常见排序算法
Posted Joye Zhou
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了常见排序算法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 冒泡排序:
很古板而又很经典的一种排序方式,就是前后两个数据进行对比,然后交换位置即可:

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace CSP { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int [] intList = new int[10]{48,39,55,32,56,69,43,29,45,67}; Console.WriteLine("Before sort:"); foreach (int a in intList) { Console.WriteLine(a); } //DESC for (int i = 0; i < intList.Count(); i++) { for (int j = i; j < intList.Count(); j++) { int MV=0; if (intList[j]>intList[i]) { MV = intList[i]; intList[i] = intList[j]; intList[j] = MV; } } } Console.WriteLine("After sort:"); foreach (int b in intList) { Console.WriteLine(b); } Console.ReadLine(); } } }
2. 选择排序:
与冒泡排序特别类似,主要区别在于从数组中arr[i]拿出第一位arr[0]作为最大(DESC)/小(ASC)值,从剩余的数组列表中找出最大(DESC)/小(ASC)值arr[j]。然后将这两个数据arr[0],arr[j]进行比较,如果arr[j]>arr[0]且为降序排列的情况下,则交换两个的值。然后继续进行下一轮的循环,取出第二个arr[1]......

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace CSP { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int[] arr = new int[10] { 48, 39, 55, 32, 56, 69, 43, 29, 45, 67 }; SelectionSort(arr); foreach (int i in arr) { Console.WriteLine(i); } Console.ReadLine(); } //DESC public static int[] SelectionSort(int[] arr) { int MaxValue; int MaxIndex=0; for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++) { MaxValue = arr[i]; for (int j = i; j < arr.Length; j++) { if (arr[j] > MaxValue) { MaxValue = arr[j]; MaxIndex = j; } } //Swap int TempValue; if (arr[i] < MaxValue) { TempValue = MaxValue; arr[MaxIndex] = arr[i]; arr[i] = TempValue; } } return arr; } } }
3. 快速排序算法(Quick Sort):
排序流程:
A. 即从待排序数组中任选其中一个元素作为基准X(一般会选择第一个或最后一个,此处以第一个值为例);
B. 将比X大的元素放在X的右边,比X小的放在左边;
根据基准值X,从右到左开始查找第一个比X大的值,然后和X交换位置。再从左至右查找第一个比X小的元素并与其交换位置。重复前面的操作直到X的左边的元素都大于X且右边的元素都小于X;
C. 对X的左侧和右侧元素重新开始进行分别进行第一步到第三步的操作,直到所有元素完成排序操作。

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace CSP { class Program { public static int SortTimes = 0; static void Main(string[] args) { int[] intiList = new int[10] { 48, 39, 55, 32, 56, 69, 43, 29, 45, 67 }; Console.WriteLine("Before sort:"); foreach (int a in intiList) { Console.WriteLine(a); } //DESC int iMin = 0; int bIndex = 0; int bVal = intiList[bIndex]; Console.WriteLine("The base value is:" + intiList[iMin].ToString()); int iMax = intiList.Count() - 1; //Quick sort. iMin = QuickSort(intiList, iMin, iMax); //1:From left to right; int iMinA = QuickSort(intiList, 0, iMin - 1); //1:From right to left; int iMinB = QuickSort(intiList, iMin + 1, iMax); //2:From left to right; QuickSort(intiList, 0, iMinA - 1); //2:From right to left; QuickSort(intiList, iMinA + 1, iMin - 1); //3:From left to right; QuickSort(intiList, iMin + 1, iMinB - 1); //3:From right to left; QuickSort(intiList, iMinB + 1, iMax); Console.WriteLine("After sort:"); foreach (int b in intiList) { Console.WriteLine(b); } Console.ReadLine(); } private static int QuickSort(int[] intiList, int iMin, int iMax) { int bIndex = iMin; while (iMin < iMax) { for (int i = iMax; i > -1; i--) { if (iMin < iMax && intiList[iMax] > intiList[bIndex]) { SortTimes++; //From right to left; Console.WriteLine(SortTimes.ToString() + " round: swap the value[" + intiList[bIndex] + ",<--" + intiList[iMax].ToString() + "];"); int mv = intiList[bIndex]; intiList[bIndex] = intiList[iMax]; intiList[iMax] = mv; bIndex = iMax; break; } iMax--; } for (int j = 0; j < iMax; j++) { if (iMin < iMax && intiList[iMin] < intiList[bIndex]) { SortTimes++; //From left to right; Console.WriteLine(SortTimes.ToString() + " round: swap the value[" + intiList[iMin].ToString() + ",-->" + intiList[bIndex] + "];"); int mv = intiList[bIndex]; intiList[bIndex] = intiList[iMin]; intiList[iMin] = mv; bIndex = iMin; break; } iMin++; } } return bIndex; } } }
执行结果:

4.归并排序算法(Merge Sort):
主要采用边排序边归并的方式进行数据的排序,由于定义了额外的数组进行数据的暂存,所以与其他排序方法相比,多占用了一部分内存:

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace CSP { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int[] arr = new int[10] { 48, 39, 55, 32, 56, 69, 43, 29, 45, 67 }; MergeSort(arr, 0, arr.Length); foreach (int i in arr) { Console.WriteLine(i); } Console.ReadLine(); } public static void MergeSort(int[] arr, int startPos, int endPos) { if (endPos > startPos + 1) { int midPos = (startPos + endPos) / 2; Console.WriteLine(startPos.ToString() + midPos.ToString()); Console.WriteLine("---------------------Start----------------------------"); MergeSort(arr, startPos, midPos); Console.WriteLine(midPos.ToString() + endPos.ToString()); Console.WriteLine("---------------------End----------------------------"); MergeSort(arr, midPos, endPos); Console.WriteLine("---------------------Merge----------------------------"); MergeLR(arr, startPos, midPos, endPos); } } public static void MergeLR(int[] arr, int startPos, int midPos, int endPos) { int[] arrTemp = new int[arr.Length]; int k = 0; int i = startPos; int j = midPos; //First Step:Compare 2 items:arr[i] and arr[j]; while (i < midPos && j < endPos) { Console.WriteLine("i=" + i + ";midPos=" + midPos.ToString() + ";j=" + j + ";endPos=" + endPos); if (arr[i] < arr[j]) { arrTemp[k++] = arr[i++]; } else { arrTemp[k++] = arr[j++]; } } //Second Step:Put the one arr[i++] or arr[j++] to arrTemp; while (i < midPos) arrTemp[k++] = arr[i++]; while (j< endPos) arrTemp[k++] = arr[j++]; //Third Step:Merge the arrTemp array to arr. for (int v = 0; v < k; v++) arr[startPos + v] = arrTemp[v]; } } }
执行分解步骤:
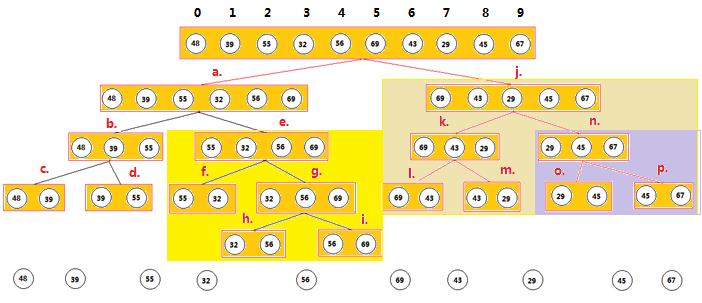
以下是与上图相匹配的具体的执行明细:

0,1,1,2 48(0):39(1) => 39,48
3,4,4,5 32(3):56(4) => 32,56
2,3,3,5 55(2):32(3) |
2,3,4,5 55(2):56(4) |=> 32,55,56
0,2,2,5 39(0):32(2) |
0,2,3,5 39(0):55(3) |=> 32,39,48,55,56
1,2,3,5 48(1):55(3) |
5,6,6,7 69(5):43(6) => 43,69
8,9,9,10 45(8):67(9) => 45,69
7,8,8,10 29(7):45(8) => 29,45
5,7,7,10 43(5):29(7) |
5,7,8,10 43(5):45(8) |
6,7,8,10 69(6):45(8) |=>29,43,45,67,69
6,7,9,10 69(6):67(9) |
0,5,5,10 32(0):29(5) |
0,5,6,10 32(0):43(6) |
1,5,6,10 39(1):43(6) |
2,5,6,10 48(2):43(6) |
2,5,7,10 48(2):45(7) |=>29,32,39,43,45,48,55,56,67,69
2,5,8,10 48(2):67(8) |
3,5,8,10 55(3):67(8) |
4,5,8,10 56(4):67(8) |
5. 插入排序
直接插入排序:故名思义,就是逐一取出带排序数组中的记录进行逐一比较,然后再进行位置的交换。在整个循环过程中需要注意的一个假设就是假设第一个数组中的记录是有序的,所以排序直接从第二个元素开始,和第一个元素进行比较,而第三个元素则和前两个元素进行比较,以此类推。
使用场合:直接插入排序适用于带排序数组的元素基本有序时使用;

