机器学习-聚类算法2
Posted 舆
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了机器学习-聚类算法2相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
聚类算法就是通过一个固定的准则将若干个数据分成不同的类,而这个准则就是算法,即分类的标准。
1.样本:
数据是这样的,300个数据点:
186.663 202.772 198.676 148.778 143.059 205.835 124.315 209.143 183.409 151.252 186.651 184.617 152.448 213.176 193.86 187.893 147.529 260.705 192.255 195.25 199.348 246.308 193.697 188.236 112.12 201.993 168.106 211.265 212.573 186.155 196.042 189.468 163.708 204.957 181.054 220.624 158.703 168.099 159.757 184.74 196.79 192.998 186.786 210.828 196.497 207.053 198.588 202.922 181.534 173.303 163.578 213.044 179.282 176.883 196.609 190.543 138.516 157.012 195.177 156.58 190.53 182.799 185.528 198.14 142.969 164.181 179.023 247.875 214.873 197.911 205.648 225.069 152.519 237.886 117.663 200.206 195.056 178.23 206.471 231.914 195.335 134.527 179.842 192.186 201.969 232.993 146.255 179.038 205.406 208.909 116.01 196.927 209.268 204.178 194.259 198.687 178.556 182.883 198.249 194.934 196.83 190.598 194.126 171.121 119.272 163.223 170.944 150.63 182.481 206.846 186.658 190.327 197.471 162.009 159.709 209.665 199.476 211.293 206.748 245.509 206.406 204.516 176.252 199.142 