MySQL 多表where查询与单表select where in哪一个效率高
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MySQL 多表where查询与单表select where in哪一个效率高相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
SELECT b.id FROM t_address a, t_unit b WHERE b.utj=1 AND b.ufreeze=2 AND a.id=b.uads and a.sid=3就这个啦!!
原因很简单
b.utj=1不满足的话,那么系统就直接找下一个数据
用的in的话,如果第一个不满足,那么就匹配第二个,第二个不满足,在匹配第三个
,全部不匹配 才找下一条数据!!
这个就可以看到了,可能用IN的话,效率可能会减慢3倍,打个比方 参考技术A 多表 inner join 比 in 快
python开发mysql:单表查询&多表查询
一 单表查询,以下是表内容
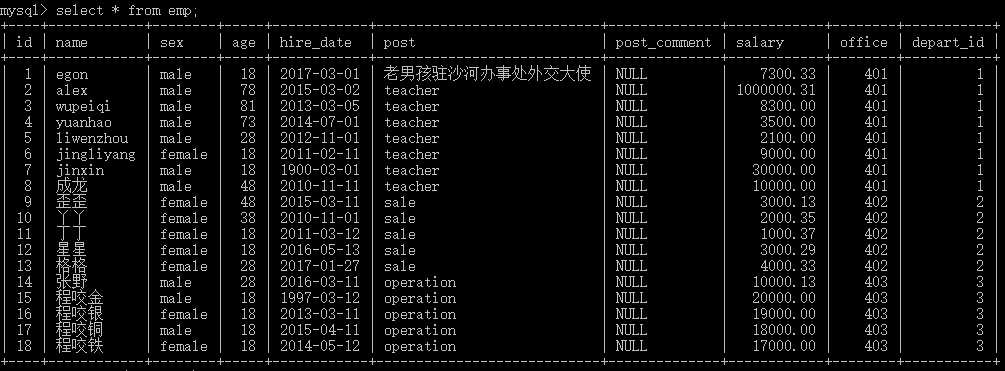
1 一 having 过滤 2 1.1 having和where 3 select * from emp where id > 15; 4 解析过程;from > where 找到数据 > 分组(没有默认一个组)> select 打印 where是出结果之前 5 select * from emp having id > 15; 6 解析过程;from > where 找到数据(没有约束条件,就是整个表)) > 分组(没有默认一个组)> select 打印 > having where是出结果之后 7 上面2个输出是一样的,因为没有分组 8 select depart_id,count(id) from emp group by depart_id; 分组完后3个组,就是3个记录,就要通过聚合取值,通过分组字段取值 9 10 select depart_id,count(id) from emp group by depart_id where depart_id=1; 报错,这里改成having就好了 11 from emp group by depart_id 得出一张虚拟的表在内存里面,有2个字段depart_id,count(id) 12 在往后接就是针对这块虚拟的表,也就是where针对的是这个虚拟表,所以报错,因为where针对的是硬盘表 13 14 小结;where和having的区别 15 where是约束来自数据库的数据,是返回结果之前起作用的,从硬盘把数据where约束拿到内存,在分组之前 16 having是过滤声明,是结果已经到内存,在分组之后 17 18 19 20 1.2 聚合 把内容压成一个字段一条记录 21 select depart_id,count(id) from emp group by depart_id having name like ‘ego%‘; 报错,结果针对虚拟表,只有depart_id,count(id)2个字段 22 select depart_id,count(id) from emp group by depart_id having count(id) > 2; 在having里面的聚合最后就是字符串字段 23 from > where > groupby > 聚合 > select > having 24 select count(id) from emp where id > 15; 解析 from > where > groupby(默认是一组) > 聚合 > select 25 select count(id) from emp; 解析 from > where (没有约束条件,就是整个表) > groupby(默认是一组) > 聚合 > select 26 select count(id) from emp having id > 15; 报错 解析 因为having是groupby后的结果,只有count(id)这个字段 27 select * from emp having avg(salary) > 10000; 报错 聚合把内容压成一个字段一条记录,这条记录的名字是avg(salary) 28 select avg(salary) from emp; 29 select max(salary) from emp having avg(salary) > 10000; 30 解析 from > where (没有约束条件,就是整个表) > groupby(默认是一组) > 聚合max > 聚合avg > select > having 31 也就是过滤针对的是select打印做出的限制,限制为真,就打印select,否则为空 32 select 10000 from emp having 20000 > 10000; 从表中拿到数据,然后where,groupby然后判断过滤后面的,如果为真,就输出select 33 34 **顺序 35 select max(salary) from emp where id > 2 group by depart_id having avg(salary) > 10000; 36 from emp > where id>2 到内存 > group by depart_id 只有depart_id字段(select只能靠聚合) > 算出结果max(salary) avg(salary) > having 满足 > select 37 depart_id max(id) avg(salary) 38 1 3 10 39 2 1 11 40 41 1.3 练习 42 1. 查询各岗位内包含的员工个数小于2的岗位名、岗位内包含员工名字、个数 43 select post,count(id),group_concat(name) from emp group by post having count(id) < 2; 44 3. 