RunTime之类与对象
Posted LeeGof
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了RunTime之类与对象相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
我们知道,Objective-C是一门动态语言,它将很多静态语言在编译时期做的事放到了运行时来处理。用C++编写的程序通过编译器直接把函数地址硬编码进入可执行文件;而Objective-C无法通过编译器直接把函数地址硬编码进入可执行文件,而是在程序运行的时候,利用Runtime根据条件判断作出决定,函数标识与函数执行的真正内容之间的关联可以动态修改。这样我们在写代码的时候,声明一个方法,但不对该方法做实现,静态语言在编译时就会报错,但OC中编译时不会报错。这种动态特性给我们带来的好处在于:我们写代码时更具有灵活性,例如我们可以把消息转发给想要的对象,或者交换一个方法的实现等等。
当然,这也意味着OC语言不仅需要一个编译器,还需要一个运行时系统来执行编译的代码。这个运行时系统就像一个操作系统一样,让它所有的工作可以正常运行。这就是我们本篇要聊的Runtime。
1.类(Class)
OC的类是由Class类型来表示的。这个Class类型是什么呢?
//objc.h文件 typedef struct objc_class *Class; //runtime.h文件 struct objc_class { Class isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY; //指向meta-class(元类) #if !__OBJC2__ Class super_class OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; //父类,如果是根类,则为NULL const char *name OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; //类名 long version OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; //类的版本信息,默认为0 long info OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; //类信息,供运行期使用的一些位标识 long instance_size OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; //该类的实例变量大小 struct objc_ivar_list *ivars OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; //该类的成员变量链表 struct objc_method_list **methodLists OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; //该类的方法链表 //用于缓存最近使用的方法。一个接收者对象接收到一个消息时,它会根据isa指针去查找能够响应这个消息的对象。
//在实际使用中,这个对象只有一部分方法是常用的,很多方法很少用或者根本用不上。这种情况下,如果每次消息来时都是methodLists中遍历一遍,性能势必很差。
//这时,cache就派上用场了。在我们每次调用过一个方法后,这个方法就会被缓存到cache列表中,下次调用的时候runtime就会优先去cache中查找,如果cache没有,才到methodLists中查找方法。
//这样,对于那些经常用到的方法的调用,提高了调用的效率。 struct objc_cache *cache OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; struct objc_protocol_list *protocols OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; //协议链表 #endif } OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
关于cache,这里用一个示例来解说:
// 第一步:执行[NSString alloc]。由于NSString没有+alloc方法,于是去父类NSObject去查找。 // 第二步:检测NSObject是否响应+alloc方法,发现响应,于是检测NSString类,并根据其所需的内存空间大小开始分配内存空间,然后把isa指针指向NSString类。同时,+alloc也被加进cache列表里面。 // 第三步:执行-init方法,如果NSString响应该方法,则直接将其加入cache;如果不响应,则去父类查找。 // 第四步:如果再以[[NSString alloc] init]这种方式来创建字符串,则会直接从cache中取出相应的方法,直接调用。 NSString *str = [[NSString alloc] init];
cache是一个指向objc_cache结构体的指针,这个结构体的定义如下:
struct objc_cache { //指定分配的缓存bucket的总数 unsigned int mask /* total = mask + 1 */ OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; //指定实际占用的缓存bucket的总数 unsigned int occupied OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; //指向Method数据结构指针的数组 Method buckets[1] OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; };
2.对象
我们知道,OC中有一个id类型,该类型的对象可以转换为任何一种对象。
struct objc_object { Class isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY; }; /// A pointer to an instance of a class. typedef struct objc_object *id;
从定义可以看到,id类型是一个objc_object结构类型的指针。objc_object结构体也只是一个指向其类的isa指针。这样,当我们向一个Objective-C对象发送消息时,运行时库会根据实例对象的isa指针找到这个实例对象所属的类。runtime库会在类的方法列表及父类的方法列表中去寻找与消息对应的selector指向的方法,找到后运行这个方法。
当创建一个特定类的实例对象时,分配的内存包含一个objc_object数据结构,然后是类的实例变量的数据。NSObject类的alloc和allocWithZone:方法使用函数class_createInstance来创建objc_object数据结构。
3.meta-class(元类)
所有的类本身也是一个对象,我们可以向这个对象发送消息(即调用类方法)。如:
[NSString string];
从上面的代码可以看到,+string消息发送给了NSString类,而这个NSString也是一个对象。既然是对象,那么它也是一个objc_object指针,它包含一个指向其类的一个isa指针。那么这个isa指针指向哪里呢?为了调用+string方法,这个类的isa指针必须指向一个包含这些类方法的一个objc_class结构体。这就引出了meta-class的概念:meta-class是一个类对象的类。
- 当我们向一个对象发送消息时,runtime会在这个对象所属的这个类的方法列表中查找方法;
- 而向一个类发送消息时,会在这个类的meta-class的方法列表中查找。
meta-class之所以重要,是因为它存储着一个类的所有方法。每个类都会有一个单独的meta-class,因为每个类的类方法基本不可能完全相同。
再深入一下,meta-class也是一个类,也可以向它发送一个消息,那么它的isa又是指向什么呢?为了不让这种结构无限延伸下去,Objective-C的设计者让所有的meta-class的isa指向基类的meta-class,以此作为它们的所属类。即任何NSObject继承体系下的meta-class都使用NSObject的meta-class作为自己的所属类,而基类的meta-class的isa指针是指向它自己。
下图描述了类及相应meta-class类的继承关系:
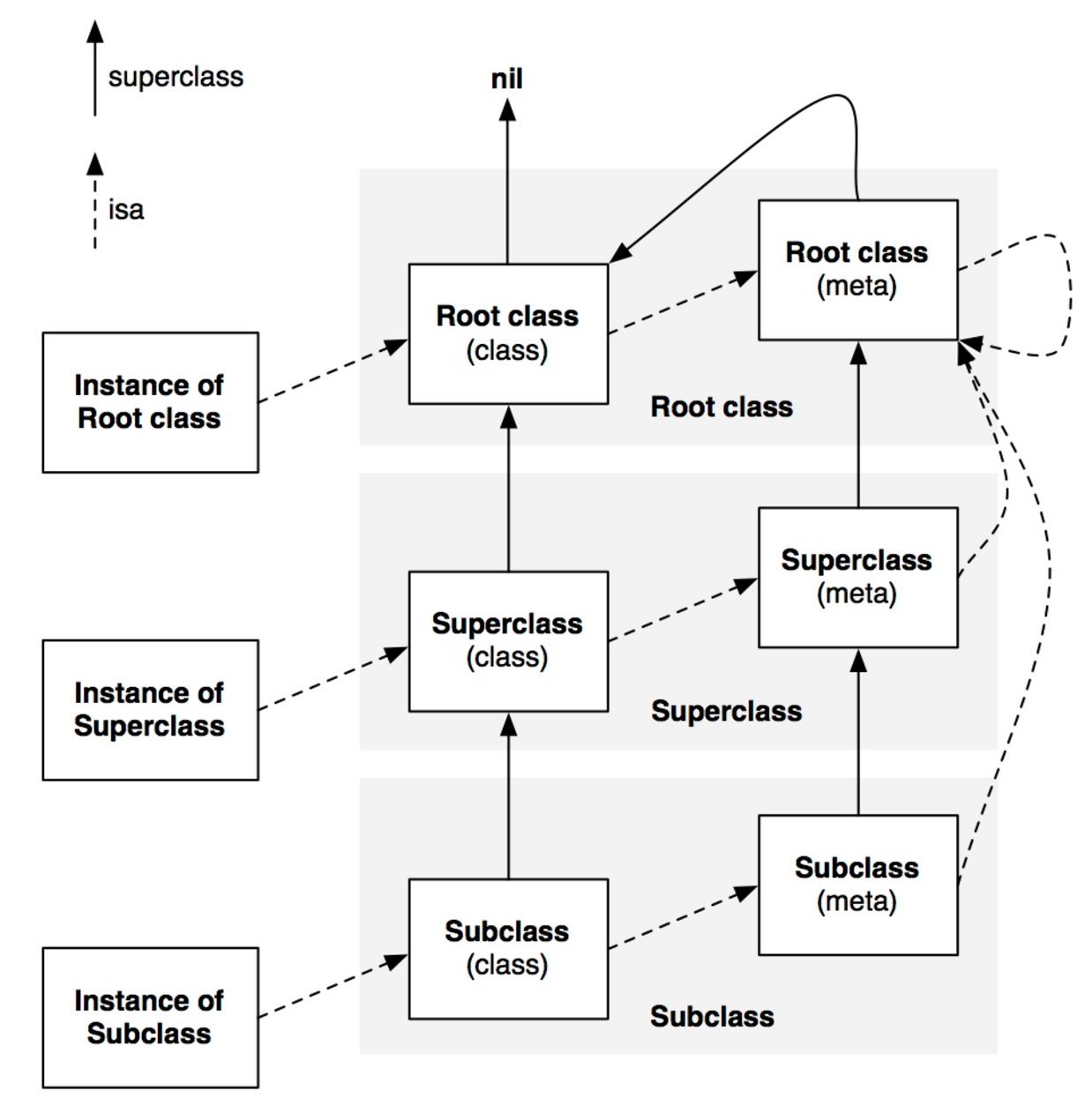
【注意】:所有meta-class中isa指针都指向根meta-class。而根meta-class则指向自身。根meta-class是通过继承Root class产生的。与Root class结构体成员一致,不同的是根meta-class的isa指针指向自身。