190.133 229.646 178.712 188.019 151.013 237.015 176.742 212.558 182.972 201.977 199.323 146.504 156.122 239.561 186.448 192.126 179.963 192.297 198.579 185.982 188.084 201.899 183.696 243.438 147.175 193.677 191.479 191.342 108.569 191.222 182.775 136.605 130.451 156.001 214.888 193.649 161.908 148.296 159.809 178.67 204.497 154.195 171.158 222.761 196.04 181.647 179.137 199.344 153.147 151.605 196.244 142.589 207.977 225.414 154.339 236.739 207.607 225.961 191.832 171.313 164.26 215.03 197.486 96.329 199.638 59.965 211.683 54.121 151.582 23.532 271.28 71.503 264.923 101.928 167.617 100.39 202.113 114.749 274.472 35.1 209.937 18.919 260.42 52.741 157.854 27.62 227.209 102.074 188.259 90.859 198.543 120.785 141.484 26.01 167.229 72.261 205.988 117.576 196.063 87.301 156.426 31.878 282.295 68.04 291.867 17.576 255.483 38.275 185.408 89.429 279.012 66.076 275.475 47.206 273.288 47.413 214.551 77.592 195.28 47.477 233.479 84.275 201.75 121.026 258.297 100.726 145.24 17.732 168.497 80.165 152.201 87.073 156.81 100.006 40.015 274.342 111.668 225.726 132.572 318.502 81.682 208.127 92.682 313.257 83.935 256.664 63.135 259.184 124.016 260.574 3.4 228.494 24.468 221.772 100.061 