I/O序列化
Posted 阿普
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了I/O序列化相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1)流序列化对象ObjectOutputStream调用writerObject写出序列化对象,ObjectInputStream调用readObject读取序列化对象,序列化的对象必须要实现Serializable接口,该接口没有任何需要待实现的方法,只需继承即可。序列化之前的对象和序列化之后的对象是两个不同的对象,两者不是相等的。
序列化代码样例:
//写出序列化 String path="G:\\\\obj.txt"; ObjectOutputStream stream=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(path)); stream.writeObject(student); stream.close(); // 读取序列化 ObjectInputStream inputStream=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(path)); Student student2=(Student)inputStream.readObject(); inputStream.close();
在序列化过程中,某些域(属性)不想被序列化,可以使用transient标记不被序列化(方法不适用transient),不可序列化的类作为一个属性表示的话一定要加上transient不然会报NotSerializableException。
例子:
private transient String _date;
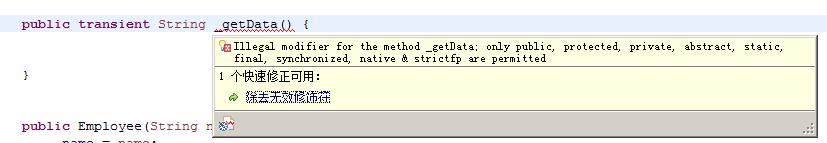
方法标记transient报错 必须去掉transient标记。
2)使用Externalizable接口可以定制自己的序列化机制,此接口有两个公开的可重写的方法readExternal和writeExternal
代码样例:
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 ExternalDemo demo = new ExternalDemo(); demo.setName("zhangsan"); ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream( Paths.get("G:\\\\", "ExternalDemo.dat").toFile())); demo.writeExternal(out); ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Paths .get("G:\\\\", "ExternalDemo.dat").toFile())); demo.readExternal(in); System.out.println(demo.getName()); }
public class ExternalDemo implements Externalizable { private String _name; public String getName() { return _name; } public void setName(String name) { _name = name; } @Override public void readExternal(ObjectInput in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 _name = (String) in.readObject(); } @Override public void writeExternal(ObjectOutput out) throws IOException { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 out.writeObject(_name); } }
3)序列化单例和类型安全的枚举
上面已介绍过普通的序列化写出和读取的对象是两个不同的对象,而对于单例来说要求写出和读取的对象是同一个对象,这就需要写一个方法来实现readResolve()。举一个例子来说明:
public class Orientation implements Serializable { private int value; private Orientation(int v) { value = v; } public static final Orientation HORIZONTAL = new Orientation(1); public static final Orientation VERTICAL = new Orientation(2); protected Orientation readResolve() { if (value==1) { return Orientation.HORIZONTAL; } else if (value==2) { return Orientation.VERTICAL; } else { return null; } } }
public static void main(String[] args) { try { // 待序列化的对象 Orientation horizontal = Orientation.HORIZONTAL; // 序列化 FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File( "G:\\\\orientation.dat")); ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream( fileOutputStream); outputStream.writeObject(horizontal); outputStream.close(); fileOutputStream.close(); // 反序列化 ObjectInputStream inputStream = new ObjectInputStream( new FileInputStream(new File("G:\\\\orientation.dat"))); Orientation horiOrientation = ((Orientation) inputStream .readObject()).readResolve(); inputStream.close(); // 校验序列化前后的对象是否一致 System.out.println(horiOrientation == horizontal); } catch (Exception exception) { } }
第一段代码中我们定义了一个私有变量value和两个静态对象HORIZONTAL,VERTICAL,当我们要序列化对象HORIZONTAL,其value=1,再次反序列化时,如果只调用inputStream的readObject方法,将返回一个新的Orientation对象;如果调用了readResolve方法,将返回序列化之前的对象HORIZONTAL,这是因为调用readResolve方法时会去校验value的值,根据其值返回对象。
以上是关于I/O序列化的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章