对于NSObject继承体系来说,其实例方法对体系中的所有实例、类和meta-class都是有效的;而类方法对于体系内的所有类和meta-class都是有效的。
下面来看一个示例:
- (void)ex_registerClassPair { //创建存储空间 Class newClass = objc_allocateClassPair([NSObject class], "GofClass", 0); /** 动态添加方法 @param cls 类类型 @param name 选择器(SEL) @param imp 函数指针 @param type 方法类型 */ SuppressUndeclaredSelectorWarning(class_addMethod(newClass, @selector(testMetaClass), (IMP)TestMetaClass, "v@:")); //注册这个类 objc_registerClassPair(newClass); id instance = [[newClass alloc] init]; SuppressUndeclaredSelectorWarning([instance performSelector:@selector(testMetaClass)]); } //隐式参数 void TestMetaClass(id self, SEL _cmd) { NSLog(@"This object is %p", self); NSLog(@"Class is %@, super class is %@", [self class], [self superclass]); Class currentClass = [self class]; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { NSLog(@"Following the isa pointer %d times gives %p", i, currentClass); currentClass = objc_getClass((__bridge void *)currentClass); } NSLog(@"NSObject\'s class is %p", [NSObject class]); NSLog(@"NSObject\'s meta class is %p", objc_getClass((__bridge void *)[NSObject class])); }
运行之后,打印结果如下:
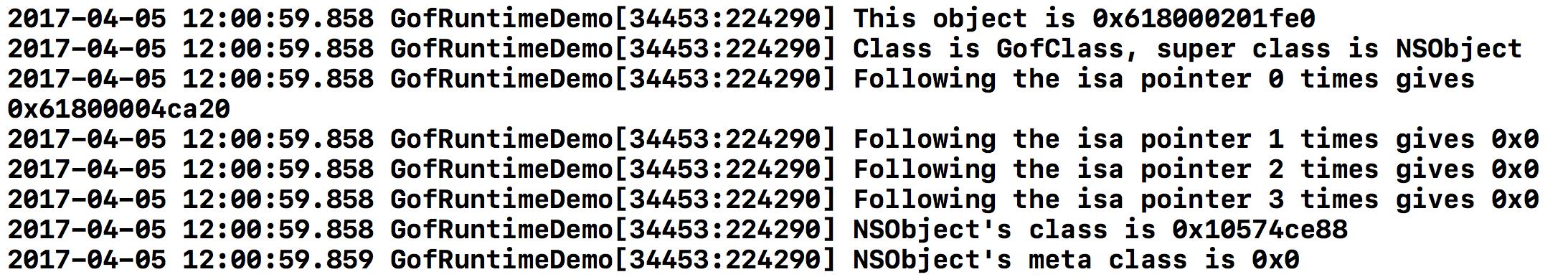
在for循环中,通过objc_getClass来获取对象的isa,并将其打印出来,依此一直回溯到NSObject的meta-class。分析打印结果,可以看到最后指针指向的地址是0x0,即NSObject的meta-class的类地址。
4.类相关函数
runtime提供了大量的函数来操作类和对象。类的操作方法大部分是以class_为前缀的,而对象的操作方法大部分是以objc_或object_为前缀。
4.1获取类名
//1.获取类名 NSLog(@"获取类名:%s", class_getName([GofBaseViewController class]));
【注意】:如果传入的cls为Nil/NULL/nil,则返回nil。
4.2获取父类
//2.获取父类 NSLog(@"获取父类:%@", class_getSuperclass([GofBaseViewController class])); NSLog(@"获取父类2:%@", [GofBaseViewController superclass]);
【注意】:如果传入的cls为Nil/NULL/nil或者cls为根类时,则返回nil。
4.3是否meta-class
//3.是否meta-class NSObject *obj = [[NSObject alloc] init]; Class objectClsObj = object_getClass(obj); Class objectClsObj_isa = object_getClass(objectClsObj); NSLog(@"是否meta-class:%d", class_isMetaClass(objectClsObj)); //否 NSLog(@"是否meta-class:%d", class_isMetaClass(objectClsObj_isa)); //是
【注意】:如果传入的cls为meta-class,则返回YES;否则返回NO;
4.4实例变量大小