316.453 98.86 271.581 13.752 219.064 110.894 212.33 41.353 304.508 15.272 280.954 56.536 239.835 37.807 221.051 5.459 224.69 63.999 248.93 78.504 363.068 138.674 288.375 95.426 268.569 95.851 352.587 115.264 219.745 19.005 214.403 24.337 251.301 138.374 262.933 3.097 201.849 111.099 296.603 68.028 279.671 225.167 197.408 281.761 153.633 265.153 201.25 234.606 199.763 242.599 161.636 288.481 181.345 232.487 146.963 239.962 247.851 230.852 155.934 287.084 207.745 258.476 253.752 245.504 250.344 231.481 220.091 289.341 158.156 224.293 218.578 274.152 194.052 266.65 199.529 220.442 169.775 273.666 154.976 278.837 166.881 287.532 188.421 269.012 263.561 254.356 209.196 326.444 240.195 269.494 130.213 274.942 181.885 351.502 294.563 239.381 257.045 285.555 174.956 237.724 166.39 318.404 240.652 228.208 161.013 219.366 203.459 233.696 243.415 228.683 182.809 280.194 173.569 238.482 195.29 236.198 181.33 223.364 173.82 286.391 157.439 220.934 198.874 273.372 212.147 260.989 286.917 182.289 367.853 362.761 317.836 209.364 310.228 177.461 291.76 205.365 375.53 237.474 355.536 187.025 392.858 294.034 353.4 251.77 341.213 306.181 318.855 258.727 362.831 193.536 338.408 284.516 335.944 