查询各岗位平均薪资大于10000的岗位名、平均工资 45 select post,avg(salary),group_concat(name) from emp group by post having avg(salary) > 10000; 46 select post 部门,avg(salary) 平均工资,group_concat(name) 职工 from emp group by post having avg(salary) > 10000; 47 3. 查询各岗位平均薪资大于10000且小于20000的岗位名、平均工资 48 select post,avg(salary),group_concat(name) from emp group by post having avg(salary) between 10000 and 20000); 49 50 51 52 二 order by 关键字 排序 默认升序,asc 53 2.1 select * from emp order by salary; 按照薪资排序,从小到大,升序 54 select * from emp order by salary asc; 升序 55 select * from emp order by salary desc; 降序 56 57 年龄从小到大,出现相同再按照薪资去排 58 select * from emp order by age,salary; 59 select * from emp order by age(asc,desc),salary(asc,desc); 60 61 2.2 优先级 62 在having后面执行的,对打印出来的限制,也就是在select之前 63 64 2.3 练习 65 1. 查询所有员工信息,先按照age升序排序,如果age相同则按照hire_date降序排序 66 select * from employee ORDER BY age asc,hire_date desc; 67 2. 查询各岗位平均薪资大于10000的岗位名、平均工资,结果按平均薪资升序排列 68 select post 岗位名,avg(salary) 平均工资 from emp group by post having avg(salary) > 10000 order by 平均工资 asc; 69 3. 查询各岗位平均薪资大于10000的岗位名、平均工资,结果按平均薪资降序排列 70 select post 岗位名,avg(salary) 平均工资 from emp group by post having avg(salary) > 10000 order by 平均工资 desc; 71 72 ** select name from emp where id > 5 having id > 16; 73 ** select 后面决定了有什么字段,having,等限制打印的一定要限制后面的字段,不然就报错,因为没有这个字段 74 75 76 三 limit 限制查询记录数 77 3.1 select * from emp limit 3; 打印升序(默认就是升序)前三条 78 select * from emp order by id desc limit 3;打印后三条 79 80 3.2 分页查询,从哪开始,往后取几条 81 select * from emp limit 0,3; 0代表第一条,3代表查询几条 82 select * from emp limit 3,3; 3代表第四条 83 select * from emp limit 6,3; 84 85 四 使用正则表达式查询 86 4.1 like 模糊查询,% 匹配多个 _ 匹配一个 87 select * from emp where name like ‘eg%‘; 88 select * from emp where name like ‘_g%‘; 89 90 4.2 正则 regexp 支持正则匹配 91 select * from emp where name regexp ‘^eg‘; 92 select * from emp where name regexp ‘eg‘; 93 94 95 五 distinct 去重 96 select distinct sex from emp; 97 98 六 数学运算符 99 select name,salary from emp; 每个人名字,薪资 100 select name,salary*12 年薪 from emp;
二 多表查询,一下是表内容
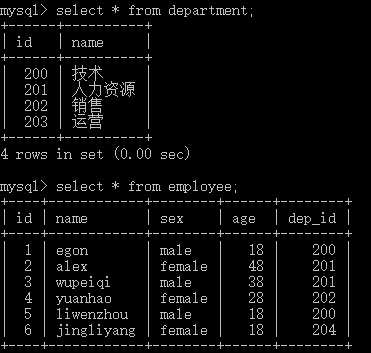
1 多表查询 2 一 简单查询 多张表 提取相同的 假设department id 和 employee dep_id 关联 3 1.1 select * from department,employee; 结果显示一张表上,是左右字段一次排开拼接这种 4 遍历第一张表,循环第二张,配对一遍,显示出来,拼接方式叫做 笛卡尔积 5 select * from department,employee where department.id=employee.dep_id; 6 select * from employee,department where department.id=employee.dep_id; 提取2表相同的部分 7 8 9 二 连表操作 10 2.1 内链接 inner join department on 11 按照on条件只取2表的相同部分,链接成一张虚拟的表 12 select * from employee inner join department on department.id=employee.dep_id; 提取2表相同的部分 13 14 