//4.获取实例变量大小 NSLog(@"获取实例变量大小:%zu", class_getInstanceSize(objectClsObj));
4.5成员变量
主要有以下相关函数:
//获取类中指定名称实例成员变量的信息 OBJC_EXPORT Ivar class_getInstanceVariable(Class cls, const char *name) OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.0, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0); //获取类成员变量的信息 OBJC_EXPORT Ivar class_getClassVariable(Class cls, const char *name) OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.5, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0); //添加成员变量 OBJC_EXPORT BOOL class_addIvar(Class cls, const char *name, size_t size, uint8_t alignment, const char *types) OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.5, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0); //获取整个成员变量列表 OBJC_EXPORT Ivar *class_copyIvarList(Class cls, unsigned int *outCount) OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.5, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0);
下面通过一个示例细看一下:
GofPerson.h文件 @interface GofPerson : NSObject { NSInteger age; } @property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *name; //!<姓名 @end GofPerson.m文件 @interface GofPerson () @property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *phone; @end @implementation GofPerson @end GofPerson *person = [[GofPerson alloc] init]; Class objectClsObj = object_getClass(person); Ivar ivar0 = class_getInstanceVariable(objectClsObj, "age"); const char *age = ivar_getName(ivar0); NSLog(@"成员变量:%s", age); Ivar ivar1 = class_getClassVariable([GofPerson class], "isa"); const char *classVariable = ivar_getName(ivar1); NSLog(@"成员变量:%s", classVariable); //在这里添加无效 class_addIvar(objectClsObj, "name1", sizeof(id), log2(sizeof(id)), "@"); unsigned int count = 0; Ivar *ivars = class_copyIvarList([GofPerson class], &count); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { Ivar ivar = ivars[i]; const char *name = ivar_getName(ivar); NSLog(@"成员变量:%s", name); }
【说明】:class_addIvar方法只能在objc_allocateClassPair函数与objc_registerClassPair之间调用。
打印结果如下:

4.6属性
和上一小节一样,我们先看看主要都有哪些函数?