264.24 275.262 155.706 317.301 137.6 339.338 217.667 288.749 228.865 389.289 156.911 365.382 196.577 267.226 131.481 380.664 243.27 284.093 340.328 328.199 129.81 383.682 227.398 285.797 210.289 305.682 121.652 351.048 214.065 380.543 165.671 344.769 297.968 358.993 180.87 319.932 229.68 334.947 229.294 275.786 280.687 361.591 214.035 396.153 205.155 332.869 188.183 269.347 245.506 349.31 136.127 127.038 103.733 3.847 117.045 109.702 20.688 130.31 99.413 143.018 42.53 102.254 134.522 51.703 127.222 145.689 44.47 79.918 25.086 74.267 80.817 67.636 40.818 76.988 66.217 99.708 92.698 155.32 118.949 141.192 111.029 146.341 92.091 68.269 95.929 88.974 112.129 32.055 13.645 123.95 98.771 119.907 89.082 80.095 44.047 61.279 137.867 117.784 97.626 166.542 0 129.274 105.707 154.582 93.265 44.732 35.537 156.558 82.69 151.633 118.047 9.606 57.817 66.352 310.759 112.875 370.382 182.441 394.08 164.391 353.638 137.656 362.721 63.942 348.123 194.11 353.612 138.251 351.363 152.021 357.519 126.935 289.905 94.706 353.809 213.003 392.191 162.078 331.554 147.666 313.834 93.734 343.987 86.263 382.006 206.06 386.329 131.662 310.848 147.063 308.198 75.715 314.647 88.739 286.943 139.761 377.336 144.399 400 164.092 363.689 199.723 297.952 131.461 361.09 80.444 372.778 172.28
