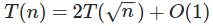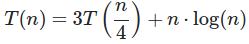[Algorithm] Greedy method
Posted 机器学习水很深
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了[Algorithm] Greedy method相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
f(n) 的形式 vs 判定形势
但,此题型过于简单,一般不出现在考题中。
Extended:
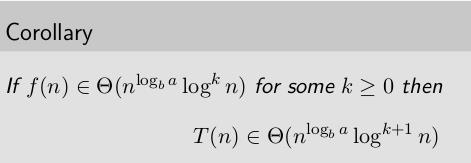
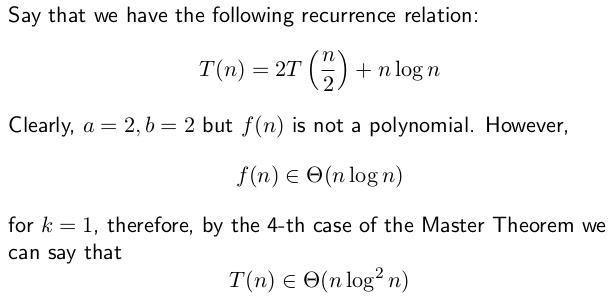
Let\'s set n = 2^m, so m = log(n)
T(n) = 2*T(n^(1/2)) + 1 =>
T(2^m) = 2*T(2^(m/2)) + 1 =>
S(M) = 2*S(M/2)) + 1
通过变量替换,变为了熟悉的、主定理能解决的 形式 => S(m) ~ O(m)
故,S(m) = T(log(n)) ~ O(log(n))
关键点:match 主定理(3)的条件。
a*f(n/b) <= c*f(n) ->
3*f(n/4) <= c*f(n) ->
3*(n/4)*log(n/4) <= c*n*log(n) ->
3/4 * n*log(n/4) <= c*n*log(n)
可见,有c<1时,是满足的。
答案就是O(nlogn)
When f(x) = x*sqrt(x+1)
这里的常数1是个tricky.
去掉它,x^(3/2)
变为x,sqrt(2)*[x^(3/2)]
可见,f(x)~Θ(x^(3/2))
T(n)=T(⌊n/2⌋)+T(⌊n/4⌋)+T(⌊n/8⌋)+n.
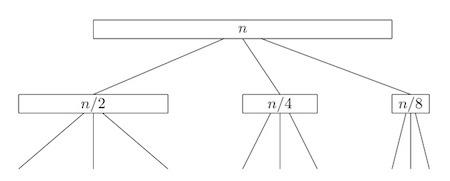
n+(7/8)*n+(7/8)^2 *n+(7/8)^3 *n+⋯ 等比数列!
so we have a geometric series and thus,
![]()
for our upper bound.
In a similar way, we could count just the contribution of the leftmost branches and conclude that T(n)≥2n.
Putting these together gives us the desired bound, T(n)=Θ(n)
Extended:
Recurrence Relation T(n)=T(n/8)+T(n/4)+lg(n)
太难:Solution.
(a) T(n) = T(n-1) + cn link
(b) T(n) = T(n-1) + log(n) link
(c) T(n) = T(n-1) + n^2 link
(d) T(n) = T(n-1) + 1/n link
(a) 递归展开,探寻规律:
T(n)=T(n−3)+(n−2)c+(n−1)c+nc
At the end we use T(2)=T(1)+2c=1+2cT(2)=T(1)+2c=1+2c. We conclude that
T(n)=1+(2+3+⋯+n)c.
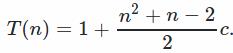
可见是O(n^2)
(b) 递归展开,探寻规律:
T(n) = T(n - 1) + log n
= T(n - 2) + log (n - 1) + log n
= T(n - 3) + log (n - 2) + log (n - 1) + log n
= ...
= T(0) + log 1 + log 2 + ... + log (n - 1) + log n
= T(0) + log n!
According to Stirling\'s formula, 可见是O(n*log(n))
(c) 递归展开,探寻规律:
T(n)=T(0)+1^2+2^2+3^2+⋯+n^2
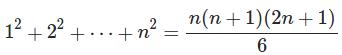
Or simply,
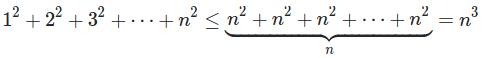
O(n^3)
(d) 这里是个调和级数
This is the nth harmonic number, Hn = 1 + 1/2 + 1/3 + ... + 1/n.
"所有调和级数都是发散于无穷的。但是其拉马努金和存在,且为欧拉常数。"
In fact, Hn = ln(n) + γ + O(1/n)
Hint:比较难,需换两次元。
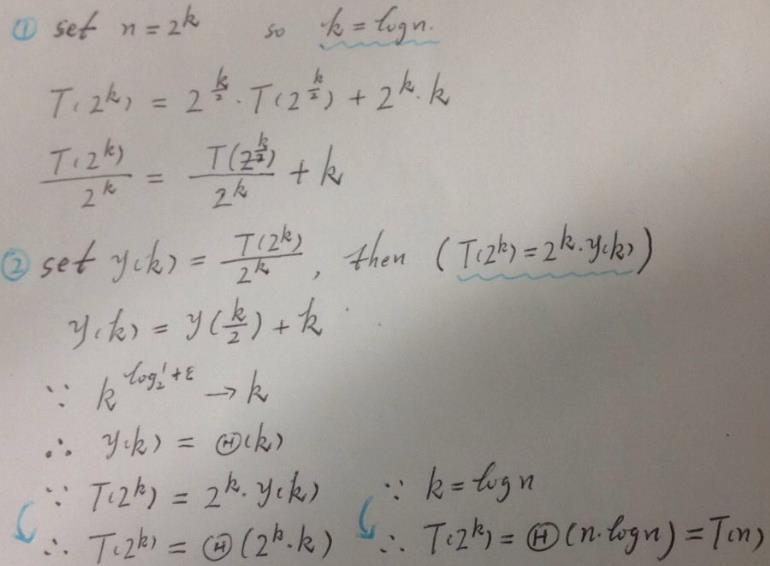
以上是关于[Algorithm] Greedy method的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章