2.2 左链接 left join department on 15 按照on条件取2表的相同部分基础上,保留左表有,右边没有的记录 16 select * from employee left join department on department.id=employee.dep_id; 17 18 2.3 右链接 right join department on 19 按照on条件取2表的相同部分基础上,保留右表有,左边没有的记录 20 select * from employee right join department on department.id=employee.dep_id; 21 22 2.4 全链接 full join 在mysql里面没有这个功能,只是个概念,还要考左,右链接拼凑出来 23 有对应关系,和没对应关系的都取出来 24 select * from employee left join department on department.id=employee.dep_id 25 union 联合的意思,将2表联合,去掉重复的部分 26 select * from employee right join department on department.id=employee.dep_id; 27 28 ** 优先级 29 from > join on 后面的条件联合 > where > gourp by > 聚合 > having > order by > limit > select 30 31 三 子查询 32 3.1 带in关键字的子查询 33 select id from department where name in (‘技术‘,‘销售‘); 查看2个部门的d 34 select * from employee where dep_id in (200.202); 查询部门id对应的员工 35 问题;怎么知道员工的id,应该是从部门表得到id 36 select * from employee where dep_id in (select id from department where name in (‘技术‘,‘销售‘)); 37 38 3.2 练习 39 1. 查询平均年龄在25岁以上的部门名 40 select name from department where id in (select dep_id from employee group by dep_id having avg(age) > 25); 41 2. 查看技术部员工姓名 42 select name from employee where dep_id in (select id from department where name=‘技术‘); 43 3. 查看人数小于2的部门,不准确,因为还有空的存在,看 4 5 题 44 select name from department where id in (select dep_id from employee group by dep_id having count(dep_id) < 2); 45 4. 提取空部门,就是没有人的部门 46 select distinct dep_id from employee; 去重,有人的部门 47 select name from department where id not in (select distinct dep_id from employee); 非有人的部门,空部门 48 5. 查看人数小于2的部门,但是有空的情况 49 select name from department where id in (select dep_id from employee group by dep_id having count(dep_id) < 2) 50 union 51 select name from department where id not in (select distinct dep_id from employee); 没有人的部门 52 53 或者: 54 select name from department where id in 55 ( 56 select dep_id from employee group by dep_id having count(id) < 2 57 union 58 select id from department where id not in (select distinct dep_id from employee) 59 ); 60 61 3.3 exists存在,判断 62 select * from employee where exists (select id from department where name=‘技术‘); 63 select id from department where name=‘技术‘ 存在 就打印前面的select,不存在就返回空 64 65 ** 子查询,括号内的查询都要select出2表相同的字段,这样才可以,语法:查询 where 相同字段 in 子查询
三 总结&表创建过程
1 总结; 2 查询语法 3 SELECT 字段1,字段2... FROM 表名 4 JOIN ON 5 WHERE 条件 6 GROUP BY field 7 HAVING 筛选 8 ORDER BY field 9 LIMIT 限制条数 10 11 关键字的执行优先级 12 from 13 join on 14 where 15 --------------- 16 group by 17 --------------- 18 聚合 19 having 20 select 21 --------------- 22 限制打印 23 distinct 24 order by 25 limit
单表创建
