详细了解哈夫曼树和背包问题
Posted Simon鑫
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了详细了解哈夫曼树和背包问题相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
写在前面
- 最近在疯狂复习数据结构和算法,虽然看完了一部完整的视频。但是转眼看看自己手中的《剑指Offer》里面还是不是很清楚。。。而且最近也突然觉得自己知识和别人比起来就是一个渣渣。各种被人家吊打。。。
- 这两个算法一个(哈夫曼树)是看最近视频动手实践的,一个(背包问题)是前段时间一个面试里面的题目,当时不知道这是一个系类的问题,昨天和大神聊完天之后才明白。所以乘着短暂的热情还在就记录下来先从哈夫曼树开始!!
1.哈夫曼树(实现基本的编码解码)
简单定义:
给定n个权值作为n个叶子结点,构造一棵二叉树,若带权路径长度达到最小,称这样的二叉树为最优二叉树,也称为哈夫曼树(Huffman Tree)。哈夫曼树是带权路径长度最短的树,权值较大的结点离根较近。复杂的文字定义我觉得以后肯定不会看。。所以直接来一张哈夫曼树的构造过程简单明了。。
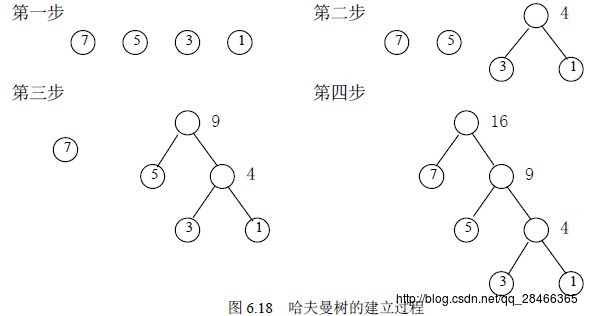
1.模型构造
// 节点类
public static class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
String data;
double weight;
Node leftChild;
Node rightChild;
Node parent;
public boolean isLeftChild() {
return parent != null && this == parent.leftChild;
}
public Node() {
}
public Node(String data, double weight) {
this.data = data;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [data=" + data + ", weight=" + weight + "]";
}
//队列排序依据
public int compareTo(Node o) {
return (int) (weight - o.weight);
}
public boolean isLeaf() {
return data.length() == 1;
}
}包含属性:
| 属性 | 定义 | 类型 |
|---|---|---|
| data | 数据 | String |
| weight | 权值 | double |
| leftChild | 左节点 | Node |
| rightChild | 右节点 | Node |
| parent | 父节点 | Node |
2.统计字符出现的次数,用出现的次数作为权值
- 这里实现的思路是:将出现的字符串(C)和次数(count)保存为一个Map<字符,次数>对象,然后再保存为List集合
public static Map<Character, Integer> statistics(char[] charArray) {
Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<Character, Integer>();
for (char c : charArray) {
Character character = new Character(c);
if (map.containsKey(character)) {
map.put(character, map.get(character) + 1);
} else {
map.put(character, 1);
}
}
return map;
}
public static List<Node> statisticsProbability(Map<Character, Integer> maps) {
List<Node> list = new ArrayList<TestHuffmanTree_Encode_Decode.Node>();
for (Map.Entry<Character, Integer> map : maps.entrySet()) {
Node node = new Node(map.getKey().toString(), map.getValue());
list.add(node);
}
return list;
}
3.根据统计的List进行哈夫曼树的构造
首先List中保存的就是Node集合,其中Node的data就是字符串,Node的weight就是出现的次数也就是权值
哈夫曼树的构造:
- 首先利用Java中的priorityQueue方法进行模拟队列
priorityQueue的用法

其中主要的方法:
| 方法 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| add | 将指定元素插入到次优先级队列 |
| poll | 获取并且移除队列头 |
| peek | 获取但是不移出队列 |
- 将List中的数据保存到队列里面去
PriorityQueue<Node> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<Node>();
for (int i = 0; i < nodes.size(); i++) {
priorityQueue.add(nodes.get(i));