//获取指定的属性 OBJC_EXPORT objc_property_t class_getProperty(Class cls, const char *name) OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.5, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0); //获取属性列表 OBJC_EXPORT objc_property_t *class_copyPropertyList(Class cls, unsigned int *outCount) OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.5, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0); //添加属性 OBJC_EXPORT BOOL class_addProperty(Class cls, const char *name, const objc_property_attribute_t *attributes, unsigned int attributeCount) OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.7, 4.3, 9.0, 1.0); //替换类的属性 OBJC_EXPORT void class_replaceProperty(Class cls, const char *name, const objc_property_attribute_t *attributes, unsigned int attributeCount) OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.7, 4.3, 9.0, 1.0);
怎么使用呢?
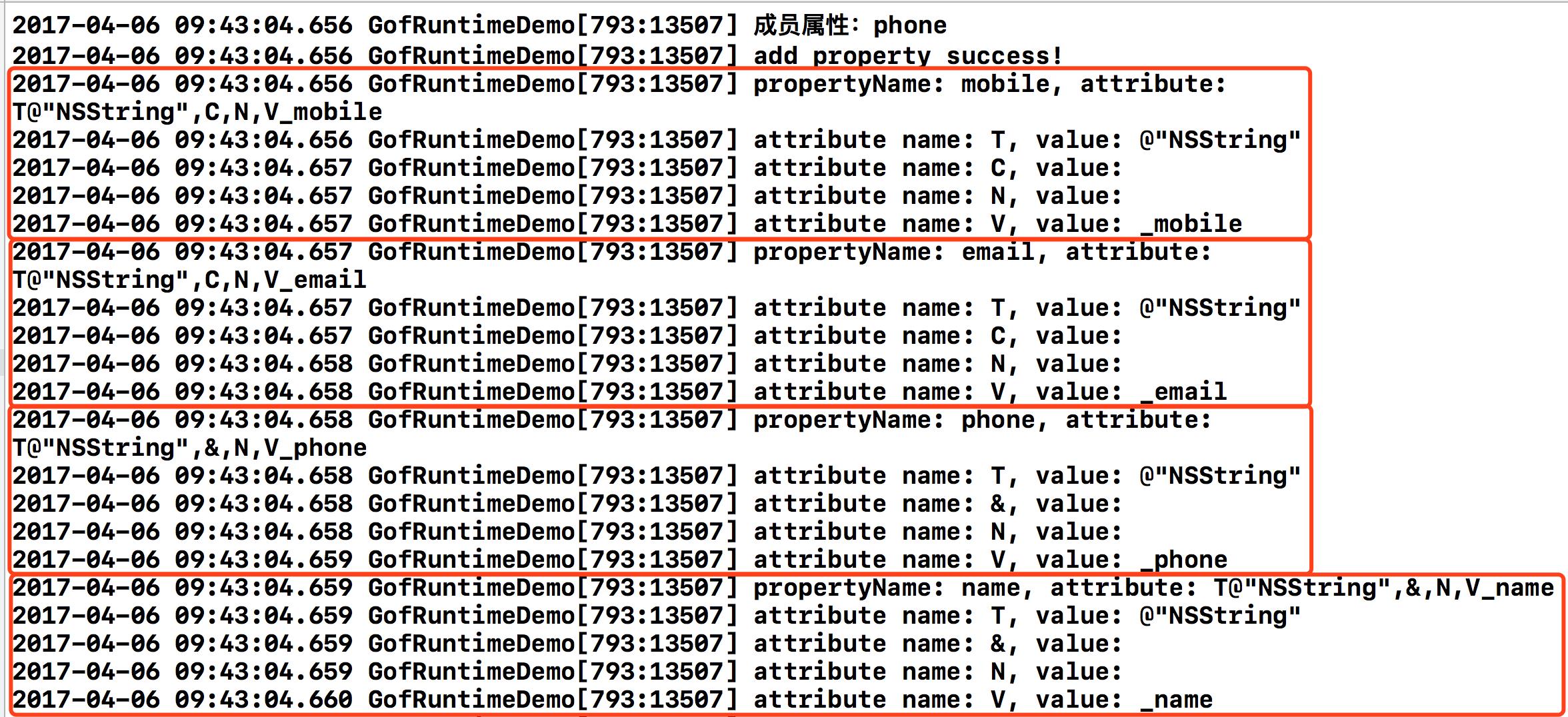
GofPerson *person = [[GofPerson alloc] init]; Class objectClsObj = object_getClass(person); //获取指定的属性 objc_property_t property0 = class_getProperty(objectClsObj, "phone"); const char *phone = property_getName(property0); NSLog(@"成员属性:%s", phone); //添加属性 objc_property_attribute_t attribute1 = {"T", "@\\"NSString\\""}; //type objc_property_attribute_t attribute2 = {"C", ""}; //copy objc_property_attribute_t attribute3 = {"N", ""}; //nonatomic objc_property_attribute_t attribute4 = {"V", "_email"}; //variable name objc_property_attribute_t attributesList[] = {attribute1, attribute2, attribute3, attribute4}; if(class_addProperty([GofPerson class], "email", attributesList, 4)) { NSLog(@"add property success!"); } else { NSLog(@"add property failure!"); } //替换属性的信息(如果没有原属性会新建一个属性) objc_property_attribute_t attribute11 = {"T", "@\\"NSString\\""}; //type objc_property_attribute_t attribute22 = {"C", ""}; //copy objc_property_attribute_t attribute33 = {"N", ""}; //nonatomic objc_property_attribute_t attribute44 = {"V", "_mobile"}; //variable name objc_property_attribute_t attributesList1[] = {attribute11, attribute22, attribute33, attribute44}; class_replaceProperty([GofPerson class], "mobile", attributesList1, 4); //获取属性列表(分类中的属性也会显示) unsigned int count = 0; objc_property_t *propertys = class_copyPropertyList([GofPerson class], &count); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { objc_property_t property = propertys[i]; const char *name = property_getName(property); const char *attribute = property_getAttributes(property); NSLog(@"propertyName: %s, attribute: %s", name, attribute); unsigned