umi-request的全局处理
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了umi-request的全局处理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A 不必多言,跟axios一样,一般都是会整一个全局文件,对每一个接口进行处理。可能不太一样的是,它的请求拦截是在中间件里进行的,使用静态的use函数即可进行前置拦截,对于请求后的后置处理,则调用原型上的use来做引入相关依赖
设置通用配置
处理重复请求
将当前请求压入队列,并在请求结束后移除。若上一个当前请求未结束,则使用CancelToken取消
队列函数
addQueue
removeQueue
利用中间件的特性,设置某些不需要缓存的请求
Java中的全局异常处理
Java中的全局异常处理
全局异常处理
- ErrorController接口和 @ControllerAdvice注解比较:
- 相同点:
- 两者都是Spring项目中的全局异常处理方式
- 不同点:
- 捕获异常位置不同:
- ErrorController接口捕获全局所有的异常,包括控制器方法中抛出的异常
- @ControllerAdvice注解只能捕获控制器方法中抛出的异常 .@Controller注解无法捕获Filter, 拦截器,请求路径等位置抛出的异常
- 实现方式不同:
- ErrorController接口是基于跳转页面的.如果有异常发生,就会跳转到 /error页面
- @ControllerAdvice是基于AOP的
- 捕获异常位置不同:
- 如果项目中两者同时存在,那么 @ControllerAdvice注解就处理控制器方法抛出的异常 ,Controller接口就处理未进入控制器方法的异常
- 相同点:
SpringBoot的全局异常处理
- SpringBoot中全局异常默认处理方式是接口ErrorController的方式:
- 跳转/error路径:
- 如果请求发生异常 ,Tomcat中的StandardHostValve类的custom方法会重定向到 /error路径
- 请求将会交由SpringMVC中的DispatcherServlet类进行处理
- 定位BasicErrorController:
- DispatcherServlet类将 /error请求和BasicErrorController中的方法进行对应
- 如果是html的请求方式 ,/error定位到errorHtml() 方法
- 如果是json的请求方式 ,/error定位到error() 方法
- DispatcherServlet类将 /error请求和BasicErrorController中的方法进行对应
- 跳转/error路径:
- SpringBoot中自定义全局异常处理类:
- SpringBoot默认的错误页不够友好,可以自定义异常处理类,继承BasicErrorController类,重写BasicController类中的errorHtml() 方法和error() 方法
@RestController
public class CustomErrorController extends BasicErrorController
@Autowired
public CustomErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes, ServerProperties serverProperties, List<ErrorViewResolver> errorViewResolvers)
super(errorAttributes, serverProperties.getError(), errorViewResolvers);
@Override
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
Map<String, Object> model = getErrorAttributes(request, isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML));
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView("customeErrorPage", model, status);
return modelAndView;
@Override
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request)
Map<String, Object> body = getErrorAttributes(request, isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.ALL));
Map<String, Object> responseBody = new HashMap<>(8);
responseBody.put("success", false);
responseBody.put("code", body.get("status"));
responseBody.put("message", body.get("error"));
return new ResponseEntity<>(responseBody, HttpStatus.OK);
@ControllerAdvice注解
- @ControllerAdvice注解的执行顺序
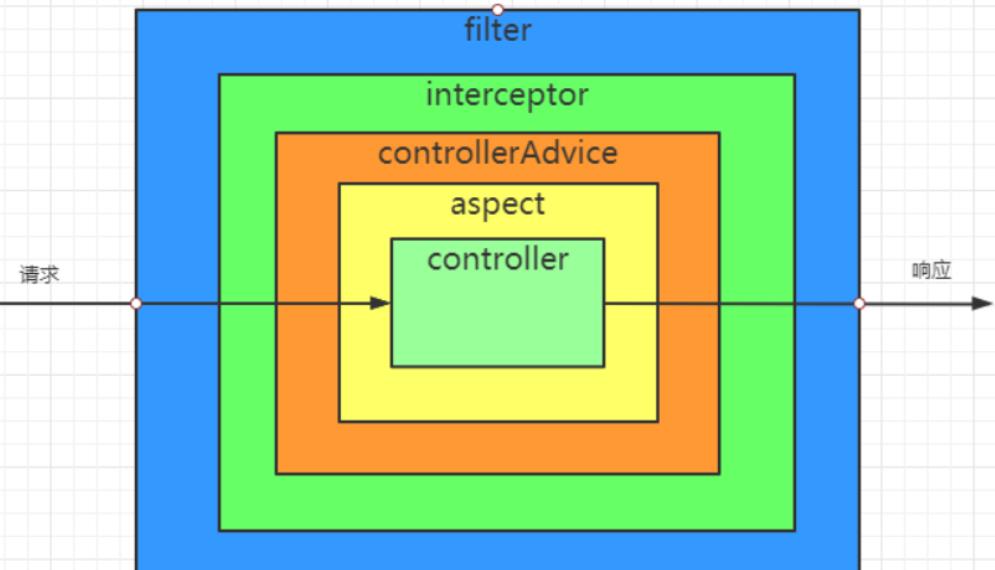
- 根据请求的执行顺序可知:
- @ControllerAdvice注解可以捕获搭配aspect和controller方法中的异常
- @ControllerAdvice注解不能捕获到filter和interceptor方法中中的异常
- 使用 @ControllerAdvice注解和 @ExceptionHandler处理异常:
/**
* 自定义异常
*/
@Data
public class ServiceException extends RuntimeException
private Integer code;
public ServiceException(Integer code, String message)
super(message);
this.code = code;
/**
* 处理异常
*/
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice(annotations = RestController.class, Controller.class)
public class GlobalExceptionHandler
@ExceptionHandler(ServiceException.class)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
public Result handleException(ServciceException exception)
log.error(exception.getMessage());
return Result.buildFailure(exception.getCode(), exception.getMessage());
@Data
public class User
@NotBlank(message = "用户姓名必须提交!")
private String name;
/**
* 异常处理实例
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/exception")
public class MethodExceptionController
@GetMapping("/user")
@ResponseBody
public Result getName(@Valid @RequestParam User user)
return Result.buildSuccess(user);
以上是关于umi-request的全局处理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章