}- 然后利用poll方法获取队列头节点,这里可能就由疑问了,哈夫曼树不是要求按照权值最小的两个开始组成树嘛。这里为什么随便从队列里面弄两个出来就可以。
其实是这样的;在Node定义的时候实现了Comparable接口并且实现了compareTo(E e)方法,这里其实就已经实现了队列里面的排序

- 然后构建两个子节点的父节点,并且声明三者之间的关系(父子,左右)
// 构建父节点
Node sumNode = new Node(node1.data + node2.data, node1.weight
+ node2.weight);
sumNode.leftChild = node1;
sumNode.rightChild = node2;
node1.parent = sumNode;
node2.parent = sumNode;- 然后再将父节点保存到队列中去:这样做的目的是为了得到根节点
priorityQueue.add(sumNode);- 最后返回根节点 priorityQueue.poll();
这样,到这里哈夫曼树的构建就完成了,但是既然学习了就深入一点,
哈夫曼树的最长用途就是用来文件压缩,因为我们知道发送一句话的时候并不是每个字母出现的频率都是一样的,有的出现的多有的出现的少,但是如果还是使用一样额编码那样会有很大的消耗,所以这里我们就用哈夫曼树实现对字符串的编码和解码
4.根据形成的二叉树进行编码
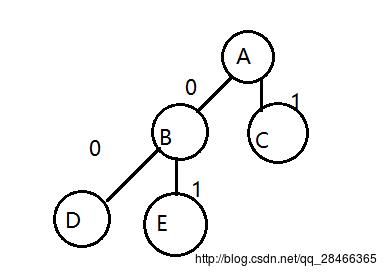
如图所示,我们需要得到的编码就如图中那样
- A:parent
- B:0
- C:1
- D:00
- E:10
所以需要做的就判断该节点为左孩子还是右孩子
// 编码
public static String encode(String originalStr) {
if (originalStr == null || originalStr.equals("")) {
return "";
}
char[] charArray = originalStr.toCharArray();
leafNodes = statisticsProbability(statistics(charArray));
createTree(leafNodes);
Map<Character, String> encodeInfo = buildEncodeInfo(leafNodes);
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer();
for (char c : charArray) {
Character character = new Character(c);
buf.append(encodeInfo.get(character));
}
return buf.toString();
}
// 遍历二叉树,如果为左则前缀为0 右前缀为1
private static Map<Character, String> buildEncodeInfo(List<Node> leafNodes) {
Map<Character, String> codewords = new HashMap<Character, String>();
for (Node node : leafNodes) {
Character character = new Character(node.data.charAt(0));
String codeword = "";
Node currrentNode = node;
do {
if (currrentNode.isLeftChild()) {
codeword = "0" + codeword;
} else {
codeword = "1" + codeword;
}
currrentNode = currrentNode.parent;
} while (currrentNode.parent != null);
codewords.put(character, codeword);
}
return codewords;
}该方法返回的为一段编码的01数字,所以现在压缩了就需要解码了
5.根据编码的二叉树进行响应的解码
解码的思路就是根据01进行区分
// 解码
public static String decode(String binaryStr) {
if (binaryStr == null && binaryStr.equals("")) {
return "";
}
char[] binaryCharArray = binaryStr.toCharArray();
LinkedList<Character> binaryList = new LinkedList<Character>();
int length = binaryCharArray.length;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
binaryList.addLast(new Character(binaryCharArray[i]));
}
Node tree = createTree(leafNodes);
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer();
while (binaryList.size() > 0) {
Node node = tree;
do {
Character c = binaryList.removeFirst();
if (c.charValue() == '0') {
node = node.leftChild;
} else {
node = node.rightChild;
}
} while (!node.isLeaf());
