14_synchronized深入
Posted HigginCui
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了14_synchronized深入相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
【脏读】
对于对象同步和异步的方法,我们在设计程序的时候,一定要考虑问题的整体,不然会出现不一致的错误,最经典的错误的就是脏读(dirty read)。
【实例代码】
package com.higgin.part4; /** * 在我们对一个对象的方法加锁的时候,需要考虑业务的整体性。 * 本例子中的setValue或getValue必须同时加上synchronized同步关键字,办证业务的原子性,不然会出现业务错误 */ public class DirtyRead { private String username="zhangsan"; private String password="123"; public synchronized void setValue(String username,String password){ this.username=username; try { Thread.sleep(2000); //延时2秒 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } this.password=password; System.out.println("setValue最终结果【 username = "+username+", password = "+password + "】"); } /** * 加和不加synchronized有区别 */ public void getValue(){ System.out.println("getValue最终结果【 username = "+username+", password = "+password + "】"); } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { final DirtyRead dr = new DirtyRead(); Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { dr.setValue("lisi", "456"); } }); t1.start(); //t1线程去设置值 Thread.sleep(1000); dr.getValue(); //相当于main线程去读取值 } }
【运行结果:不加synchronized】
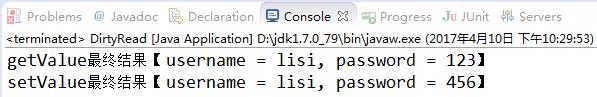
【运行结果:加上synchronized】
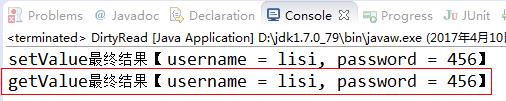
【关于synchronized代码块】
直接使用synchronized声明的方法是在有些情况下是有弊端的,比如A线程调用的同步方法执行一个时间很长的任务,那么B线程就必须等待比较长的时间才能执行,这样的情况下可以使用synchronized代码块去优化代码执行时间,也就是通常所说的减小锁的粒度。
【synchronized代码块加锁:对象锁、类锁、任意对象锁】
package com.higgin.part6; public class DiffLock { public void method1(){ synchronized(this){ //对象锁 System.out.println("method1"); } } public void method2(){ synchronized(DiffLock.class){ //类锁 System.out.println("method2"); } } private Object obj = new Object(); public void method3(){ synchronized(obj){ //任意对象锁 System.out.println("method3"); } } }
【关于String类型的锁】
注意不要使用String的常量加锁,容易出现死循环问题。
package com.higgin.part6; /** * synchronized代码块对字符串的锁,注意String常量池的缓存功能 */ public class StringLock { public void method() { //分别使用new String("abc")和"abc" synchronized ("abc") { //这里是一个String类型的常量锁 try { while(true){ System.out.println("当前线程 : " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "开始"); Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println("当前线程 : " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "结束"); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { final StringLock stringLock = new StringLock(); Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { stringLock.method(); } },"t1"); Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { stringLock.method(); } },"t2"); t1.start(); //这里本质上t1、t2抢占的是同一个String锁("abc"),t1一直未释放锁,导致t2无法获得锁执行代码 t2.start(); } }
【运行结果:使用"abc"常量字符串作为锁,t2线程一直无法执行】
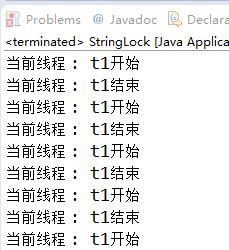
【运行结果:使用new String("abc")非常量字符作为锁,t2和t1竞争执行】

以上是关于14_synchronized深入的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章