedQueue = Initialize(); DeletedQueue->CurrentSize = (1 << MinTree) - 1; //此处为右移再-1 for(j = MinTree - 1;j >= 0; j--) { DeletedQueue->TheTrees [j] = DeletedTree; DeletedTree = DeletedTree->NextSibling ; DeletedQueue->TheTrees [j]->NextSibling = NULL; } H->TheTrees [MinTree] = NULL; H->CurrentSize -= DeletedQueue->CurrentSize + 1; Merge(H,DeletedQueue); //H为原来的二项队列删除具有最小元素的根节点的二项树后的二项队列, //DeletedQueue为具有最小元素的根节点的二项树删除最小节点后剩余元素组成的二项队列 return MinItem; //返回最小值 } int main () { BinQueue H = Initialize(); Insert(13, H); Insert(23, H); Insert(24, H); /*Insert(51, H); Insert(65, H); Insert(12, H); Insert(14, H); Insert(24, H); Insert(21, H); Insert(65, H); Insert(16, H); Insert(26, H); Insert(18, H);*/ // cout << H->CurrentSize <<endl; //cout << H->TheTrees [2]->Element << endl; cout << Find_Min (H)<< endl; cout << Delete(H) << endl; cout << Delete(H) << endl; cout << Delete(H) << endl; cout << Delete(H) << endl; return 0; }
例子中值得学习的地方很多,比如对合并时候几种情况的处理用switch语句分类实现,插入操作用合并操作实现等。
夜深了,,,
我在想什么
以上是关于数据结构--二项队列的思想与实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章