第四章(上)
Posted GreenOpen专注图像处理
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了第四章(上)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
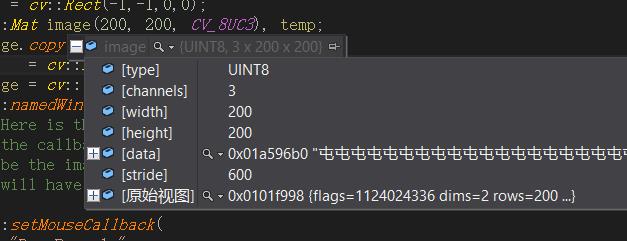

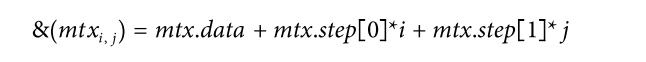

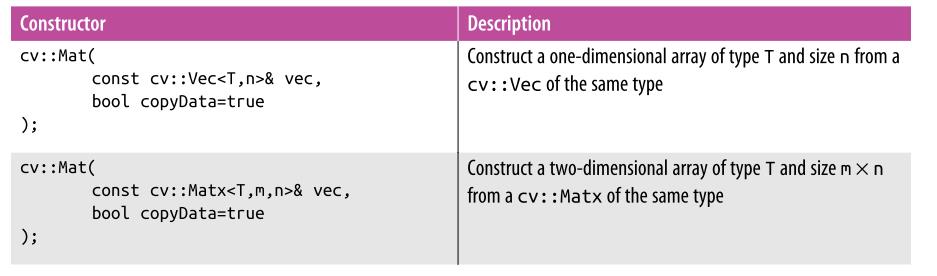
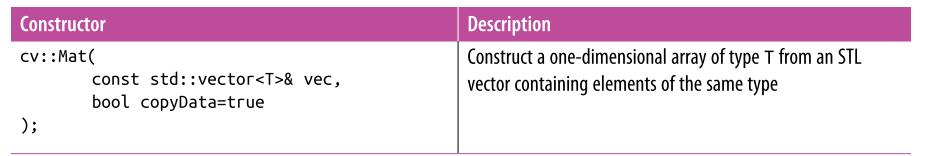
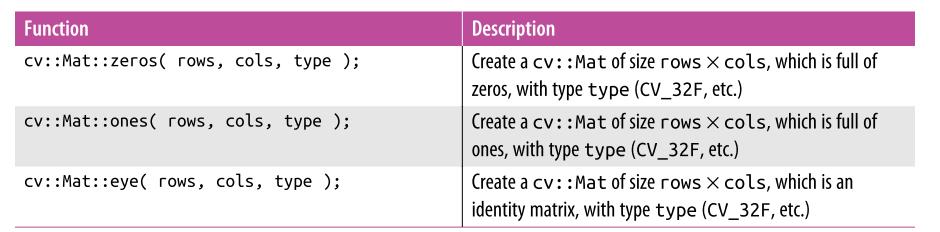
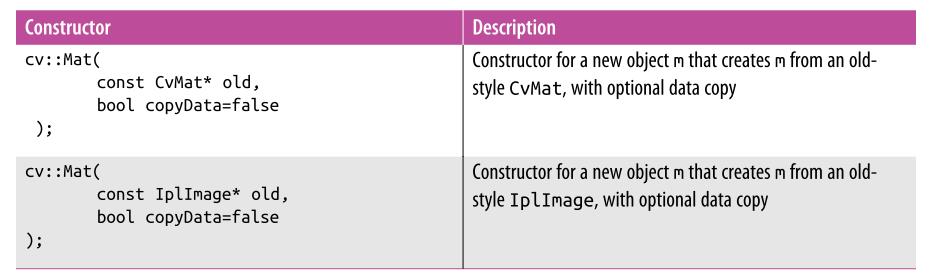
遍历图像的4种方式(来自 cnblogs ronny)
一、at<typename>(i,j)
Mat类提供了一个at的方法用于取得图像上的点,它是一个模板函数,可以取到任何类型的图像上的点。下面我们通过一个图像处理中的实际来说明它的用法。
在实际应用中,我们很多时候需要对图像降色彩,因为256*256*256实在太多了,在图像颜色聚类或彩色直方图时,我们需要用一些代表性的颜色代替丰富的色彩空间,我们的思路是将每个通道的256种颜色用64种代替,即将原来256种颜色划分64个颜色段,每个颜色段取中间的颜色值作为代表色。
void colorReduce(Mat& image,int div){
for(int i=0;i<image.rows;i++){
for(int j=0;j<image.cols;j++){
image.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[0]=image.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[0]/div*div+div/2;
image.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[1]=image.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[1]/div*div+div/2;
image.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[2]=image.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[2]/div*div+div/2;
}
}
}通过上面的例子我们可以看出,at方法取图像中的点的用法:
image.at<uchar>(i,j):取出灰度图像中i行j列的点。
image.at<Vec3b>(i,j)[k]:取出彩色图像中i行j列第k通道的颜色点。其中uchar,Vec3b都是图像像素值的类型,不要对Vec3b这种类型感觉害怕,其实在core里它是通过typedef Vec<T,N>来定义的,N代表元素的个数,T代表类型。
二、高效一点:用指针来遍历图像
上面的例程中可以看到,我们实际喜欢把原图传进函数内,但是在函数内我们对原图像进行了修改,而将原图作为一个结果输出,很多时候我们需要保留原图,这样我们需要一个原图的副本。
void colorReduce(const Mat& image,Mat& outImage,int div)
{ // 创建与原图像等尺寸的图像
outImage.create(image.size(),image.type());
int nr=image.rows; // 将3通道转换为1通道
int nl=image.cols*image.channels();
for(int k=0;k<nr;k++)
{ // 每一行图像的指针
const uchar* inData=image.ptr<uchar>(k);
uchar* outData=outImage.ptr<uchar>(k);