1 #创建表 2 create table employee( 3 id int not null unique auto_increment, 4 name varchar(20) not null, 5 sex enum(‘male‘,‘female‘) not null default ‘male‘, #大部分是男的 6 age int(3) unsigned not null default 28, 7 hire_date date not null, 8 post varchar(50), 9 post_comment varchar(100), 10 salary double(15,2), 11 office int, #一个部门一个屋子 12 depart_id int 13 ); 14 15 #插入记录 16 #三个部门:教学,销售,运营 17 insert into employee(name,sex,age,hire_date,post,salary,office,depart_id) values 18 (‘egon‘,‘male‘,18,‘20170301‘,‘老男孩驻沙河办事处外交大使‘,7300.33,401,1), #以下是教学部 19 (‘alex‘,‘male‘,78,‘20150302‘,‘teacher‘,1000000.31,401,1), 20 (‘wupeiqi‘,‘male‘,81,‘20130305‘,‘teacher‘,8300,401,1), 21 (‘yuanhao‘,‘male‘,73,‘20140701‘,‘teacher‘,3500,401,1), 22 (‘liwenzhou‘,‘male‘,28,‘20121101‘,‘teacher‘,2100,401,1), 23 (‘jingliyang‘,‘female‘,18,‘20110211‘,‘teacher‘,9000,401,1), 24 (‘jinxin‘,‘male‘,18,‘19000301‘,‘teacher‘,30000,401,1), 25 (‘成龙‘,‘male‘,48,‘20101111‘,‘teacher‘,10000,401,1), 26 27 (‘歪歪‘,‘female‘,48,‘20150311‘,‘sale‘,3000.13,402,2),#以下是销售部门 28 (‘丫丫‘,‘female‘,38,‘20101101‘,‘sale‘,2000.35,402,2), 29 (‘丁丁‘,‘female‘,18,‘20110312‘,‘sale‘,1000.37,402,2), 30 (‘星星‘,‘female‘,18,‘20160513‘,‘sale‘,3000.29,402,2), 31 (‘格格‘,‘female‘,28,‘20170127‘,‘sale‘,4000.33,402,2), 32 33 (‘张野‘,‘male‘,28,‘20160311‘,‘operation‘,10000.13,403,3), #以下是运营部门 34 (‘程咬金‘,‘male‘,18,‘19970312‘,‘operation‘,20000,403,3), 35 (‘程咬银‘,‘female‘,18,‘20130311‘,‘operation‘,19000,403,3), 36 (‘程咬铜‘,‘male‘,18,‘20150411‘,‘operation‘,18000,403,3), 37 (‘程咬铁‘,‘female‘,18,‘20140512‘,‘operation‘,17000,403,3) 38 ;
多表创建
1 多表查询 2 整体是一个数据,方便管理,节省空间拆成不同的表 3 company.employee 4 company.department 5 6 ==============================被关联表 7 创建 被关联表 8 create table department( 9 id int, 10 name varchar(20) 11 )charset utf8; 12 插入数据 13 insert into department values 14 (200,‘技术‘), 15 (201,‘人力资源‘), 16 (202,‘销售‘), 17 (203,‘运营‘); 18 19 20 ===============================关联表 21 创建 关联表 22 create table employee( 23 id int primary key auto_increment, 24 name varchar(20), 25 sex enum(‘male‘,‘female‘) not null default ‘male‘, 26 age int, 27 dep_id int 28 )charset utf8; 29 插入数据 30 insert into employee(name,sex,age,dep_id) values 31 (‘egon‘,‘male‘,18,200), 32 (‘alex‘,‘female‘,48,201), 33 (‘wupeiqi‘,‘male‘,38,201), 34 (‘yuanhao‘,‘female‘,28,202), 35 (‘liwenzhou‘,‘male‘,18,200), 36 (‘jingliyang‘,‘female‘,18,204) 37 ; 38 39 ** 暂时不加入外键,如果假如外键,关联表在拆入数据的时候,插入204,上面的表没有下面的表对应关系 40 上有下没有,下有上没有,就会报错 41 上表有203下面没有,下面204上面没有 42 ** 虽然没有外键,咱们假设department id 和 employee dep_id 关联
以上是关于MySQL 多表where查询与单表select where in哪一个效率高的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章