int attributeCount; objc_property_attribute_t *attributeList = property_copyAttributeList(property, &attributeCount); for (unsigned int j = 0; j < attributeCount; j++) { objc_property_attribute_t attribute = attributeList[j]; const char *name = attribute.name; const char *value = attribute.value; NSLog(@"attribute name: %s, value: %s", name, value); } } free(propertys);
打印结果如下:
4.7方法
主要有以下函数来做方法操作:
//添加方法 OBJC_EXPORT BOOL class_addMethod(Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, const char *types) OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.5, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0); //获取实例方法 OBJC_EXPORT Method class_getInstanceMethod(Class cls, SEL name) OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.0, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0); //获取类方法 OBJC_EXPORT Method class_getClassMethod(Class cls, SEL name) OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.0, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0); //获取所有方法的数组 OBJC_EXPORT Method *class_copyMethodList(Class cls, unsigned int *outCount) OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.5, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0); //替代方法的实现 OBJC_EXPORT IMP class_replaceMethod(Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, const char *types) OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.5, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0); //返回方法的具体实现 OBJC_EXPORT IMP class_getMethodImplementation(Class cls, SEL name) OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.5, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0); OBJC_EXPORT IMP class_getMethodImplementation_stret(Class cls, SEL name) OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.5, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0) OBJC_ARM64_UNAVAILABLE; //类实例是否响应指定的selector OBJC_EXPORT BOOL class_respondsToSelector(Class cls, SEL sel) OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.5, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0);
我们先给上面定义的GofPerson类添加几个方法:
//GofPerson.h @interface GofPerson : NSObject { NSInteger age; } @property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *name; //!