这些数据显示成图形,如下图:
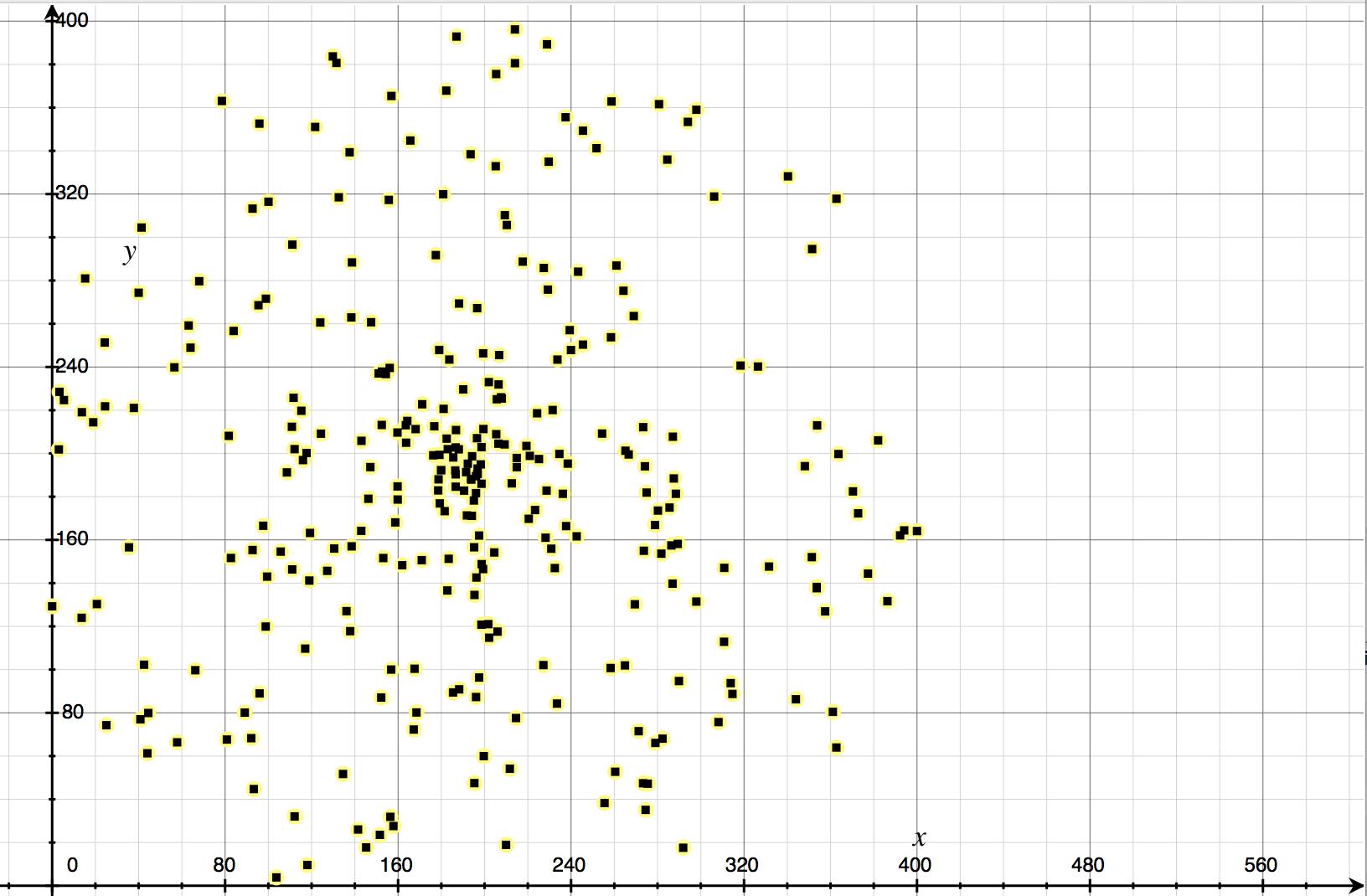
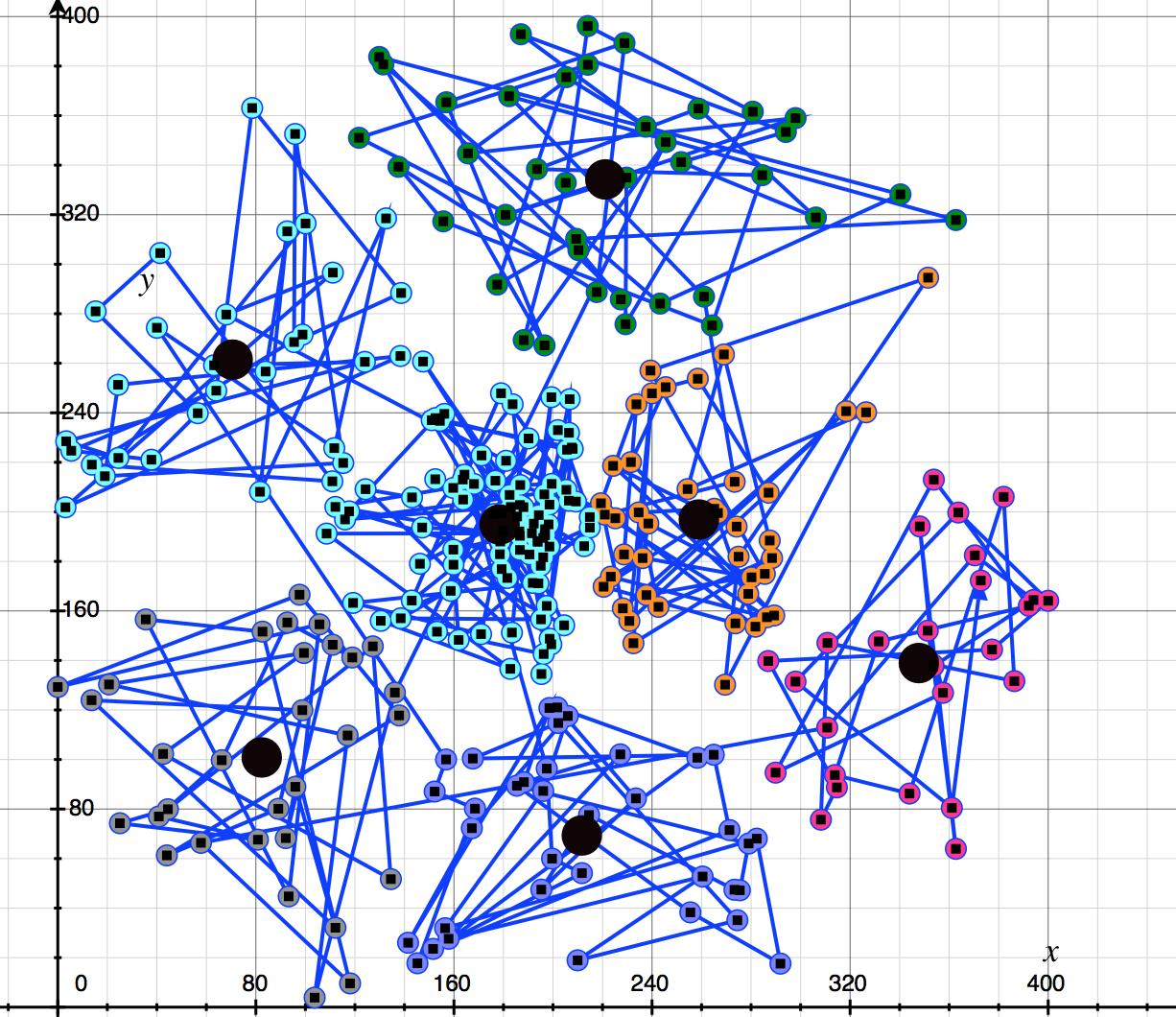
如上图,这是三百个数据点,单凭肉眼看,我无法分别点和点,那个和哪个是同一类,这些点很没有规律,但是请看下图:
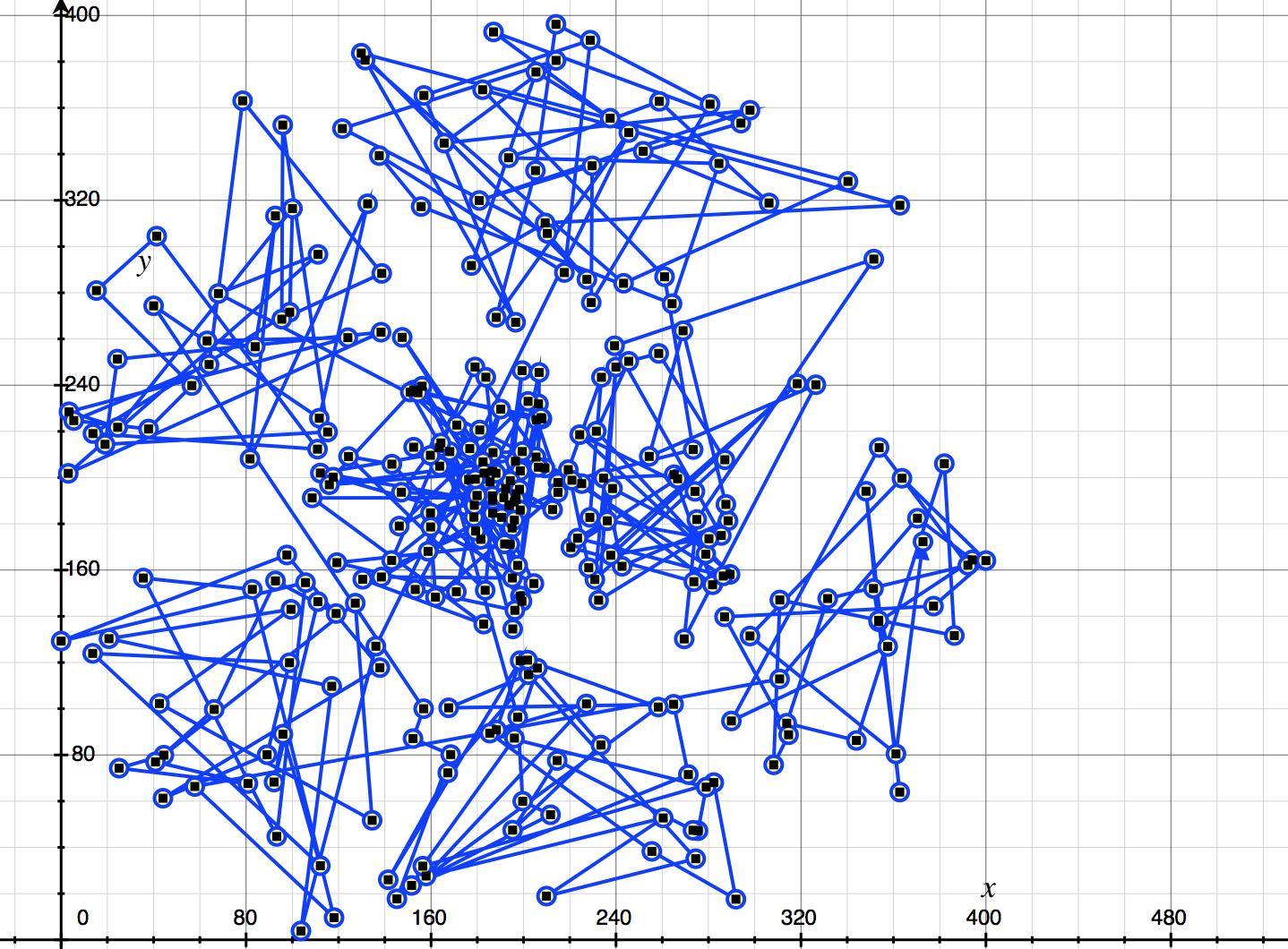
如上图:我便可以看清楚这个点与点之间是有联系的,经过连线我看到了点与点之间的关系,将它们可以分成七个类(簇),大致的块我都可以说出来,这些个点程序是怎么找出来的。
2.核心思想:
1. 将数据分为k个非空子集
2. 计算每个类中心点(k-means<centroid>中心点是所有点的average),记为seed point
3. 将每个object聚类到最近seed point
4. 返回2,当聚类结果不再变化的时候stop
代码:来自于维基百科:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
from math import pi, sin, cos
from collections import namedtuple
from random import random, choice
from copy import copy
try:
import psyco
psyco.full()
except ImportError:
pass
FLOAT_MAX = 1e100
class Point:
__slots__ = ["x", "y", "group"]
def __init__(self, x=0.0, y=0.0, group=0):
self.x, self.y, self.group = x, y, group
"""
创建数据源,先初始化300个点对象,再循环赋值
"""
def generate_points(npoints, radius):
points = [Point() for _ in xrange(npoints)]
# note: this is not a uniform 2-d distribution
for p in points:
r = random() * radius
ang = random() * 2 * pi
p.x = r * cos(ang)
p.y = r * sin(ang)
return points
