机器学习笔记(Washington University)- Regression Specialization-week four
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了机器学习笔记(Washington University)- Regression Specialization-week four相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. Ridge regression
A way to automatically balance between bias and varaince situations and regulate
overfitting when using many features. because the model has a lot of flexibility to explain
the data.
2. Overfitting
Formally, when we can find a model with higher traning error but lower true error compared
with the trained model, then the trained model is overfiting the dataset.
Overfitting is associated with very large magnitude estimated coefficients.
And Not like enough data,if we have few observations, the model will overfit rapidly as the
model complexity increases.
3. Desired total cost
want to balance:
1. How well function fits data.
2. Magnitude of coefficientrs.
Total cost = measure of fit + measure of magnitude of coefficients
measure of magnitude of coefficients = sum of squares of regression coefficients (L2 Norm)
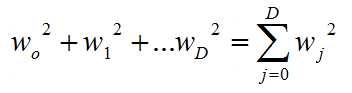
so the regression is selected to minimize:
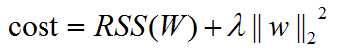 (lambda is the tuning parameter)
(lambda is the tuning parameter)
when lambda is small, just as before, W = W(least square solution)
when lambda is large, W = 0
when lambda is in between, then 0<= |W|<=W(least square solution)
so the lambda is controlling the model complexity.
4. The formula for the new gradient
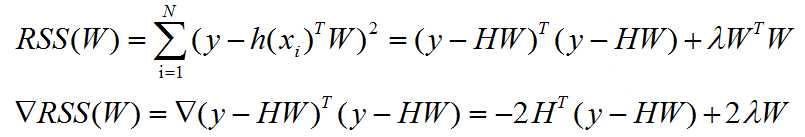
5. solution
Close-form :
we can set the gradient to zero, and we can get the solution like shown below
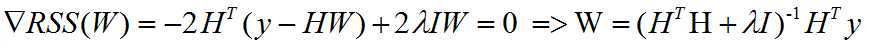
when lambda is zero, it is the old solution,
when lambda is infinity, we are like to divide by infinity, so the solution to W is zero
the first item is invertible, even if the observations (N) is smaller than D(faetures)
when the intercept is kept out from shrinking, we just set the (1,1) element of I to be zero
Gradient descent:
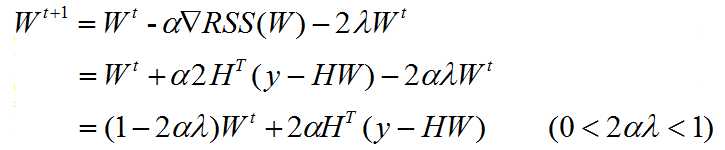
The interpretation of this formula is:
No matter what, we firstly shrink the W vector, then we modify it to fit our data.
when the intercept is kept out from shrinking, we just add a if-statement to set
the w0 to update just like the old solution. no lambda involved.
6. K-fold cross validataion
The data set is divided into K blocks
For a certain lambda
For K=1...K
1. Estimate w on the training blocks
2.compute error on validation blocks: error_K(labda)
then we compute the average error of all the error_K, we will choose the best lamda to minimize this error.
leave-one-out cross validation just means that K=N(data size)
Typically, K=5 or 10
以上是关于机器学习笔记(Washington University)- Regression Specialization-week four的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章