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace CSP { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int[] arr = new int[10] { 48, 39, 55, 32, 56, 69, 43, 29, 45, 67 }; //DESC InsertionSort(arr); foreach (int i in arr) { Console.WriteLine(i); } Console.ReadLine(); } public static void InserttionSort(int[] arr) { for (int i = 1; i < arr.Length; i++) { for (int j = i; j > 0; j--) { if (arr[j-1] < arr[j]) { int temp = arr[j - 1]; arr[j - 1] = arr[j]; arr[j] = temp; } } } } } }
折半插入排序:将待排序元素依次插入已经排序的序列中0~X中,在插入的过程中使用了折半搜索的方式找到合适的插入位置Y将该元素插入位置Y,然后将其他元素Y~X逐次向后移动一位;

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace CSP { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int[] arr = new int[10] { 48, 39, 55, 32, 56, 69, 43, 29, 45, 67 }; //DESC BinaryInserttionSort(arr); foreach (int i in arr) { Console.WriteLine(i); } Console.ReadLine(); } public static void BinaryInserttionSort(int[] arr) { int Temp; int pos=0; for (int i = 1; i < arr.Length; i++) { Temp = arr[i]; int stPos = 0; int edPos = i-1; while (stPos <= edPos) { pos = (stPos + edPos) / 2; if (arr[i] > arr[pos]) { edPos = pos - 1; } else { stPos = pos + 1; } } if (edPos < 0) { edPos = 0; } for (int j = i; j > edPos; j--) { arr[j] = arr[j - 1]; } arr[stPos] = Temp; } } } }
6. 堆排序
堆排序工作原理:从list.Count / 2 - 1(最后一个根节点)开始逆向对整个堆所有节点进行堆化操作以实现大根堆,则此时根节点的值即为最大值。取根节点的值与最后一个节点值进行位置交换,然后对根节点值进行堆化操作,待操作完成后,取当前根节点的值与倒数第二个节点进行位置交换,然后再对根节点进行堆化操作,依此循环,直到完成根元素与自身的交换为止。

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows.Forms; namespace CSP { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { List<int> lt = new List<int>(); lt.Add(48); lt.Add(39); lt.Add(55); lt.Add(32); lt.Add(56); lt.Add(69); lt.Add(43); lt.Add(29); lt.Add(45); lt.Add(67); List<int> ltNew = HeapSort(lt,lt.Count); foreach (int i in ltNew) { Console.WriteLine(i); } Console.ReadLine(); } ///<summary> ///堆排序 ///</summary> public static List<int> HeapSort(List<int> list, int top) { List<int> topNode = new List<int>(); //从list.Count / 2 - 1开始对整个堆所有节点进行堆化操作,进而实现大根堆 for (int i = list.Count / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) { HeapAdjust(list, i, list.Count); } //交换元素位置并对根结点进行堆化操作 for (int i = list.Count - 1; i >= list.Count - top; i--) { int temp = list[0]; list[0] = list[i]; list[i] = temp; topNode.Add(temp); HeapAdjust(list, 0, i); } return topNode; } /// <summary> /// 针对单个节点进行元素位置的调整 /// </summary> /// <param name="list"></param> /// <param name="parent"></param> /// <param name="length"></param> static void HeapAdjust(List<int> list, int parent, int length) { int temp = list[parent]; int child = 2 * parent + 1; while (child < length) { if (child + 1 < length && list[child] < list[child + 1]) child++; if (temp >= list[child]) break; list[parent] = list[child]; parent = child; child = 2 * parent + 1; } list[parent] = temp; } } }
总结,经过不断研究,终于掌握了几种常见的排序算法,希望能为未来的工作带来便利的同时,也希望能与数据结构相关知识互通互融,并不断加深自己的理解!
以上是关于常见排序算法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