<姓名 + (GofPerson *)createPersonWithName:(NSString *)nameString age:(NSInteger)ageInt; - (void)setName:(NSString *)nameString age:(NSInteger)ageInt; @end //GofPerson.m @interface GofPerson () @property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *phone; @end @implementation GofPerson + (GofPerson *)createPersonWithName:(NSString *)nameString age:(NSInteger)ageInt { GofPerson *person = [[GofPerson alloc] init]; [person setName:@"LeeGof" age:18 phone:@"13800138000"]; return person; } - (void)setName:(NSString *)nameString age:(NSInteger)ageInt { self.name = nameString; age = ageInt; } - (void)setName:(NSString *)nameString age:(NSInteger)ageInt phone:(NSString *)phoneString { self.name = nameString; age = ageInt; self.phone = phoneString; } - (void)dealloc { NSLog(@"GofPerson dealloc"); } @end
然后我们来对上面的方法操作函数做一个简单的示例:
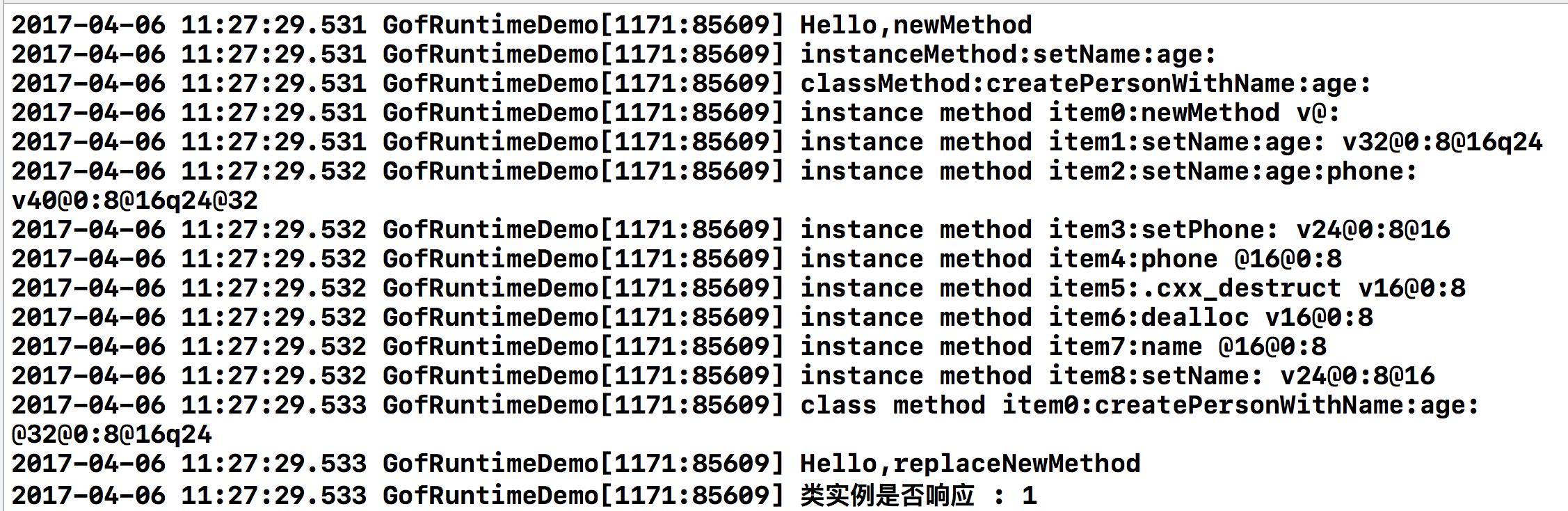
/** 操作方法 */ - (void)operateMethod { GofPerson *person = [[GofPerson alloc] init]; Class objectClsObj = object_getClass(person); Class objectClsObj_isa = object_getClass(objectClsObj); //添加方法 SuppressUndeclaredSelectorWarning(class_addMethod(objectClsObj, @selector(newMethod), (IMP)testNewMethod, "v@:")); //调用新添加的方法 SuppressUndeclaredSelectorWarning([person performSelector:@selector(newMethod)]); //获取实例方法,如果方法不存在,返回nil Method instanceMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(objectClsObj, @selector(setName:age:)); NSLog(@"instanceMethod:%s", sel_getName(method_getName(instanceMethod))); //获取类方法 Method classMethod = class_getClassMethod(objectClsObj, @selector(createPersonWithName:age:)); NSLog(@"classMethod:%s", sel_getName(method_getName(classMethod))); //获取实例方法列表 unsigned int count = 0; Method *methods = class_copyMethodList(objectClsObj, &count); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { Method methodItem = methods[i]; const char *methodType = method_getTypeEncoding(methodItem);// 获取方法参数类型和返回类型 NSLog(@"instance method item%d:%s %s",i, sel_getName(method_getName(methodItem)), methodType); } free(methods); //获取类方法列表 unsigned int countClass = 0; Method *classMethods = class_copyMethodList(objectClsObj_isa, &countClass); for (int i = 0; i < countClass; i++) { Method methodItem = classMethods[i]; const char *methodType = method_getTypeEncoding(methodItem);// 获取方法参数类型和返回类型 NSLog(@"class method item%d:%s %s",i, sel_getName(method_getName(methodItem)), methodType); } free(classMethods); //替换方法实现 如果类中不存在newMethod指定的方法,则会和class_addMethod函数一样添加方法 SuppressUndeclaredSelectorWarning(class_replaceMethod(objectClsObj, @selector(newMethod), (IMP)replaceNewMethod, "v@:")); //调用替换的方法 SuppressUndeclaredSelectorWarning([person performSelector:@selector(newMethod)]); //获取方法的具体实现. 该函数在向类实例发送消息时会被调用,并返回一个指向方法实现函数的指针。返回的函数指针可能是一个指向runtime内部的函数,而不一定是方法的实际实现。