def nearest_cluster_center(point, cluster_centers):
"""Distance and index of the closest cluster center"""
def sqr_distance_2D(a, b):
return (a.x - b.x) ** 2 + (a.y - b.y) ** 2
min_index = point.group
min_dist = FLOAT_MAX
for i, cc in enumerate(cluster_centers):
d = sqr_distance_2D(cc, point)
if min_dist > d:
min_dist = d
min_index = i
return (min_index, min_dist)
\'\'\'
points是数据点,nclusters是给定的簇类数目
cluster_centers包含初始化的nclusters个中心点,开始都是对象->(0,0,0)
\'\'\'
def kpp(points, cluster_centers):
cluster_centers[0] = copy(choice(points)) #随机选取第一个中心点
d = [0.0 for _ in xrange(len(points))] #列表,长度为len(points),保存每个点离最近的中心点的距离
for i in xrange(1, len(cluster_centers)): # i=1...len(c_c)-1
sum = 0
for j, p in enumerate(points):
d[j] = nearest_cluster_center(p, cluster_centers[:i])[1]#第j个数据点p与各个中心点距离的最小值
sum += d[j]
sum *= random()
for j, di in enumerate(d):
sum -= di
if sum > 0:
continue
cluster_centers[i] = copy(points[j])
break
for p in points:
p.group = nearest_cluster_center(p, cluster_centers)[0]
\'\'\'
points是数据点,nclusters是给定的簇类数目
\'\'\'
def lloyd(points, nclusters):
cluster_centers = [Point() for _ in xrange(nclusters)]#根据指定的中心点个数,初始化中心点,均为(0,0,0)
# call k++ init
kpp(points, cluster_centers) #选择初始种子点
