设计模式之解释器模式
Posted 帝国攻城狮
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了设计模式之解释器模式相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一,模式定义
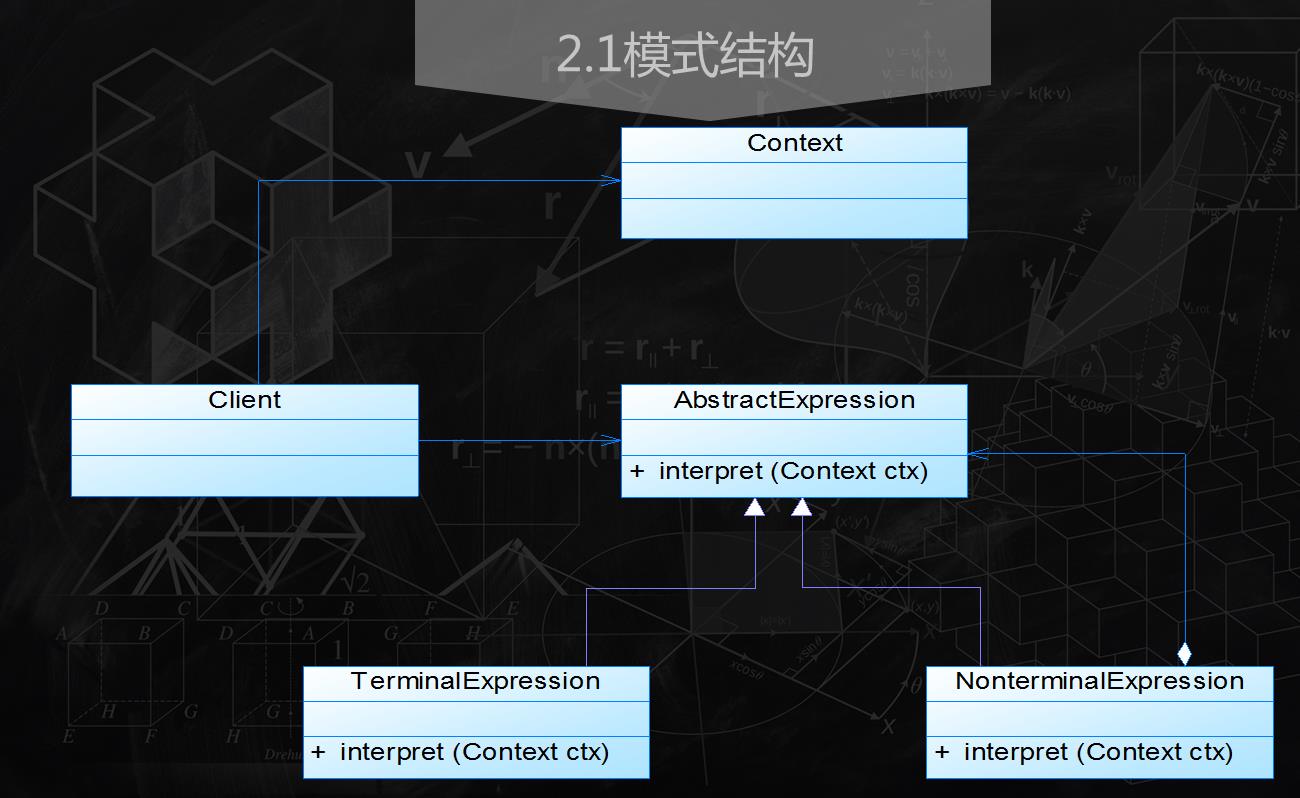
二,模式结构
三,模式实例
四,模式应用
一,定义:解释器模式就是自定义一套语法规范,用于解释语句
二,
,
三,先定义一个抽象表达式类Node.java
package com.lts.interpret; //定义抽象表达式类 public interface Node { public int interpret();//解释方法 }
分别定义一个终结符表达式类ValueNode和非终结符表达式类SymbolNode实现该接口
package com.lts.interpret; //定义终结符表达式类 public class ValueNode implements Node{ private int value; public ValueNode(int value) { this.value=value; } public int interpret(){ return this.value; } }
package com.lts.interpret; //定义非终结符表达式类 public abstract class SymbolNode implements Node{ protected Node left; protected Node right; public SymbolNode(Node left,Node right){ this.left=left; this.right=right; } }
在SymbolNode下定义三个子类MulNode,DivNode和ModNode分别实现乘法,除法和求余的功能
package com.lts.interpret; //乘法类继承非终结符表达式类 public class MulNode extends SymbolNode{ public MulNode(Node left,Node right){ super(left,right); } public int interpret(){ return super.left.interpret()*super.right.interpret(); } }
package com.lts.interpret; //除法类继承非终结符表达式类 public class DivNode extends SymbolNode{ public DivNode(Node left,Node right){ super(left,right); } public int interpret(){ return super.left.interpret()/super.right.interpret(); } }
package com.lts.interpret; //求模类继承非终结符表达式类 public class ModNode extends SymbolNode{ public ModNode(Node left,Node right){ super(left,right); } public int interpret(){ return super.left.interpret()%super.right.interpret(); } }
最后定义一个解释器类Calculator用于封装解释器的功能