//例如,如果类实例无法响应selector,则返回的函数指针将是运行时消息转发机制的一部分。 IMP implement = class_getMethodImplementation(objectClsObj, @selector(setName:age:)); //获取方法的具体实现.该方法的返回值类型为struct IMP implement1 = class_getMethodImplementation_stret(objectClsObj, @selector(setName:age:)); //判断类实例是否响应指定的selector BOOL canResponse = class_respondsToSelector(objectClsObj, @selector(setName:age:)); NSLog(@"类实例是否响应 : %d", canResponse); } //隐式参数 void testNewMethod(id self, SEL _cmd) { NSLog(@"Hello,newMethod"); } void replaceNewMethod(id self, SEL _cmd) { NSLog(@"Hello,replaceNewMethod"); }
看一下打印结果:
4.8协议
协议相关的操作包含以下函数:
//类是否实现指定的协议.可以使用NSObject类的conformsToProtocol:方法来代替
OBJC_EXPORT BOOL class_conformsToProtocol(Class cls, Protocol *protocol)
OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.5, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0);
//添加协议
OBJC_EXPORT BOOL class_addProtocol(Class cls, Protocol *protocol)
OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.5, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0);
//返回类实现的协议列表
OBJC_EXPORT Protocol * __unsafe_unretained *class_copyProtocolList(Class cls, unsigned int *outCount)
OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.5, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0);
看一个简单的示例:
GofPerson *person = [[GofPerson alloc] init]; Class objectClsObj = object_getClass(person); Protocol *coding = objc_getProtocol("NSCoding"); //类是否实现了协议 BOOL isImplement = class_conformsToProtocol(objectClsObj, coding); NSLog(@"类是否实现了协议: %d", isImplement); //添加协议 BOOL isSuccess = class_addProtocol(objectClsObj, coding); NSLog(@"添加协议是否成功:%d", isSuccess); //类是否实现了协议 BOOL isImplement1 = class_conformsToProtocol(objectClsObj, coding); NSLog(@"类是否实现了协议: %d", isImplement1); unsigned int count = 0; Protocol * __unsafe_unretained *protocols = class_copyProtocolList(objectClsObj, &count); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { Protocol *item = protocols[i]; NSLog(@"protocol item%d:%s",i, protocol_getName(item)); }
free(protocols);
打印结果:

4.9版本
版本相关的操作包含以下函数:
//获取版本号 OBJC_EXPORT int class_getVersion(Class cls) OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.0, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0); //设置版本号 OBJC_EXPORT void class_setVersion(Class cls, int version) OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.0, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0);
这两个函数比较简单,示例如下:
//获取版本 int version = class_getVersion([GofPerson class]); NSLog(@"版本:%d", version); //设以上是关于RunTime之类与对象的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章