lenpts10 = len(points) >> 10
changed = 0
while True:
# group element for centroids are used as counters
for cc in cluster_centers:
cc.x = 0
cc.y = 0
cc.group = 0
for p in points: #与该种子点在同一簇的数据点的个数
cluster_centers[p.group].group += 1
cluster_centers[p.group].x += p.x
cluster_centers[p.group].y += p.y
for cc in cluster_centers:#生成新的中心点
cc.x /= cc.group
cc.y /= cc.group
# find closest centroid of each PointPtr
changed = 0 #记录所属簇发生变化的数据点的个数
for p in points:
min_i = nearest_cluster_center(p, cluster_centers)[0]
if min_i != p.group:
changed += 1
p.group = min_i
# stop when 99.9% of points are good
if changed <= lenpts10:
break
for i, cc in enumerate(cluster_centers):
cc.group = i
return cluster_centers
def print_eps(points, cluster_centers, W=400, H=400):
Color = namedtuple("Color", "r g b");
colors = []
for i in xrange(len(cluster_centers)):
colors.append(Color((3 * (i + 1) % 11) / 11.0,
(7 * i % 11) / 11.0,
(9 * i % 11) / 11.0))
max_x = max_y = -FLOAT_MAX
min_x = min_y = FLOAT_MAX
for p in points:
if max_x < p.x: max_x = p.x
if min_x > p.x: min_x = p.x
if max_y < p.y: max_y = p.y
if min_y > p.y: min_y = p.y
scale = min(W / (max_x - min_x),
H / (max_y - min_y))
cx = (max_x + min_x) / 2