for(int i=0;i<nl;i++)
{
outData[i]=inData[i]/div*div+div/2;
}
}
}从上面的例子中可以看出,取出图像中第i行数据的指针:image.ptr<uchar>(i)。
值得说明的是:程序中将三通道的数据转换为1通道,在建立在每一行数据元素之间在内存里是连续存储的,每个像素三通道像素按顺序存储。也就是一幅图像数据最开始的三个值,是最左上角的那像素的三个通道的值。
三、更高效的方法
上面已经提到过了,一般来说图像行与行之间往往存储是不连续的,但是有些图像可以是连续的,Mat提供了一个检测图像是否连续的函数isContinuous()。当图像连通时,我们就可以把图像完全展开,看成是一行。
void colorReduce(const Mat& image,Mat& outImage,int div)
{
int nr=image.rows;
int nc=image.cols;
outImage.create(image.size(),image.type());
if(image.isContinuous()&&outImage.isContinuous())
{
nr=1;
nc=nc*image.rows*image.channels();
}
for(int i=0;i<nr;i++)
{
const uchar* inData=image.ptr<uchar>(i);
uchar* outData=outImage.ptr<uchar>(i);
for(int j=0;j<nc;j++)
{
*outData++=*inData++/div*div+div/2;
}
}
}用指针除了用上面的方法外,还可以用指针来索引固定位置的像素:
image.step返回图像一行像素元素的个数(包括空白元素),image.elemSize()返回一个图像像素的大小。
&image.at<uchar>(i,j)=image.data+i*image.step+j*image.elemSize();
四、还有吗?用迭代器来遍历。
下面的方法可以让我们来为图像中的像素声明一个迭代器:
MatIterator_<Vec3b> it;
Mat_<Vec3b>::iterator it;如果迭代器指向一个const图像,则可以用下面的声明:
MatConstIterator<Vec3b> it;
Mat_<Vec3b>::const_iterator it;下面我们用迭代器来简化上面的colorReduce程序:
void colorReduce(const Mat& image,Mat& outImage,int div)
{ outImage.create(image.size(),image.type()); MatConstIterator_<Vec3b> it_in=image.begin<Vec3b>(); MatConstIterator_<Vec3b> itend_in=image.end<Vec3b>(); MatIterator_<Vec3b> it_out=outImage.begin<Vec3b>(); MatIterator_<Vec3b> itend_out=outImage.end<Vec3b>(); while(it_in!=itend_in)
{
(*it_out)[0]=(*it_in)[0]/div*div+div/2;
(*it_out)[1]=(*it_in)[1]/div*div+div/2;
(*it_out)[2]=(*it_in)[2]/div*div+div/2;
it_in++;
it_out++;
}
}如果你想从第二行开始,则可以从image.begin<Vec3b>()+image.rows开始。(
tips:在opencv中,两种生成随机数的方法
randu(src,-1.0f,1.0f);
rng.fill(src,RNG::UNIFORM,0.f,1.f);

以上是关于第四章(上)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章