HDU 1121 Complete the Sequence 差分
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了HDU 1121 Complete the Sequence 差分相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
题目链接:
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1121
Complete the Sequence
Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 451 Accepted Submission(s): 283
Problem Description
You probably know those quizzes in Sunday magazines: given the sequence 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, what is the next number? Sometimes it is very easy to answer, sometimes it could be pretty hard. Because these "sequence problems" are very popular, ACM wants to implement them into the "Free Time" section of their new WAP portal.
ACM programmers have noticed that some of the quizzes can be solved by describing the sequence by polynomials. For example, the sequence 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 can be easily understood as a trivial polynomial. The next number is 6. But even more complex sequences, like 1, 2, 4, 7, 11, can be described by a polynomial. In this case, 1/2.n^2-1/2.n+1 can be used. Note that even if the members of the sequence are integers, polynomial coefficients may be any real numbers.
Polynomial is an expression in the following form:
P(n) = aD.n^D+aD-1.n^D-1+...+a1.n+a0
ACM programmers have noticed that some of the quizzes can be solved by describing the sequence by polynomials. For example, the sequence 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 can be easily understood as a trivial polynomial. The next number is 6. But even more complex sequences, like 1, 2, 4, 7, 11, can be described by a polynomial. In this case, 1/2.n^2-1/2.n+1 can be used. Note that even if the members of the sequence are integers, polynomial coefficients may be any real numbers.
Polynomial is an expression in the following form:
P(n) = aD.n^D+aD-1.n^D-1+...+a1.n+a0
. If aD <> 0, the number D is called a degree of the polynomial. Note that constant function P(n) = C can be considered as polynomial of degree 0, and the zero function P(n) = 0 is usually defined to have degree -1.
Input
There is a single positive integer T on the first line of input. It stands for the number of test cases to follow. Each test case consists of two lines. First line of each test case contains two integer numbers S and C separated by a single space, 1 <= S < 100, 1 <= C < 100, (S+C) <= 100. The first number, S, stands for the length of the given sequence, the second number, C is the amount of numbers you are to find to complete the sequence.
The second line of each test case contains S integer numbers X1, X2, ... XS separated by a space. These numbers form the given sequence. The sequence can always be described by a polynomial P(n) such that for every i, Xi = P(i). Among these polynomials, we can find the polynomial Pmin with the lowest possible degree. This polynomial should be used for completing the sequence.
The second line of each test case contains S integer numbers X1, X2, ... XS separated by a space. These numbers form the given sequence. The sequence can always be described by a polynomial P(n) such that for every i, Xi = P(i). Among these polynomials, we can find the polynomial Pmin with the lowest possible degree. This polynomial should be used for completing the sequence.
Output
For every test case, your program must print a single line containing C integer numbers, separated by a space. These numbers are the values completing the sequence according to the polynomial of the lowest possible degree. In other words, you are to print values Pmin(S+1), Pmin(S+2), .... Pmin(S+C).
It is guaranteed that the results Pmin(S+i) will be non-negative and will fit into the standard integer type.
It is guaranteed that the results Pmin(S+i) will be non-negative and will fit into the standard integer type.
Sample Input
4
6 3
1 2 3 4 5 6
8 2
1 2 4 7 11 16 22 29
10 2
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2
1 10
3
Sample Output
7 8 9
37 46
11 56
3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
题解:
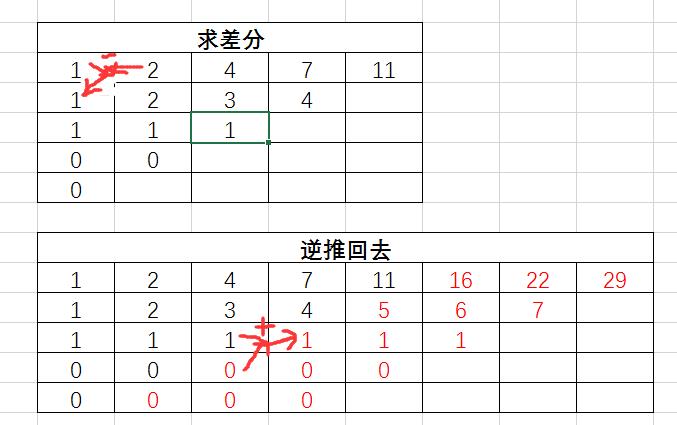
参考别人写的,跑了下样例帮助理解>-<:http://blog.csdn.net/wangjie_wang/article/details/9149683
ac代码:

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstring> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 const int maxn = 111; 8 9 int s, c; 10 int f[maxn][maxn]; 11 12 void init() { 13 memset(f, 0, sizeof(f)); 14 } 15 16 int main() { 17 int tc; 18 scanf("%d", &tc); 19 while (tc--) { 20 init(); 21 scanf("%d%d", &s, &c); 22 for (int i = 0; i < s; i++) scanf("%d", &f[0][i]); 23 for (int i = 1; i <= s - 1; i++) { 24 for (int j = 0; j < s - i; j++) { 25 f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j + 1] - f[i - 1][j]; 26 } 27 } 28 for (int i = 1; i <= c; i++) f[s - 1][i] = f[s - 1][i - 1]; 29 for (int i = s - 2; i >= 0; i--) { 30 for (int j = s - i; j < s + c - i; j++) { 31 f[i][j] = f[i][j - 1] + f[i + 1][j - 1]; 32 } 33 } 34 printf("%d", f[0][s]); 35 for (int i = s + 1; i < s + c; i++) printf(" %d", f[0][i]); 36 printf("\n"); 37 } 38 return 0; 39 }
以上是关于HDU 1121 Complete the Sequence 差分的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