buf.append(node.data);
}
return buf.toString();
}6.数据测试

到这里哈夫曼树的创建和使用就基本结束了。。感觉算法是个无底洞啊。。。
2.背包问题
- 问题描述:
1.给定 n 个背包,其重量分别为 w1,w2,……,wn, 价值分别为 v1,v2,……,vn
2.要放入总承重为 totalWeight 的箱子中,
3.求可放入箱子的背包价值总和的最大值。
一样,首先构造模型
1.构造模型
包含两个属性:
| 属性 | 定义 | 类型 |
|---|---|---|
| weight | 重量 | int |
| value | 价值 | int |
public class Knapsack {
/** 背包重量 */
private int weight;
/** 背包物品价值 */
private int value;
/***
* 构造器
*/
public Knapsack(int weight, int value) {
this.value = value;
this.weight = weight;
}
public int getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public String toString() {
return "[weight: " + weight + " " + "value: " + value + "]";
}
} 包含一个构造器
2.问题分析
假设给定的重量为5 背包的数量为5 我们需要解决的是给定重量为5的时候找到的最大价值
那么现在可以这样分析
- 给定的重量为1的时候,分别求给0,1,2,3,4,5个背包的时候能够得到的最大价值
- 。。。
- 给定的重量为5的时候,分别求给0,1,2,3,4,5个背包的时候能够得到的最大价值
通过这样的动态划分就可以得到一个二维矩阵,而矩阵中填入的值就是得到的最大价值
示例分析
1.求最佳矩阵
假设给定的5个背包分别为A(2,10),B(3,15),C(2,6),D(2,7),E(4,10);给定的最大容量为5
那么刚刚的矩阵就可以写出来 矩阵N(背包数量,重量)
| 价值 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| 2 | 0 | 10 | 15 | 10 | 25 |
| 3 | 0 | 10 | 15 | 16 | 25 |
| 4 | 0 | 10 | 15 | 13 | 25 |
| 5 | 0 | 10 | 14 | 17 | 25 |
×其中横向为重量,竖向为当前(可供挑选的背包)的背包
2.求最佳背包组成
知道了最佳背包的矩阵,那么我们现在就可以开始求当前重量下可以由哪些背包组成最大价值了 n=总背包数量 =5,j=总的重量 =5
求解最优背包组成:
求N(n,j)>N(n-1,j); 得到n=2 同时此时将j = j-N(2).weight; j = 2
接着求n(n,2)>N(n-1,j) 得到n=1; 此时 j = j-N(1).weight; j=0
到这里就都求出来了。加入的背包为A(2,10) B(3,15) 最大价值为N(n,5) = 25;
3.代码示例
public void save(){
//就是在totalWeight中依次(totalWeight=1,2,3..)最优的背包组成
for (int i = 0; i <= totalWeight; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) {
if(i==0 || j==0){
bestvalues[j][i] =0;
}
else{
//假如当前的重量比当前背包的重量小
//意思就是当前背包的重量已经超过了总重量
//那么最优矩阵就是在这个背包前一个了
if(i<bags[j-1].getWeight()){
bestvalues[j][i] = bestvalues[j-1][i];
}
else{
int iweight = bags[j-1].getWeight();
int ivalue = bags[j-1].getValue();
bestvalues[j][i] = Math.max(bestvalues[j-1][i],ivalue+bestvalues[j-1][i-iweight]);
}
}
}
}
if(bestSolution==null){
bestSolution = new ArrayList<Knapsack>();
}
//找到最优价值是由那几个背包组成
int tempWeight = totalWeight;
for (int i = n; i >=1; i--) {
if(bestvalues[i][tempWeight]>bestvalues[i-1][tempWeight]){
bestSolution.add(bags[i-1]);
tempWeight -=bags[i-1].getWeight();
}
if(tempWeight == 0){break;}
}
bestValue = bestvalues[n][totalWeight];
}4.效果演示

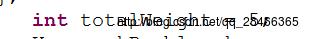
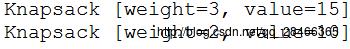
写在最后:一入算法深思海,写这篇博客也差不多用了三四个小时吧,其中大部分内容是参考其他人的博客。说实话现在脑子有点炸,但是想着马上就可以去郑州内心还是有点小许的期待。。
以上是关于详细了解哈夫曼树和背包问题的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章