package com.lts.interpret; import java.util.*; public class Calculator { private String statement; private Node node; public void build(String statement){ Node left=null,right=null; Stack stack=new Stack(); String[] statementArr=statement.split(" ");//把字符串分割成字符串数组 for(int i=0;i<statementArr.length;i++){ if(statementArr[i].equalsIgnoreCase("*")){ left=(Node)stack.pop(); int val=Integer.parseInt(statementArr[++i]); right=new ValueNode(val); stack.push(new MulNode(left,right)); } else if(statementArr[i].equalsIgnoreCase("/")){ left=(Node)stack.pop(); int val=Integer.parseInt(statementArr[++i]); right=new ValueNode(val); stack.push(new DivNode(left,right)); } else if(statementArr[i].equalsIgnoreCase("%")) { left=(Node)stack.pop(); int val=Integer.parseInt(statementArr[++i]); right=new ValueNode(val); stack.push(new ModNode(left,right)); } else{ stack.push(new ValueNode(Integer.parseInt(statementArr[i]))); } } this.node=(Node)stack.pop(); } public int compute(){ return node.interpret(); } }
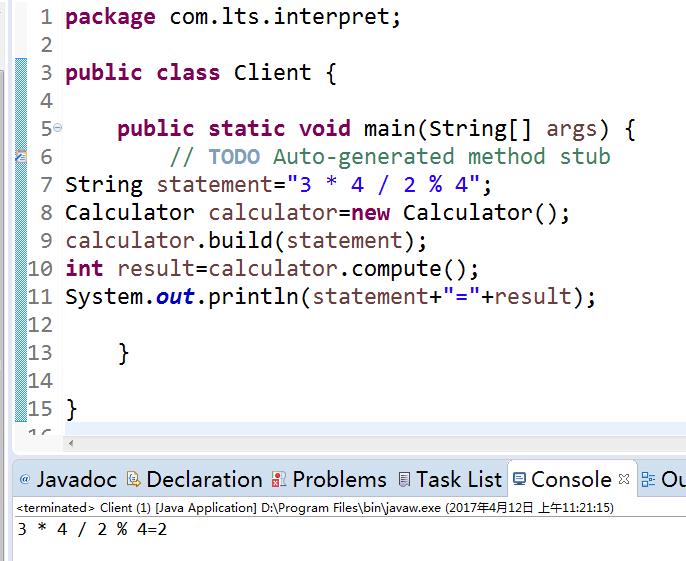
在客户端做测试
package com.lts.interpret; public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub String statement="3 * 4 / 2 % 4"; Calculator calculator=new Calculator(); calculator.build(statement); int result=calculator.compute(); System.out.println(statement+"="+result); } }
运行结果:
四,模式应用:
优点:易于修改和拓展文法,修改文法只需在对应的类上修改,拓展文法只需要增加对应的类即可
缺点:执行效率较低,在调用compute方法里的interpret()时,Node下的所有子类的interpret方法也会递归执行,降低了效率,同时应用场景有限
总结:解释器模式适用于对程序运行效率要求不高,表达式文法简单的情况。如编译器和科学计算器等
以上是关于设计模式之解释器模式的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章