cy = (max_y + min_y) / 2
print "%%!PS-Adobe-3.0\\n%%%%BoundingBox: -5 -5 %d %d" % (W + 10, H + 10)
print ("/l {rlineto} def /m {rmoveto} def\\n" +
"/c { .25 sub exch .25 sub exch .5 0 360 arc fill } def\\n" +
"/s { moveto -2 0 m 2 2 l 2 -2 l -2 -2 l closepath " +
" gsave 1 setgray fill grestore gsave 3 setlinewidth" +
" 1 setgray stroke grestore 0 setgray stroke }def")
for i, cc in enumerate(cluster_centers):
print ("%g %g %g setrgbcolor" %
(colors[i].r, colors[i].g, colors[i].b))
for p in points:
if p.group != i:
continue
print ("%.3f %.3f c" % ((p.x - cx) * scale + W / 2,
(p.y - cy) * scale + H / 2))
print ("\\n0 K中心 %g %g s" % ((cc.x - cx) * scale + W / 2,
(cc.y - cy) * scale + H / 2))
print "\\n%%%%EOF"
def main():
npoints = 300
k = 7 # # clusters
points = generate_points(npoints, 10)
cluster_centers = lloyd(points, k)
print_eps(points, cluster_centers)
main()
3.计算结果:
计算出的7个点是:
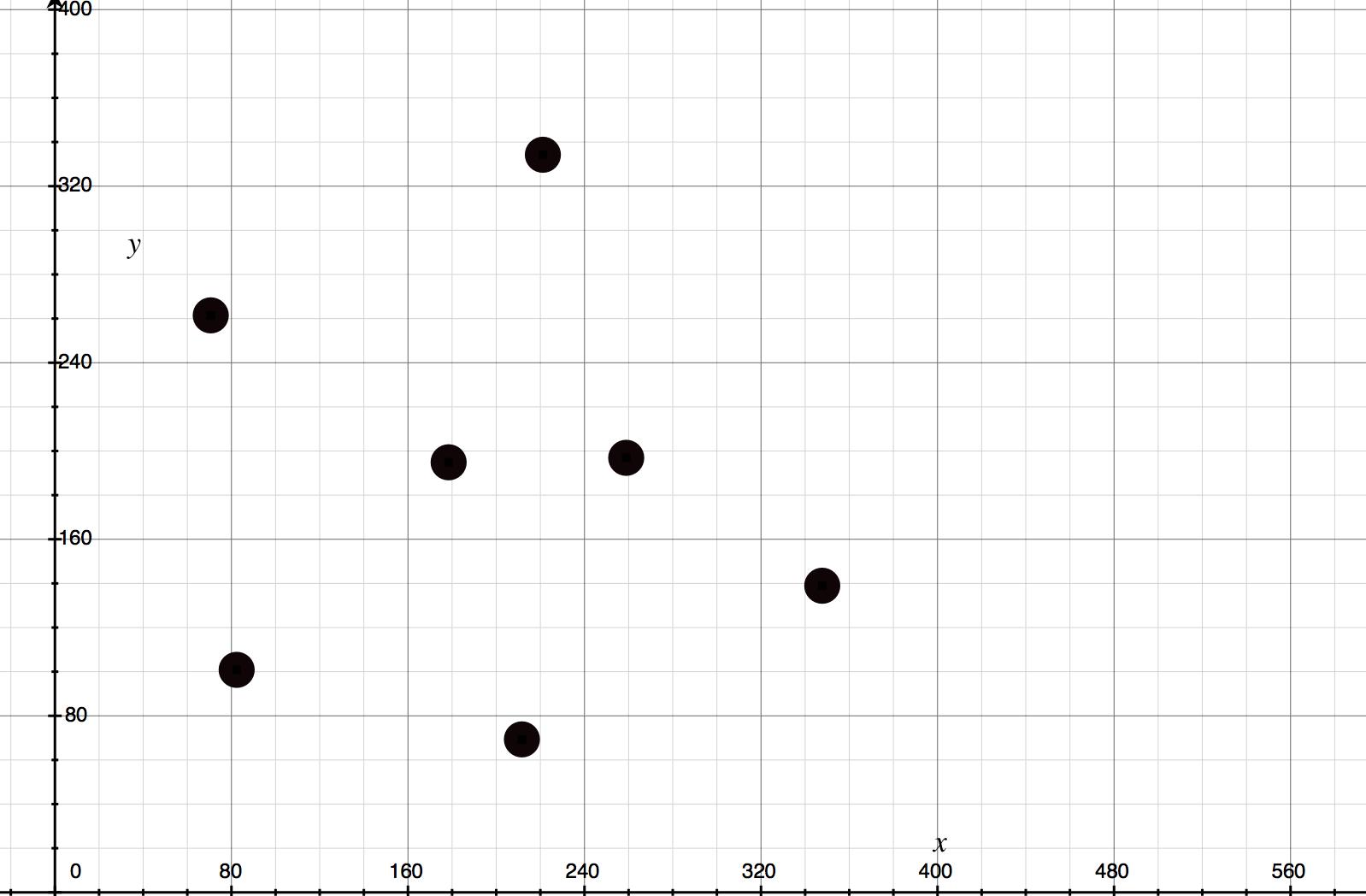
数据视图:
178.432 194.88 211.643 69.3258 70.6203 261.456 258.91 196.902 221.139 334.234 82.3629 100.829 347.752 138.943
全局分类结果:
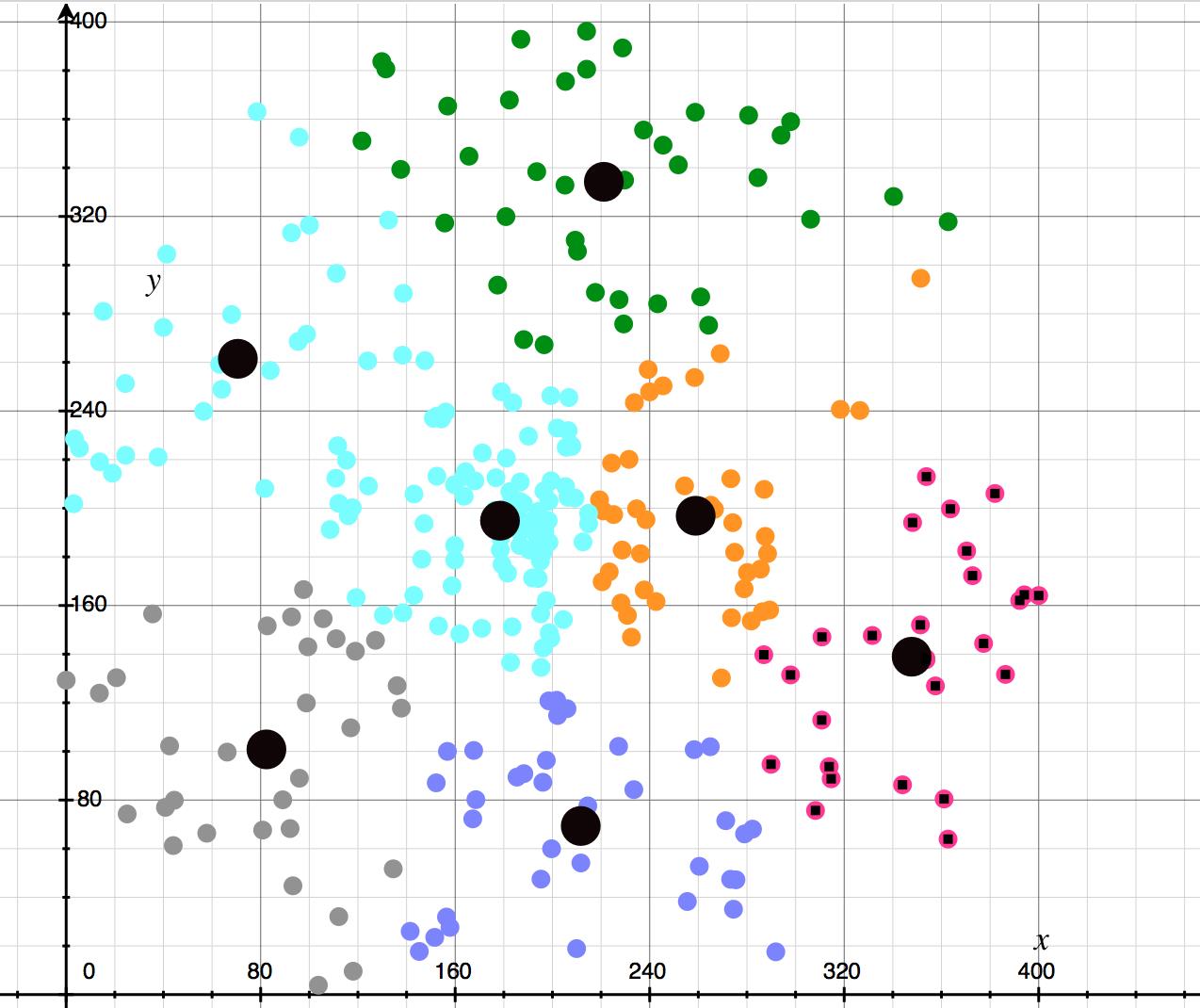
结果二:
以上是关于机器学习-聚类算法2的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章